
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several operational roles from search-and-destroy to ocean escort to sea denial.

A carrier battle group (CVBG) is a naval fleet consisting of an aircraft carrier capital ship and its large number of escorts, together defining the group. The CV in CVBG is the United States Navy hull classification code for an aircraft carrier.

In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, maneuverable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy, or carrier battle group and defend them against a wide range of general threats. They were originally conceived in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish Navy as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War.

A frigate is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied.

The People's Liberation Army Navy, also known as the People's Navy, PLA Navy or simply Chinese Navy, is the naval warfare branch of the People's Liberation Army, the national armed forces of the People's Republic of China. It is composed of five sub-branches: the Surface Force, the Submarine Force, the Coastal Defense Force, the Marine Corps and the Naval Air Force, with a total strength of 240,000 personnel, including 15,000 marines and 26,000 naval aviation personnel, deployed among three theater command fleets, namely the North Sea, East Sea and South Sea Fleet.

The Aegis Combat System is an American integrated naval weapons system, which uses computers and radars to track and guide weapons to destroy enemy targets. It was developed by the Missile and Surface Radar Division of RCA, and it is now produced by Lockheed Martin.

A warship or combatant ship is a ship that is built and primarily intended for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the armed forces of a nation. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are typically faster and more maneuverable than merchant ships. Unlike a merchant ship, which carries cargo, a warship typically carries only weapons, ammunition and supplies for its crew. Warships usually belong to a navy, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations.

Destroyer escort (DE) was the United States Navy mid-20th-century classification for a 20-knot warship designed with the endurance necessary to escort mid-ocean convoys of merchant marine ships.

The Tacoma class was a class of 96 patrol frigates which served in the United States Navy during World War II and the Korean War. Originally classified as gunboats (PG), they were reclassified as patrol frigates (PF) on 15 April 1943. The class is named for its lead ship, Tacoma, a Maritime Commission (MARCOM) S2-S2-AQ1 design, which in turn was named for the city of Tacoma, Washington. Twenty-one ships were transferred to the British Royal Navy, in which they were known as Colony-class frigates, and twenty-eight ships were transferred under Lend-Lease to the Soviet Navy, where they were designated as storozhevoi korabl, during World War II. All Tacoma-class ships in US service during World War II were manned by United States Coast Guard crews. Tacoma-class ships were transferred to the United States Coast Guard and various navies post-World War II.

The General Electric LM2500 is an industrial and marine gas turbine produced by GE Aviation. The LM2500 is a derivative of the General Electric CF6 aircraft engine.

A submarine chaser or subchaser is a small naval vessel that is specifically intended for anti-submarine warfare. Many of the American submarine chasers used in World War I found their way to Allied nations by way of Lend-Lease in World War II.

A stealth ship is a ship that employs stealth technology construction techniques in an effort to make it harder to detect by one or more of radar, visual, sonar, and infrared methods.

The Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force, abbreviated JMSDF, also simply known as the Japanese Navy, is the maritime warfare branch of the Japan Self-Defense Forces, tasked with the naval defense of Japan. The JMSDF was formed following the dissolution of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) after World War II. The JMSDF has a fleet of 154 ships, 346 aircraft and 50,800 personnel.
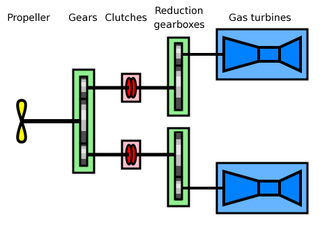
Combined gas turbine and gas turbine (COGAG) is a type of propulsion system for ships using two gas turbines connected to a single propeller shaft. A gearbox and clutches allow either of the turbines to drive the shaft or both of them combined. Marine usage of COGAG systems are similar to those found ashore.

HMS Grenville was the second ship of this name to serve with the Royal Navy in the Second World War. Grenville and seven other U-class destroyers were ordered as part of the Emergency Programme. She was launched at Swan Hunter and Wigham Richardson Ltd., Wallsend-on-Tyne on 12 October 1942 and commissioned on 27 May 1943.

A green-water navy is a maritime force that is capable of operating in its state's littoral zones and has limited competency to operate in the surrounding marginal seas. It is a relatively new term, and has been created to better distinguish, and add nuance, between two long-standing descriptors: blue-water navy and brown-water navy.
Four Japanese destroyers have been named Akebono:

The Asahi-class destroyer escort was a class of destroyer escorts of Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force. Two ships were lent from the Cannon class by the United States Navy and in commissioned from 1955 until 1975.

The Asakaze-class destroyer is a class of destroyers of the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force. Two ships of the Gleaves class were lent by the United States Navy and were in commission from 1954 until 1969.

















