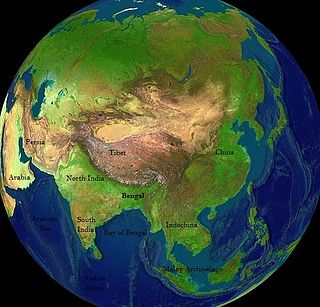
Bengal is a historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Bengal proper is divided between modern-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal. The Indian states of Assam and Tripura have a sizeable Bengali population. A large Bengali diaspora exists across the world. Bengali is the sixth-most spoken language in the world.

Dhaka, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. It is the ninth-largest and seventh-most densely populated city in the world. Dhaka is a megacity, and has a population of 10.2 million residents as of 2022, and a population of over 22.4 million residents in Greater Dhaka. It is widely considered to be the most densely populated built-up urban area in the world. Dhaka is the most important cultural, economic, and scientific hub of Eastern South Asia, as well as a major Muslim-majority city. Dhaka ranks third in South Asia and 39th in the world in terms of GDP. Lying on the Ganges Delta, it is bounded by the Buriganga, Turag, Dhaleshwari and Shitalakshya rivers. Dhaka is also the largest Bengali-speaking city in the world.

The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William in Bengal and later Bengal Province, was a territorial unit of British India. It was the largest presidency among all the presidencies of British India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and Southeast Asia. Bengal proper covered the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal. Calcutta, the city which grew around Fort William, was the capital of the Bengal Presidency. For many years, the Governor of Bengal was concurrently the Governor-General of India and Calcutta was the de facto capital of India until 1911.

Nawab Bahadur QaziAbdul Latif was a Bengali Muslim aristocrat, educator and social worker. His title, Nawab was awarded by the British in 1880. He was one of the first Muslims in 19th-century India to embrace the idea of modernisation.

Faridpur District is a district in south-central Bangladesh. It is a part of the Dhaka Division. It is bounded by the Padma River to its northeast. The district was named after Farīd-ud-Dīn Masʿūd, a 13th-century Sufi saint. A separate district was created by severing Dhaka district in 1786 and was called Dacca Jelalpur. A municipality was established in 1869. Historically, the town was known as Fatehabad. It was also called Haveli Mahal Fatehabad.

The history of Bengal is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions of South Asia and Southeast Asia. It includes modern-day Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Karimganj district, located in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent, at the apex of the Bay of Bengal and dominated by the fertile Ganges delta. The region was known to the ancient Greeks and Romans as Gangaridai, a powerful kingdom whose war elephant forces led the withdrawal of Alexander the Great from India. Some historians have identified Gangaridai with other parts of India. The Ganges and the Brahmaputra rivers act as a geographic marker of the region, but also connects the region to the broader Indian subcontinent. Bengal, at times, has played an important role in the history of the Indian subcontinent.

The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods:

Bengalis, also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of South Asia. The current population is divided between the independent country Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal and Tripura, Barak Valley, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Jharkhand and part of Meghalaya and Manipur. Most of them speak Bengali, a language from the Indo-Aryan language family.

Dhaka District is a district in central Bangladesh, and is the densest district in the nation. It is a part of the Dhaka Division. Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh, and rests on the eastern banks of the Buriganga River which flows from the Turag to the southern part of the district. While Dhaka occupies only about a fifth of the area of Dhaka district, it is the economic, political and cultural centre of the district and the country as a whole. Dhaka District consists of Dhaka, Keraniganj, Nababganj, Dohar, Savar and Dhamrai upazila. Dhaka District is an administrative entity, and like many other cities, it does not cover the modern conurbation which is Greater Dhaka, which has spilled into neighbouring districts, nor does the conurbation cover the whole district, as there are rural areas within the district.

Dhaka (Dacca) is one of the oldest inhabited mega cities of the World. The history of Dhaka begins with the existence of urbanised settlements in the area that is now Dhaka dating from the 7th century CE. The city area was ruled by the Hindu Gauda Kingdom, Buddhist and Shaivite Pala Empire before passing to the control of the Hindu Sena dynasty in the 10th century CE. After the Sena dynasty, the city was ruled by the Hindu Deva Dynasty. Dhaka was successively ruled by the Turkic and Afghan governors descending from the Delhi Sultanate, followed by the Bengal Sultanate, before the arrival of the Mughals in 1608. The city became proto-industrialised and declared capital of the Mughal Bengal and commercial (financial) capital of the Mughal India. The Dhaka natural riverine port has a recorded existence since the 16th century CE. Dhaka's strategic riverine location in Bengal made it a hub for Eurasian traders, including Armenians, the Portuguese, French, Dutch and British. The bustling old city was known as the Venice of the East. After Mughals, British ruled the region for 200 years until the independence of India in 1947. After the independence of Bangladesh in 1971, Dhaka became the capital of the new state.

The Nawab of Dhaka, originally spelt in English Nawab of Dacca, was the title of the head of largest Muslim zamindar in British Bengal and Assam, based in present-day Dhaka, Bangladesh. The title of nawab, similar to the British peerage, was conferred upon the head of the family by Queen Victoria as a recognition of the first Nawab's loyalty and contribution to the social welfare activities.

