Related Research Articles
Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) is a surgical procedure in which a portion of the sympathetic nerve trunk in the thoracic region is destroyed. ETS is used to treat excessive sweating in certain parts of the body, facial blushing, Raynaud's disease and reflex sympathetic dystrophy. By far the most common complaint treated with ETS is sweaty palms. The intervention is controversial and illegal in some jurisdictions. Like any surgical procedure, it has risks; the endoscopic sympathetic block (ESB) procedure and those procedures that affect fewer nerves have lower risks.
The rebound effect, or rebound phenomenon, is the emergence or re-emergence of symptoms that were either absent or controlled while taking a medication, but appear when that same medication is discontinued, or reduced in dosage. In the case of re-emergence, the severity of the symptoms is often worse than pretreatment levels.

The ciliary ganglion is a bundle of nerve parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. It is 1–2 mm in diameter and in humans contains approximately 2,500 neurons. The ganglion contains postganglionic parasympathetic neurons. These neurons supply the pupillary sphincter muscle, which constricts the pupil, and the ciliary muscle which contracts to make the lens more convex. Both of these muscles are involuntary since they are controlled by the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system.

Adie syndrome, also known as Holmes-Adie syndrome, is a neurological disorder characterized by a tonically dilated pupil that reacts slowly to light but shows a more definite response to accommodation. It is frequently seen in females with absent knee or ankle jerks and impaired sweating.
Philip Seeman, was a Canadian schizophrenia researcher and neuropharmacologist, known for his research on dopamine receptors.
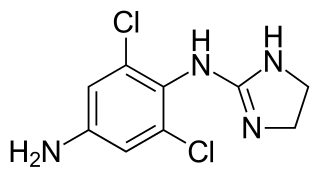
Apraclonidine (INN), also known under the brand name Iopidine, is a sympathomimetic used in glaucoma therapy. It is an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist and a weak α1 adrenergic receptor agonist.
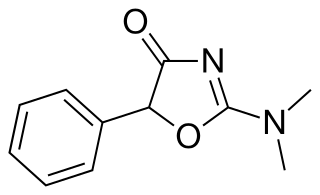
Thozalinone (USAN) is a psychostimulant that has been used as an antidepressant in Europe. It has also been trialed as an anorectic. Thozalinone is described as a "dopaminergic stimulant", and likely acts via inducing the release of dopamine and to a minimal extent norepinephrine; similar to analogue pemoline, it is seemingly devoid of abuse potential unlike common psychostimulants that increase catecholamines.
Alpha-2 blockers are a subset of the alpha blocker class of drugs and are antagonists to the α2 adrenergic receptor. They are mainly used in research, having found limited clinical application in human medicine. Alpha-2 blockers increase noradrenaline release.
Tardive psychosis is a term for a hypothetical form of psychosis, proposed in 1978. It was defined as a condition caused by long term use of neuroleptics, noticeable when the medication had become decreasingly effective, requiring higher doses, or when not responding to higher doses.

Ricardo Miledi was a Mexican neuroscientist known for his work deciphering the role of calcium in neurotransmitter release. He also helped to develop a technique for studying native receptors in frog oocytes for drug development.

Denervation is any loss of nerve supply regardless of the cause. If the nerves lost to denervation are part of the neuronal communication to a specific function in the body then altered or a loss of physiological functioning can occur. Denervation can be caused by injury or be a symptom of a disorder like ALS and post-polio syndrome and POTS. Additionally, it can be a useful surgical technique to alleviate major negative symptoms, such as in renal denervation. Denervation can have many harmful side effects such as increased risk of infection and tissue dysfunction.
Chit Chan Gunn, is the founder and president of The Institute for the Study and Treatment of Pain (iSTOP) in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, a not-for-profit information centre for Gunn Intramuscular Stimulation (IMS). Dr. Gunn developed a process called Intramuscular Stimulation (IMS) to treat neuropathic pain. In 2001 Dr Gunn was inducted into the Order of British Columbia and in 2002 into the Order of Canada for his contributions in the field of pain study. He is a clinical professor at the University of Washington.
Ross' syndrome consists of Adie's syndrome plus segmental anhidrosis.
Renal sympathetic denervation (RSDN) is a minimally invasive, endovascular catheter based procedure using radiofrequency ablation or ultrasound ablation aimed at treating resistant hypertension. Nerves in the wall of the renal artery are ablated by applying radiofrequency pulses or ultrasound to the renal arteries. This causes reduction of sympathetic afferent and efferent activity to the kidney and blood pressure can be decreased. Early data from international clinical trials without sham controls was promising - demonstrating large blood pressure reductions in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension. However, in 2014 a prospective, single-blind, randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial failed to confirm a beneficial effect on blood pressure. A 2014 consensus statement from The Joint UK Societies did not recommend the use of renal denervation for treatment of resistant hypertension on current evidence. More recent sham-controlled trials suggest renal denervation can lead to lower systolic blood pressure.
Dopamine supersensitivity psychosis is a hypothesis that attempts to explain the phenomenon in which psychosis occurs despite treatment with escalating doses of antipsychotics. Dopamine supersensitivity may be caused by the dopamine receptor D2 antagonizing effect of antipsychotics, causing a compensatory increase in D2 receptors within the brain that sensitizes neurons to endogenous release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Because psychosis is thought to be mediated—at least in part—by the activity of dopamine at D2 receptors, the activity of dopamine in the presence of supersensitivity may paradoxically give rise to worsening psychotic symptoms despite antipsychotic treatment at a given dose. This phenomenon may co-occur with tardive dyskinesia, a rare movement disorder that may also be due to dopamine supersensitivity.
Disuse supersensitivity, also pharmacological disuse supersensitivity or pharmacological denervation supersensitivity, is the increased sensitivity by a postsynaptic cell because of decreased input by incoming axons, e.g., due to the exposure to an antagonist drug.
Supersensitivity may refer to:

Salomon Zender Langer is an Argentinian pharmacologist whose family had fled from Poland to Argentina in the early 1930s and were thus saved from the Holocaust during the Second World War.
Benjamin Weiss is an American neuropharmacologist, Emeritus Professor of Pharmacology and Physiology at Drexel University College of Medicine. He is best known for his work with cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. He was the first to propose, based on his experimental work, that selective inhibition of phosphodiesterases which are expressed differentially in all tissues, could be used as a target for drug development. His work is the basis for many marketed and developmental human drugs that selectively inhibit cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases.
Regional acceleratory phenomenon (RAP) is a sudden acceleration of normal tissue processes in reaction to noxious stimuli. It has been exploited in treatments such as the healing of atrophic or oligotrophic nonunions and surgically facilitated orthodontic therapy.
References
- ↑ S. Thesleff, L.C. Sellin, "Denervation supersensitivity", Trends in Neurosciences, Volume 3, Issue 5, May 1980, Pages 122-126 doi : 10.1016/0166–2236(80)90046-6
- ↑ S. Z. Langer, "Denervation Supersensitivity", in: Principles of Receptor Research Volume 2 of the series Handbook of Psychopharmacology pp 245-280
- ↑ Meurant, G. (1983). INTERNATIONAL REVIEW OF RESEARCH IN MENTAL RETARDATION. Elsevier Science. p. 151. ISBN 9780080857893.