Related Research Articles

Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostratigraphy, biostratigraphy, and chronostratigraphy.

In geology and related fields, a stratum is a layer of rock or sediment characterized by certain lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by visible surfaces known as either bedding surfaces or bedding planes. Prior to the publication of the International Stratigraphic Guide, older publications have defined a stratum as either being either equivalent to a single bed or composed of a number of beds; as a layer greater than 1 cm in thickness and constituting a part of a bed; or a general term that includes both bed and lamina.

Lithostratigraphy is a sub-discipline of stratigraphy, the geological science associated with the study of strata or rock layers. Major focuses include geochronology, comparative geology, and petrology.

Relative dating is the science of determining the relative order of past events, without necessarily determining their absolute age. In geology, rock or superficial deposits, fossils and lithologies can be used to correlate one stratigraphic column with another. Prior to the discovery of radiometric dating in the early 20th century, which provided a means of absolute dating, archaeologists and geologists used relative dating to determine ages of materials. Though relative dating can only determine the sequential order in which a series of events occurred, not when they occurred, it remains a useful technique. Relative dating by biostratigraphy is the preferred method in paleontology and is, in some respects, more accurate. The Law of Superposition, which states that older layers will be deeper in a site than more recent layers, was the summary outcome of 'relative dating' as observed in geology from the 17th century to the early 20th century.

In geology, a bed is a layer of sediment, sedimentary rock, or pyroclastic material "bounded above and below by more or less well-defined bedding surfaces". Specifically in sedimentology, a bed can be defined in one of two major ways. First, Campbell and Reineck and Singh use the term bed to refer to a thickness-independent layer comprising a coherent layer of sedimentary rock, sediment, or pyroclastic material bounded above and below by surfaces known as bedding planes. By this definition of bed, laminae are small beds that constitute the smallest (visible) layers of a hierarchical succession and often, but not always, internally comprise a bed.
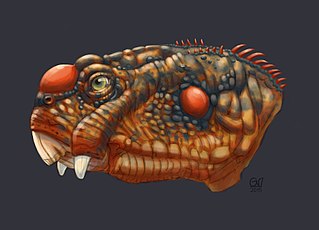
The Daptocephalus Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone found in the Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a majorly fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. This biozone has outcrops located in the upper Teekloof Formation west of 24°E, the majority of the Balfour Formation east of 24°E, and the Normandien Formation in the north. It has numerous localities which are spread out from Colesberg in the Northern Cape, Graaff-Reniet to Mthatha in the Eastern Cape, and from Bloemfontein to Harrismith in the Free State. The Daptocephalus Assemblage Zone is one of eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group and is considered Late Permian (Lopingian) in age. Its contact with the overlying Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone marks the Permian-Triassic boundary.

The Pristerognathus Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone which correlates to the upper Abrahamskraal Formation and lowermost Teekloof Formation, Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. The thickest outcrops, reaching not more than 300 metres (980 ft), occur just east of Sutherland through to Beaufort West in the south and Victoria West in the north. Exposures are also found west of Colesberg and south of Graaff-Reinet. The Pristerognathus Assemblage Zone is the third biozone of the Beaufort Group.

The Tropidostoma Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod assemblage zone or biozone which correlates to the lower Teekloof Formation, Adelaide Subgroup of the Beaufort Group, a fossiliferous and geologically important geological Group of the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. The thickest outcrops, reaching approximately 240 metres (790 ft), occur from east of Sutherland through to Beaufort West and Victoria West, to areas south of Graaff-Reinet. Its northernmost exposures occur west/north-west of Colesberg. The Tropidostoma Assemblage Zone is the fourth biozone of the Beaufort Group.

Sedimentary structures include all kinds of features in sediments and sedimentary rocks, formed at the time of deposition.
In stratigraphy, paleontology, geology, and geobiology an erathem is the total stratigraphic unit deposited during a certain corresponding span of time during an era in the geologic timescale.

A stratigraphic column is a representation used in geology and its subfield of stratigraphy to describe the vertical location of rock units in a particular area. A typical stratigraphic column shows a sequence of sedimentary rocks, with the oldest rocks on the bottom and the youngest on top.
The Bissett Formation is a Mesozoic geologic formation. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.