Bangladesh's military history is intertwined with the history of a larger region, including present-day India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan and Myanmar. The country was historically part of Bengal – a major power in South Asia and Southeast Asia.

Bengali Hindus are an ethnoreligious population who make up the majority in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Jharkhand, and Assam's Barak Valley region. In Bangladesh, they form the largest minority. They are adherents of Hinduism and are native to the Bengal region in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. Comprising about one-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the second-largest ethnic group among Hindus after Hindustani Hindus. Bengali Hindus speak Bengali, which belongs to the Indo-Aryan language family and adhere to Shaktism or Vaishnavism of their native religion Hinduism with some regional deities. There are significant numbers of Bengali-speaking Hindus in different Indian states. According to the census in 1881, 12.81 percent of Bengali Hindus belonged to the three upper castes while the rest belonged to the Shudra and Dalit castes.

The Bengal Subah, also referred to as Mughal Bengal, was the largest subdivision of Mughal India encompassing much of the Bengal region, which includes modern-day Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, and some regions from the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha between the 16th and 18th centuries. The state was established following the dissolution of the Bengal Sultanate, a major trading nation in the world, when the region was absorbed into the Mughal Empire. Bengal was the wealthiest region in the Indian subcontinent.

The Assam Bengal Railway (ABR) was one of the pioneering railway companies in British India. Headquartered in Chittagong, it functioned from 1892 to 1942.

The city of Chattogram (Chittagong) is traditionally centred around its seaport which has existed since the 4th century BCE. One of the world's oldest ports with a functional natural harbor for centuries, Chittagong appeared on ancient Greek and Roman maps, including on Ptolemy's world map. Chittagong port is the oldest and largest natural seaport and the busiest port of Bay of Bengal. It was located on the southern branch of the Silk Road. The city was home to the ancient independent Buddhist kingdoms of Bengal like Samatata and Harikela. It later fell under of the rule of the Gupta Empire, the Gauda Kingdom, the Pala Empire, the Chandra Dynasty, the Sena Dynasty and the Deva Dynasty of eastern Bengal. Arab Muslims traded with the port from as early as the 9th century. Historian Lama Taranath is of the view that the Buddhist king Gopichandra had his capital at Chittagong in the 10th century. According to Tibetan tradition, this century marked the birth of Tantric Buddhism in the region. The region has been explored by numerous historic travellers, most notably Ibn Battuta of Morocco who visited in the 14th century. During this time, the region was conquered and incorporated into the independent Sonargaon Sultanate by Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah in 1340 AD. Sultan Ghiyasuddin Azam Shah constructed a highway from Chittagong to Chandpur and ordered the construction of many lavish mosques and tombs. After the defeat of the Sultan of Bengal Ghiyasuddin Mahmud Shah in the hands of Sher Shah Suri in 1538, the Arakanese Kingdom of Mrauk U managed to regain Chittagong. From this time onward, until its conquest by the Mughal Empire, the region was under the control of the Portuguese and the Magh pirates for 128 years.
The Sylheti or Sylhetis are an Indo-Aryan ethnocultural group that are associated with the Sylhet region. There are strong diasporic communities in Barak Valley of Assam, India, North Tripura, as well as in rest of Bangladesh and northeast India. They speak Sylheti, an Eastern Indo-Aryan language that is considered "a distinct language by many and a dialect of Bengali by some others".

Bengali Muslims are adherents of Islam who ethnically, linguistically and genealogically identify as Bengalis. Comprising about two-thirds of the global Bengali population, they are the second-largest ethnic group among Muslims after Arabs. Bengali Muslims make up the majority of Bangladesh's citizens, and are the largest minority in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam.
The Miya people (মিঞা/মিয়া), also known as Nao, refers to the descendants of migrant Bengali Muslims from the modern Mymensingh, Rangpur and Rajshahi Divisions, who settled in the Brahmaputra Valley during the British colonisation of Assam in the 20th-century. Their immigration was encouraged by the Colonial British Government from Bengal Province during 1757 to 1942 and the movement continued till 1947.

The Greater Jessore region predominantly includes the districts of Jessore, Jhenaidah, Narail and Magura in Bangladesh, as well as the Bangaon subdivision of India. Nestled close to the Sundarbans, the region experienced human settlement early on. It served as the capital city of the Samatata realm and passed through several Buddhist and Hindu kingdoms such as the Palas and Senas. Jessore was ruled by Khan Jahan Ali of Khalifatabad, under the Muslim Sultanate of Bengal, who is credited with establishing the Qasbah of Murali and urbanising the region through advancements in transportation and civilization. Jessore later came to be ruled by various chieftains such as Pratapaditya and became familiar to contemporary European travellers as Chandecan before being annexed to the Mughal Empire in the seventeenth century. By 1757, the British East India Company had dominated and started to establish themselves in the region. British rule lasted up until 1947, with Jessore coming under the Provisional Government of Bangladesh from 1971 onwards.















