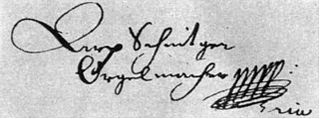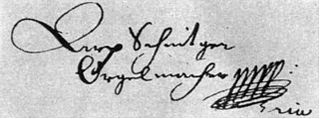
Arp Schnitger was an influential Northern German organ builder. Considered the paramount manufacturer of his time, Schnitger built or rebuilt over 150 organs. He was primarily active in Northern Europe, especially the Netherlands and Germany, where a number of his instruments still survive.

Lübeck Cathedral is a large brick-built Lutheran cathedral in Lübeck, Germany, and part of the Lübeck World Heritage Site. It was started in 1173 by Henry the Lion as a cathedral for the Bishop of Lübeck. It was partly destroyed in a bombing raid in World War II (1942), when the Arp Schnitger organ was destroyed by fire, but was subsequently reconstructed.

The Martinikerk is the oldest church in Groningen, Netherlands. The church and its associated tower are named after Saint Martin of Tours (316–397), the patron saint of the Bishopric of Utrecht to which Groningen belonged.

The Martinitoren is the tallest church steeple in the city of Groningen, Netherlands, and the bell tower of the Martinikerk.

Harald Vogel is a German organist, organologist, and author. He is a leading expert on Renaissance and Baroque keyboard music. He has been professor of organ at the University of the Arts Bremen since 1994.

Jürgen Ahrend was a German organ builder famous for restoring instruments such as the Gothic Rysum organ and the Arp Schnitger organs of the Martinikerk in Groningen, Netherlands, and of St. Jacobi in Hamburg as well as building original instruments. He ran the workshop Jürgen Ahrend Orgelbau in Leer from 1972 to 2004, operating internationally.

The Broerkerk in Groningen, Netherlands, was a medieval church connected to the Franciscan cloister in Groningen. The church was situated in the Broerstraat in Groningen. The Broerkerk was the first church in the town used by the Protestants.
Cornelius Herman "Cor" Edskes was a Dutch organbuilder and organologist who was one of the most important authorities on the history of organ building in Northern Europe. He acted as the consultant for the restoration of many of Europe's most important historical organs, including those in the Nieuwe Kerk (Amsterdam) and Roskilde Cathedral.

St. Martin's Church is a Protestant church in Bolsward, Netherlands, and one of the medieval churches in Friesland. The current church was built between 1446 and 1461, the small medieval church which stood at that location previously was demolished to build the new one. The tower of the church was built in the 15th century and the gabled roof was added in the 17th century. It became a Protestant church during the Reformation. There was a major renovation which, apart from work on the tower, ended in 1955.

The west gallery organ of the Martinikerk in Groningen dates from the 15th century; it took its present form in the 18th century when it was expanded by Arp Schnitger, his son Franz Caspar Schnitger and his successor Albertus Antonius Hinsz. It has 52 speaking stops on three manuals and pedal, and is one of the largest and most famous baroque organs in Northern Europe.

The organ of the Dorpskerk in Noordbroek in the Dutch province of Groningen was first built in 1696 by Arp Schnitger. Today it has 24 stops over two manuals and pedal. The case and the disposition are largely preserved as they were in 1809.

The organ of St. Ludgeri in Norden was built from 1686 to 1692 by Arp Schnitger. It has 46 stops, five divisions, three manuals and pedal, and is thus the second-largest surviving Schnitger organ in Germany and until 2018 the largest organ in East Frisia. Historically and musically it is considered an art-work of international rank.

The organ of the Grasberg church, or Findorffkirche, in Grasberg was built in 1693–1694 by Arp Schnitger, originally for the orphanage at Rödingsmarkt in Hamburg, and transferred to Grasberg in 1788. It is one of the few instruments by Schnitger to have been structurally changed as early as the 18th century. The organ has 21 stops, over two manuals and pedal. 15 stops are still original Schnitger work.

The west gallery organ in the Aa-kerk in Groningen was built by Arp Schnitger in 1699–1702. Originally built for the Academiekerk in Groningen it was moved to the Aa-kerk in 1815. Today it has 40 stops on three manuals and pedal, and is a monument of European significance.
Stef Tuinstra is a Dutch organist, organ expert and author.

Bernhardt Hilbrand Edskes was a Dutch-Swiss organist, organologist, and organ builder based in Wohlen.
Sietze K. de Vries is a Dutch organist, church musician and academic teacher. In the context of his international concert activities, he became known for his renowned organ improvisations on chorale, psalm, and hymn melodies in numerous styles and the Genevan Psalter in numerous styles, but most especially in that of the Renaissance and the Baroque.

Albertus Antonius Hinsz was an organ builder in the Netherlands, who followed in the tradition of Arp Schnitger.
Heinrich Hermann Freytag was a German/Dutch organ builder. A pupil of Albertus Antonius Hinsz, he became one of the most important organ builders in the Netherlands around 1800. His work, of a high standard, follows in the traditions established by Arp Schnitger.
Franz Caspar Schnitger was a German organ-builder active in the Netherlands.