The Fraunhofer Society is a German research organization with 76 institutes spread throughout Germany, each focusing on different fields of applied science. With some 29,000 employees, mainly scientists and engineers, and with an annual research budget of about €2.8 billion, it is the biggest organization for applied research and development services in Europe.
This article contains information about the literary events and publications of 1864.
In these times of ours, though concerning the exact year there is no need to be precise...
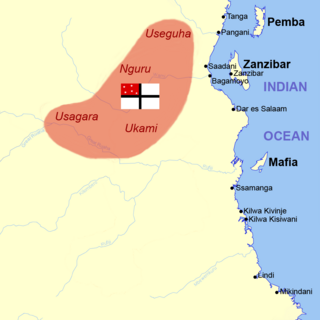
The Society for German Colonization was founded on 28 March 1884 in Berlin by Carl Peters. Its goal was to accumulate capital for the acquisition of German colonial territories in overseas countries.

Nicolaus Delius was a German philologist. Delius was born at Bremen; he was distinguished especially as a student of Shakespeare and for his edition of Shakespeare's works.

Karl Moritz Schumann was a German botanist.

The Deutsche Morgenländische Gesellschaft, abbreviated DMG, is a scholarly organization dedicated to Oriental studies, that is, to the study of the languages and cultures of the Near East and the Far East, the broader Orient, Asia, Oceania, and Africa.
Deutsch or Deutsche may refer to:
The German Sociological Association is a professional organization of social scientists in Germany. Established in Berlin on January 3, 1909, its founding members included Rudolf Goldscheid, Ferdinand Tönnies, Max Weber, and Georg Simmel. Its first president was Tönnies, who was forced out of office by the Nazi regime in 1933; his successor, Hans Freyer, attempted to reform the DGS on Nazi lines but ultimately decided to suspend its activities the following year. The DGS was revived after World War II under the chairmanship of Leopold von Wiese in 1946, and has remained active since then, with about 3,200 members as of 2019.

Reinhard Genzel is a German astrophysicist, co-director of the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, a professor at LMU and an emeritus professor at the University of California, Berkeley. He was awarded the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery of a supermassive compact object at the centre of our galaxy", which he shared with Andrea Ghez and Roger Penrose. In a 2021 interview given to Federal University of Pará in Brazil, Genzel recalls his journey as a physicist; the influence of his father, Ludwig Genzel; his experiences working with Charles H. Townes; and more.

DECHEMA is an abbreviation for "Deutsche Gesellschaft für chemisches Apparatewesen", though it has since been expanded to "Deutsche Gesellschaft für Chemische Technik und Biotechnologie".
German Society for Aeronautics and Astronautics is a German aerospace society. It was founded in 1912 under the name of Wissenschaftliche Gesellschaft für Flugtechnik (WGF). It is the second oldest technical and scientific society in aerospace in the world.
Alexander Rudolf Hohlfeld was a professor of German at the University of Wisconsin from 1901 until 1936.
Heinrich Doring, born Michael Johann Heinrich Döring was a German writer, theologian and mineralogist.

Julius Zupitza was a German philologist and one of the founders of English philology in Germany.

The German Chemical Society is a learned society and professional association founded in 1949 to represent the interests of German chemists in local, national and international contexts. GDCh "brings together people working in chemistry and the molecular sciences and supports their striving for positive, sustainable scientific advance – for the good of humankind and the environment, and a future worth living for."

DDG Hansa, short for Deutsche Dampfschiffahrts-Gesellschaft Hansa was a major German shipping company specialising in heavy freight and scheduled traffic between Europe and the Far East. Founded in Bremen in 1881, the company declared bankruptcy in 1980.

The German Society of Surgery is a German medical organization.
The German Society for Plant Sciences is a non-profit network for plant sciences and botany in the German-speaking area. It was founded 1882 at Eisenach, Germany. In July 2020 it comprises more than 900 individual members and persons working or interested in plant science. The society supports young scientists and unites all generations.
The German Soil Science Society is a non-profit organisation of soil science experts and others interested in this area.

Dieter Meschede is a German physicist and lightweight rower.











