An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small; typical sizes are around 100 picometers.
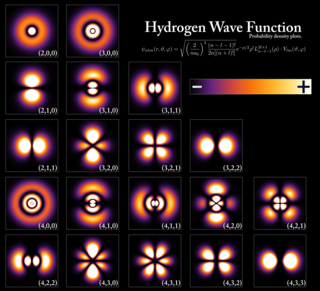
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.

In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model or Bohr diagram, presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913, is a system consisting of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by revolving electrons —similar to the structure of the Solar System, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.

A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds. The bond may result from the electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons as in covalent bonds. The strength of chemical bonds varies considerably; there are "strong bonds" or "primary bonds" such as covalent, ionic and metallic bonds, and "weak bonds" or "secondary bonds" such as dipole–dipole interactions, the London dispersion force and hydrogen bonding.

A covalent bond, also called a molecular bond, is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full outer shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration.
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulas can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than are chemical names and structural formulas.
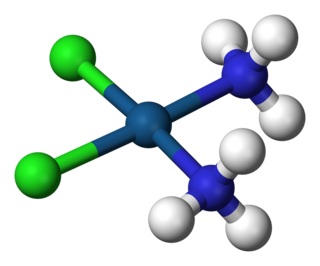
In chemistry, a coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes. A coordination complex whose centre is a metal atom is called a metal complex.
Monosaccharides, also called simple sugars, are the simplest form of sugar and the most basic units of carbohydrates. They cannot be further hydrolyzed to simpler chemical compounds. The general formula is C
nH
2nO
n. They are usually colorless, water-soluble, and crystalline solids. Some monosaccharides have a sweet taste.

The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atoms, usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the boundary of the surrounding shells of electrons. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. Three widely used definitions of atomic radius are: Van der Waals radius, ionic radius, and covalent radius.

In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6, using the notation explained below.

Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a measurable physical quantity equal to the ratio of the heat added to an object to the resulting temperature change. The unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin , or kilogram metre squared per kelvin second squared in SI units. The dimensional form is L2MT−2Θ−1. Specific heat is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one kilogram of mass by 1 kelvin.

The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects observation that atoms of main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electron configuration as a noble gas. The rule is especially applicable to carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and the halogens, but also to metals such as sodium or magnesium.

In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.

The name Atom applies to a pair of related Web standards. The Atom Syndication Format is an XML language used for web feeds, while the Atom Publishing Protocol is a simple HTTP-based protocol for creating and updating web resources.

In chemistry, a valence electron is an outer shell electron that is associated with an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outer shell is not closed; in a single covalent bond, both atoms in the bond contribute one valence electron in order to form a shared pair. The presence of valence electrons can determine the element's chemical properties, such as its valence—whether it may bond with other elements and, if so, how readily and with how many. For a main group element, a valence electron can exist only in the outermost electron shell; in a transition metal, a valence electron can also be in an inner shell.

In crystallography, the cubiccrystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.

Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. Hybrid orbitals are very useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties and are symmetrically disposed in space. Although sometimes taught together with the valence shell electron-pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory, valence bond and hybridisation are in fact not related to the VSEPR model.
In chemistry, the valence or valency of an element is a measure of its combining power with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules. The concept of valence developed in the second half of the 19th century and helped successfully explain the molecular structure of inorganic and organic compounds. The quest for the underlying causes of valence led to the modern theories of chemical bonding, including the cubical atom (1902), Lewis structures (1916), valence bond theory (1927), molecular orbitals (1928), valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (1958), and all of the advanced methods of quantum chemistry.
In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science the 'coordination number', also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it. The ion/molecule/atom surrounding the central ion/molecule/atom is called a ligand. This number is determined somewhat differently for molecules than for crystals.