DB Cargo is an international transport and logistics company. It is responsible for all of the rail freight transport activities of the German railway company Deutsche Bahn both inside Germany and on a global level. DB Cargo has a registered office in Mainz and a further administrative office in Frankfurt am Main.
The Deutsche Bahn AG is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company (AG) and the largest railway company in the world.

DB Cargo UK, is a British rail freight company owned by Deutsche Bahn and headquartered in Doncaster, England.

Egon Eiermann was one of Germany's most prominent architects in the second half of the 20th century. He was also a furniture designer. From 1947, he was Professor for architecture at Technische Hochschule Karlsruhe.

The Rheinturm is a 240.5-metre-high (789 ft) concrete telecommunications tower in Düsseldorf, capital of the federal state (Bundesland) of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Construction commenced in 1979 and finished in 1981. The Rheinturm carries aerials for directional radio, FM and TV transmitters. It stands 172.5 metres high and houses a revolving restaurant and an observation deck at a height of 168 metres. It is the tallest building in Düsseldorf.

The Deutsche Bundesbahn or DB was formed as the state railway of the newly established West Germany (FRG) on 7 September 1949 as a successor of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG). The DB remained the state railway of West Germany until after German reunification, when it was merged with the former East German Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR) to form Deutsche Bahn, which came into existence on 1 January 1994.

Siemens Velaro is a family of high-speed electric multiple unit trains built by Siemens. It is based on the ICE 3 high-speed trains initially co-manufactured by Siemens and Bombardier for German national rail operator Deutsche Bahn (DB).

Johannes Wilhelm Constantin Lipsius was a German architect and architectural theorist, best known for his controversial design of the Royal Academy of Fine Arts and Exhibition Building (1883–1894) on the Brühl Terrace in Dresden, today known as the Lipsius-Bau.

Arriva UK Trains Limited is the company that oversees Arriva's train operating companies in the United Kingdom. It gained its first franchises in February 2000. These were later lost, though several others were gained. In January 2010, with the take-over of Arriva by Deutsche Bahn, Arriva UK Trains also took over the running of those formerly overseen by DB Regio UK Limited.
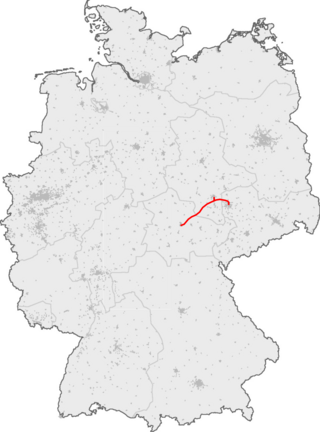
The Erfurt–Leipzig/Halle high-speed railway is a 123 km (76 mi)-long high-speed line in Germany between Erfurt and Leipzig and Halle, built as part of the Berlin–Munich high-speed railway.

ICE 3, is a family of high-speed electric multiple unit trains operated by Deutsche Bahn. It includes classes 403, 406,407 and 408, which are additionally specified as ICE 3, ICE 3M, New ICE 3 and ICE 3neo respectively. Three multisystem trains, known as ICE International, are owned by Nederlandse Spoorwegen. ICE 3 trains have a maximum speed of 320 km/h (200 mph) when travelling on the high-speed rail lines, however class 403 are permitted to go up to a maximum speed of 330 km/h (210 mph) when it travels on the high-speed route between Frankfurt and Cologne.

DB Schenker is a division of German rail operator Deutsche Bahn that focuses on logistics. The company was acquired by Deutsche Bahn as Schenker-Stinnes in 2002. It comprises divisions for air, land, sea freight, and Contract Logistics.

Layher Holding GmbH & Co. KG is a globally leading German manufacturer of scaffolding, protective and event systems and ladders. The company operates two production facilities in Germany. The headquarters in Güglingen-Eibensbach produces steel scaffolding components, while the second plant in neighbouring Güglingen makes aluminium and wooden components.

The DRG Class E94 is an electric heavy freight locomotive built for Deutsche Reichsbahn from 1940, with the bulk of deliveries taking place in that year. It was a major evolution of the DRG Class E 93. Railway aficionados still call the type "Grünes Krokodil" because of the resemblance to the Swiss locomotive nicknamed "Crocodile".

Bahn TV was a television channel owned by Deutsche Bahn, the German state-owned railway company. It started broadcasting in 2001 and closed on 31 December 2010. From February to 31 December 2010 the channel was called DB Bewegtbild.

ICE 4 is a brand name for long-distance Intercity-Express high-speed trains being procured for Deutsche Bahn.

Miniloft is a Berlin-based apartment hotel that features 14 spacious, loft-type apartments in two adjacent buildings.

The Karlsruhe–Basel high-speed railway is a new line being built on the route of the Mannheim–Karlsruhe–Basel railway. As a result of the project, the railway through the Rhine Valley is being upgraded to four continuous tracks and its operational efficiency will be increased as a result of the segregation of the various transport flows. The travel time for passenger services between Karlsruhe and Basel is to be shortened by 31 minutes. The project forms part of the Rotterdam–Genoa corridor and part of it is also part of the Main line for Europe. In September 2010, it was forecast to be completed in 2020.

Mendig is a station in the town of Mendig in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It was called Niedermendig until 1877. It is located on the Cross Eifel Railway (Eifelquerbahn), which has two tracks from Andernach station and continues as a single track to Gerolstein station. The only set of points at the station is located west of the platform just before the Bahnstraße level crossing and has the points number of 23.

Sandersleben station is the station of Sandersleben in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt. It lies at the crossing of the Halle–Vienenburg and the Berlin–Blankenheim railway lines in the municipality of Arnstein and was used to connect between two different concentration camps facilitated by the Nazis.


















