
Veazie is a town in Penobscot County, Maine, United States. The population was 1,919 at the 2010 census. The town is named after General Samuel Veazie, an early lumber baron and railroad operator. Veazie was originally part of Bangor, using Penobscot River water power to operate sawmills. It became a separate town in 1853 because Gen. Veazie, its wealthiest citizen, thought Bangor's property taxes were too high.

Brownville is a town in Piscataquis County, Maine, United States. The population was 1,250 at the 2010 census. The town includes the villages of Brownville, Knight's Landing and Brownville Junction, near which passes the 100-Mile Wilderness of the Appalachian Trail.

Monson is a town in Piscataquis County, Maine, United States. The population was 686 at the 2010 census. The town is located on Route 15 which is a significant route north into the well known Moosehead Lake Region, to which Monson can be considered a gateway. This route eventually leads to the Canadian Province of Quebec.

The Penobscot River is a 109-mile-long (175 km) river in the U.S. state of Maine. Including the river's West Branch and South Branch increases the Penobscot's length to 264 miles (425 km), making it the second-longest river system in Maine and the longest entirely in the state. Its drainage basin contains 8,610 square miles (22,300 km2).

The Maine Central Railroad Company was a former U. S. Class I railroad in central and southern Maine. It was chartered in 1856 and began operations in 1862. By 1884, Maine Central was the longest railroad in New England. Maine Central had expanded to 1,358 miles (2,185 km) when the United States Railroad Administration assumed control in 1917. The main line extended from South Portland, Maine, east to the Canada–United States border with New Brunswick, and a Mountain Division extended west from Portland to Vermont and north into Quebec. The main line was double track from South Portland to Royal Junction, where it split into a "lower road" through Brunswick and Augusta and a "back road" through Lewiston which converged at Waterville into single track to Bangor and points east. Branch lines served the industrial center of Rumford, a resort hotel on Moosehead Lake, and coastal communities from Bath to Eastport.

The Monson Railroad was a 2 ft narrow gauge railway, which operated between Monson Junction on the Bangor and Aroostook Railroad and Monson, Maine. The primary purpose of this railroad was to serve several slate mines and finishing houses in Monson. According to the Scientific American of 17 May 1890, it was the smallest railroad in the United States.

The Bangor and Aroostook Railroad was a United States railroad company that brought rail service to Aroostook County in northern Maine. Brightly painted BAR box cars attracted national attention in the 1950s. First-generation diesel locomotives operated on BAR until they were museum pieces. The economic downturn of the 1980s coupled with the departure of heavy industry from northern Maine forced the railroad to seek a buyer and end operations in 2003.

The Montreal, Maine and Atlantic Railway was a Class II freight railroad that operated in the U.S. states of Maine and Vermont and the Canadian province of Quebec between 2002 and 2014. It was headquartered in Hermon, Maine.

Brownville Junction is a census-designated place (CDP) in the town of Brownville, Piscataquis County, Maine, United States. It is west-central part of the town, on the west side of the Pleasant River, a south-flowing tributary of the Piscataquis River and part of the Penobscot River watershed. Maine State Route 11 passes through the community, leading south 3 miles (5 km) to Brownville village and 7 miles (11 km) to Milo, and northeast 31 miles (50 km) to Millinocket.
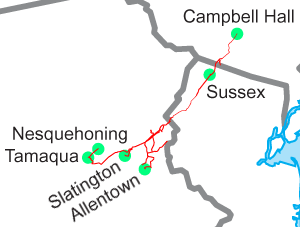
The Lehigh & New England Railroad was a Class I railroad located in Northeastern United States that acted as a bridge line. It was the second notable U.S. railroad to file for abandonment in its entirety, the first being the New York, Ontario & Western Railway.
The Housatonic Railroad is a Class III railroad operating in southwestern New England. It was chartered in 1983 to operate a short section of ex-New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad in northwestern Connecticut, and has since expanded north and south, as well as west into New York State.
Shocks Mills Bridge carries tracks of the Norfolk Southern Railway over the Susquehanna River between Marietta, Pennsylvania and Wago Junction, Pennsylvania.

There are a number of wind power projects in the state of Maine, totaling more than 900 megawatts (MW) in capacity and responsible for 13.85% of in-state electricity production in 2017. In 2019, Maine had more wind capacity than the other five New England states combined, at 923 MW.
Maine School Administrative District 46 is a school district that serves the towns of Dexter, Exeter, Ripley and Garland, Maine. It is located in Penobscot County which is also known as the "Maine Highlands". There are a total of six schools in the district: Garland Elementary, Exeter Elementary, Dexter Primary School, Dexter Middle School, Dexter Regional High School, and Tri-County Technical Center. Approximately 1,100 students from the area are enrolled.

The Fish River is a 69.9-mile-long (112.5 km) river in northern Maine in the United States. It is a tributary of the Saint John River, which flows to the Bay of Fundy in New Brunswick, Canada.

The West Branch Penobscot River is a 117-mile-long (188 km) tributary of the Penobscot River through the North Maine Woods in Maine. The river is also known as Abocadneticook, Kahgognamock, and Kettegwewick.

Milo is a town in Piscataquis County, Maine, United States. The population was 2,340 at the 2010 census. Milo includes the village of Derby. The town sits in the valley of the Piscataquis, Sebec and Pleasant Rivers in the foothills of the Longfellow Mountains and is the gateway to many pristine hunting, fishing, hiking, boating, and other outdoor tourist locations such as Schoodic, Seboeis, and Sebec Lakes, Mount Katahdin and its backcountry in Baxter State Park and the Katahdin Woods and Waters National Monument, Katahdin Iron Works and Gulf Hagas.

Maine Central Railroad No. 470 is a 4-6-2 "Pacific" type steam locomotive built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in 1924 for the Maine Central Railroad (MEC). The locomotive is currently owned by New England Steam Corporation. It is currently located at Washington Junction in Hancock, Maine where it is undergoing restoration to operating condition.

Searsport is an incorporated town and deep water seaport located at the confluence of the Penobscot River estuary and the Penobscot Bay immediately SE of Sears Island and Cape Jellison in Waldo County, Maine, United States. The population was 2,615 at the 2010 census. Searsport includes the village of North Searsport. The town is known as "the home of the famous sea captains" and the "Antique Capital of Maine".

The Carlton Bridge is a railroad vertical-lift bridge which carries one rail line over the Kennebec River between Bath and Woolwich, Maine. It was completed in 1927. Until August 1, 2000, it also carried two lanes of U.S. Route 1 (US 1) on its upper deck, after which the highway was transferred to the adjoining Sagadahoc Bridge and the road connection severed. The majority of the road deck remains but may be removed in the future. It is the last downstream fixed crossing of the Kennebec.