The Ojo Alamo Formation is a geologic formation in New Mexico spanning the Mesozoic/Cenozoic boundary. Non-avian dinosaur fossils have controversially been identified in beds of this formation dating from after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, but these have been explained as either misidentification of the beds in question or as reworked fossils, fossils eroded from older beds and redeposited in the younger beds.

The Red Beds of Texas and Oklahoma are a group of Early Permian-age geologic strata in the southwestern United States cropping out in north-central Texas and south-central Oklahoma. They comprise several stratigraphic groups including the Clear Fork Group, the Wichita Group, and the Pease River Group. The Red Beds were first explored by American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope starting in 1877. Fossil remains of many Permian tetrapods have been found in the Red Beds, including those of Dimetrodon, Edaphosaurus, Seymouria, Platyhystrix, and Eryops. A recurring feature in many of these animals is the sail structure on their backs.
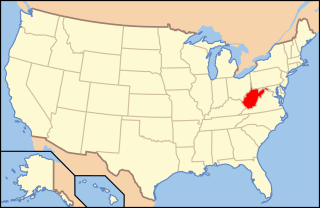
Paleontology in West Virginia refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of West Virginia. West Virginia's fossil record begins in the Cambrian. From that time through the rest of the early Paleozoic, the state was at least partially submerged under a shallow sea. The Paleozoic seas of West Virginia were home to creatures like corals, eurypterids, graptolites, nautiloids, and trilobites at varying times. During the Carboniferous period, the sea was replaced by lushly vegetated coastal swamps. West Virginia is an excellent source of fossil plants due to these deposits. These swamps were home to amphibians. A gap in the local rock record spans from the Permian to the end of the Cenozoic. West Virginia was never the site of glacial activity during the Ice Age, but the state was home to creatures like mammoths, mastodons, and giant ground sloths. One local ground sloth, Megalonyx jeffersonii, was subject to the scholarly investigations of Thomas Jefferson, who misinterpreted the large-clawed remains as belonging to a lion-like predator. In 2008, this species was designated the West Virginia state fossil.
The Cutoff Formation is a geologic formation in Texas and New Mexico, US. It preserves fossils dating back to the Permian period.
The Cub Mountain Formation is a geologic formation in southern New Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Eocene epoch. The formation also records the progressive unroofing of nearby mountainous uplifts during the Laramide orogeny.
Chronological dating, or simply dating, is the process of attributing to an object or event a date in the past, allowing such object or event to be located in a previously established chronology. This usually requires what is commonly known as a "dating method". Several dating methods exist, depending on different criteria and techniques, and some very well known examples of disciplines using such techniques are, for example, history, archaeology, geology, paleontology, astronomy and even forensic science, since in the latter it is sometimes necessary to investigate the moment in the past during which the death of a cadaver occurred. These methods are typically identified as absolute, which involves a specified date or date range, or relative, which refers to dating which places artifacts or events on a timeline relative to other events and/or artifacts. Other markers can help place an artifact or event in a chronology, such as nearby writings and stratigraphic markers.
In geology, a diastem is a short interruption in sedimentation with little or no erosion. They can also be described as very short unconformities .In 1917 Joseph barrel of USA estimated the rate of deposition of succession from the available radiometric age. His accumulation showed that the strata accumulation was at the rate of thousands of years per foot rather than hundreds. He stated that diastems are universal in sedimentary rocks and explain them as a product of fluctuation of base level.

The Bokkeveld Group is the second of the three main subdivisions of the Cape Supergroup in South Africa. It overlies the Table Mountain Group and underlies the Witteberg Group. The Bokkeveld Group rocks are considered to range between Lower Devonian (Lochkovian) to Middle Devonian (Givetian) in age.
References
- ↑ Kowalewsky, Michal; Bambach, Richard K. (2003). Harries, Peter J. (ed.). High-resolution approaches in stratigraphic paleontology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 2.
- ↑ Kowalewsky, Michal; Bambach, Richard K. (2003). Harries, Peter J. (ed.). High-resolution approaches in stratigraphic paleontology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 39.