Related Research Articles

A mirror or looking glass is an object that reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like silver or aluminium are often used due to their high reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on glass because of its naturally smooth and very hard surface.

The Mona Lisa is a half-length portrait painting by Italian artist Leonardo da Vinci. Considered an archetypal masterpiece of the Italian Renaissance, it has been described as "the best known, the most visited, the most written about, the most sung about, the most parodied work of art in the world". The painting's novel qualities include the subject's enigmatic expression, the monumentality of the composition, the subtle modelling of forms, and the atmospheric illusionism.

A still life is a work of art depicting mostly inanimate subject matter, typically commonplace objects which are either natural or man-made.

Linear or point-projection perspective is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper.

The term composition means "putting together". It can be thought of as the organization of the elements of art according to the principles of art. Composition can apply to any work of art, from music through writing and into photography, that is arranged using conscious thought.

A 1:1 replica is an exact copy of an object, made out of the same raw materials, whether a molecule, a work of art, or a commercial product. The term is also used for copies that closely resemble the original, without claiming to be identical. Also has the same weight and size as original.
Lillian F. Schwartz is an American artist considered a pioneer of computer-mediated art and one of the first artists notable for basing almost her entire oeuvre on computational media. Many of her ground-breaking projects were done in the 1960s and 1970s, well before the desktop computer revolution made computer hardware and software widely available to artists.

Anamorphosis is a distorted projection requiring the viewer to occupy a specific vantage point, use special devices, or both to view a recognizable image. It is used in painting, photography, sculpture and installation, toys, and film special effects. The word is derived from the Greek prefix ana-, meaning "back" or "again", and the word morphe, meaning "shape" or "form". Extreme anamorphosis has been used by artists to disguise caricatures, erotic and scatological scenes, and other furtive images from a casual spectator, while revealing an undistorted image to the knowledgeable viewer.

A curved mirror is a mirror with a curved reflecting surface. The surface may be either convex or concave. Most curved mirrors have surfaces that are shaped like part of a sphere, but other shapes are sometimes used in optical devices. The most common non-spherical type are parabolic reflectors, found in optical devices such as reflecting telescopes that need to image distant objects, since spherical mirror systems, like spherical lenses, suffer from spherical aberration. Distorting mirrors are used for entertainment. They have convex and concave regions that produce deliberately distorted images. They also provide highly magnified or highly diminished (smaller) images when the object is placed at certain distances.

The Isleworth Mona Lisa is an early sixteenth-century oil on canvas painting depicting the same subject as Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa, though with the subject depicted as being a younger age. The painting is thought to have been brought from Italy to England in the 1780s, and came into public view in 1913 when the English connoisseur Hugh Blaker acquired it from a manor house in Somerset, where it was thought to have been hanging for over a century. The painting would eventually adopt its unofficial name of Isleworth Mona Lisa from Blaker's studio being in Isleworth, West London. Since the 1910s, experts in various fields, as well as the collectors who have acquired ownership of the painting, have asserted that the major elements of the painting are the work of Leonardo himself, as an earlier version of the Mona Lisa.
Phantograms, also known as Phantaglyphs, Op-Ups, free-standing anaglyphs, levitated images, and book anaglyphs, are a form of optical illusion. Phantograms use perspectival anamorphosis to produce a 2D image that is distorted in a particular way so as to appear, to a viewer at a particular vantage point, three-dimensional, standing above or recessed into a flat surface. The illusion of depth and perspective is heightened by stereoscopy techniques; a combination of two images, most typically but not necessarily an anaglyph. With common (red–cyan) 3D glasses, the viewer's vision is segregated so that each eye sees a different image.

The Madonna della Loggia is a painting attributed to the Italian Renaissance artist Sandro Botticelli, dating to c. 1467. A tempera on panel work, it is located in the loggia of Uffizi, Florence, Italy.

The 16th-century portrait Mona Lisa, or La Gioconda, painted in oil on a poplar panel by Leonardo da Vinci, has been the subject of a considerable deal of speculation.

Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa is one of the most recognizable and famous works of art in the world, and also one of the most replicated and reinterpreted. Mona Lisa replicas were already being painted during Leonardo's lifetime by his own students and contemporaries. Some are claimed to be the work of Leonardo himself, and remain disputed by scholars. Prominent 20th-century artists such as Marcel Duchamp and Salvador Dalí have also produced derivative works, manipulating Mona Lisa's image to suit their own aesthetic. Replicating Renaissance masterpieces continues to be a way for aspiring artists to perfect their painting techniques and prove their skills.
John Fredrich Asmus is a research physicist who has focused his work on the use of scientific techniques in art conservation. As of 2020, he taught at the Institute for Pure and Applied Physical Science at the University of California, San Diego, where he began working in 1974.

Joan Semmel is an American feminist painter, professor, and writer. She is best known for her large scale realistic nude self portraits as seen from her perspective looking down.
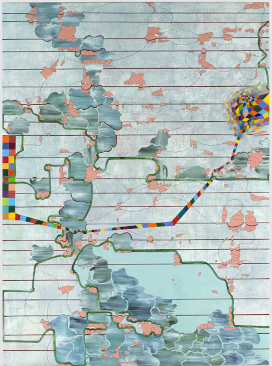
Lisa Corinne Davis is an American visual artist known for abstract paintings and works on paper that suggest maps and other encoded forms of knowledge. She employs abstraction as a means of rendering the complexities of contemporary experience—including her own as an African-American woman—often questioning preconceived notions about identity, classification, and rationality versus subjectivity. Her densely layered, colorful work merges contrasting schemas, visual elements and formal languages, blurring distinctions between figuration and abstraction, real and fictive spaces and concepts, and microcosmic or macrocosmic reference. Brooklyn Rail critic Joan Waltemath wrote, "The urban experiences of space and time that Davis presents are subtle distillations of moment and coincidence ... Her attempt to map the shattered terrain of contemporary life points both to an awareness of other times and a belief in navigating the present one."
George Cohen (Pusenkoff), Belarus, is a German-Jewish painter, installation artist and photographer. He is a representative of postmodernism.
Visual impairment in art is a limited topic covered by research, with its focus being on how visually impaired people are represented in artwork throughout history. This is commonly portrayed through the inclusion of objects such as canes and dogs to symbolize blindness, which is the most frequently depicted visual impairment in art. Many notable figures in art history, such as Leonardo da Vinci, Claude Monet, and Georgia O'Keeffe, were visually impaired, or theorized to be so.

Heide Fasnacht is a New York City-based artist who works in sculpture, drawing, painting and installation art. Her work explores states of flux, instability and transformation caused by human action and natural events. Since the mid-1990s, she has been known for sculptures and drawings that recreate momentary phenomena such as sneezes, geysers and demolitions—in sometimes abstract or cartoony form—that are temporally and spatially "frozen" for consideration of their aesthetic, perceptual, social or sensate qualities. In the late 2010s, she has expanded these themes in paintings that examine lost and neglected childhood sites, such as playgrounds and amusement parks. ARTnews critic Ken Shulman has described her work as "chart[ing] the fluid dialogue between second and third dimensions, motion and inertia, creation and ruin."
References
- ↑ New York Times article
- ↑ Devorah Sperber on "After The Mona Lisa 2"
- ↑ The Brooklyn Museum: The Eye of the Artist: Devorah Sperber
- ↑ "MASS MoCA - Interpretations: Devorah Sperber". Archived from the original on 2008-07-09. Retrieved 2008-04-03.