Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types of material. As a method of printmaking, it is, along with engraving, the most important technique for old master prints, and remains in wide use today. In a number of modern variants such as microfabrication etching and photochemical milling, it is a crucial technique in modern technology, including circuit boards.

A retroreflector is a device or surface that reflects radiation back to its source with minimum scattering. This works at a wide range of angle of incidence, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence. Being directed, the retroflector's reflection is brighter than that of a diffuse reflector. Corner reflectors and cat's eye reflectors are the most used kinds.

A bumper sticker is an adhesive label or sticker designed to be attached to the rear of a car or truck, often on the bumper. They are commonly sized at around 25.4 cm by 7.6 cm and are typically made of PVC.

A warning sign is a type of sign which indicates a potential hazard, obstacle, or condition requiring special attention. Some are traffic signs that indicate hazards on roads that may not be readily apparent to a driver.

A cat's eye or road stud is a retroreflective safety device used in road marking and was the first of a range of raised pavement markers.

An acetate disc is a type of phonograph record generally used from the 1930s to the late 1950s for recording and broadcast purposes and sees limited use as of 2009. Despite their name, "acetate" discs do not contain any acetate.

Metal fabrication is the creation of metal structures by cutting, bending and assembling processes. It is a value-added process involving the creation of machines, parts, and structures from various raw materials.

A raised pavement marker is a safety device used on roads. These devices are usually made with plastic, ceramic, thermoplastic paint, glass or occasionally metal, and come in a variety of shapes and colors. Raised reflective markers, such as plastic, ceramic, or metal ones, include a lens or sheeting that enhances their visibility by retroreflecting automotive headlights, while glass road studs gather automotive headlights with a dome shape and reflect the lights with a reflective layer within. Some other names for specific types of raised pavement markers include convex vibration lines, Botts' dots, delineators, cat's eyes, road studs, or road turtles. Sometimes they are simply referred to as "reflectors".

3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer control, with the material being added together, typically layer by layer.
Electric resistance welding (ERW) is a welding process in which metal parts in contact are permanently joined by heating them with an electric current, melting the metal at the joint. Electric resistance welding is widely used, for example, in manufacture of steel pipe and in assembly of bodies for automobiles. The electric current can be supplied to electrodes that also apply clamping pressure, or may be induced by an external magnetic field. The electric resistance welding process can be further classified by the geometry of the weld and the method of applying pressure to the joint: spot welding, seam welding, flash welding, projection welding, for example. Some factors influencing heat or welding temperatures are the proportions of the workpieces, the metal coating or the lack of coating, the electrode materials, electrode geometry, electrode pressing force, electric current and length of welding time. Small pools of molten metal are formed at the point of most electrical resistance as an electric current is passed through the metal. In general, resistance welding methods are efficient and cause little pollution, but their applications are limited to relatively thin materials.

Road surface marking is any kind of device or material that is used on a road surface in order to convey official information; they are commonly placed with road marking machines. They can also be applied in other facilities used by vehicles to mark parking spaces or designate areas for other uses. In some countries and areas, road markings are conceived as horizontal traffic signs, as opposed to vertical traffic signs placed on posts.

Avery Dennison Corporation is a multinational manufacturer and distributor of pressure-sensitive adhesive materials, apparel branding labels and tags, RFID inlays, and specialty medical products. The company is a member of the Fortune 500 and is headquartered in Mentor, Ohio.

Falsework consists of temporary structures used in construction to support a permanent structure until its construction is sufficiently advanced to support itself. For arches, this is specifically called centering. Falsework includes temporary support structures for formwork used to mold concrete in the construction of buildings, bridges, and elevated roadways.

Wassenaar Arrangement Semi-automatic Rifles are a line of rifles sold in the United States by Century International Arms. The rifles are manufactured in Romania by the Cugir Arms Factory and are a semi-automatic variant of the Pistol Mitralieră model 1963/1965, a Romanian licensed derivative of the Soviet AKM assault rifle. Century imports them and modifies them in order to comply with national legislation before sale to the general public via licensed traders. The WASR series takes its name from the 1996 Wassenaar Arrangement, a multilateral export control regime to monitor and limit the proliferation of certain conventional weapons and dual-use technologies.

Clearview, also known as Clearview Hwy, is the name of a humanist sans-serif typeface family for guide signs used on roads in the United States, Canada, Indonesia, the Philippines, Israel, Brazil and Sri Lanka. It was developed by independent researchers with the help of the Texas Transportation Institute and the Pennsylvania Transportation Institute, under the supervision of the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA). It was once expected to replace the FHWA typefaces in many applications, although newer studies of its effectiveness have called its benefits into question.

Retroreflective sheeting is flexible retroreflective material primarily used to increase the nighttime conspicuity of traffic signs, high-visibility clothing, and other items so they are safely and effectively visible in the light of an approaching driver's headlamps. They are also used as a material to increase the scanning range of barcodes in factory settings. The sheeting consists of retroreflective glass beads, microprisms, or encapsulated lenses sealed onto a fabric or plastic substrate. Many different colors and degrees of reflection intensity are provided by numerous manufacturers for various applications. As with any retroreflector, sheeting glows brightly when there is a small angle between the observer's eye and the light source directed toward the sheeting but appears nonreflective when viewed from other directions.
Lam Research Corporation is an American supplier of wafer-fabrication equipment and related services to the semiconductor industry. Its products are used primarily in front-end wafer processing, which involves the steps that create the active components of semiconductor devices and their wiring (interconnects). The company also builds equipment for back-end wafer-level packaging (WLP) and for related manufacturing markets such as for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).

Button copy is a type of physical design for road signs in the United States. Round plastic retroreflective buttons made of transparent plastic are placed in rows following the contours of sign legend elements, usually painted white, such as letters, numbers, arrows, and borders. In daylight, the buttons visually blend with the white sign legend elements and so are minimally conspicuous. At night, light from each approaching vehicle's headlamps strikes the retroreflective buttons and is reflected back towards the eyes of the vehicle's driver. Thus the sign is made sufficiently conspicuous and legible for adequately fast and accurate recognition and interpretation by drivers.
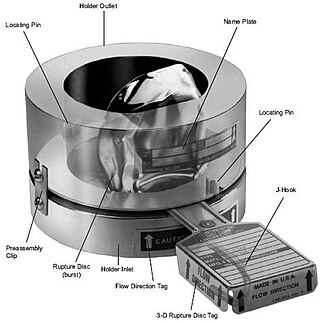
A rupture disc, also known as a pressure safety disc, burst disc, bursting disc, or burst diaphragm, is a non-reclosing pressure relief safety device that, in most uses, protects a pressure vessel, equipment or system from overpressurization or potentially damaging vacuum conditions.

The McDonald's Sign, also known as McDonald's Store #433 Sign, in Pine Bluff, Arkansas, United States, is one of only a few surviving examples of a single-arch McDonald's sign. The sign was erected in 1962 and remained at its original location until 2007. That year, McDonald's Store #433 moved and the sign was renovated and moved to the new location. The McDonald's sign was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places in 2006, but is no longer standing at 2819 S. Olive St.