Related Research Articles

The Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, more commonly known as The Iditarod, is an annual long-distance sled dog race held in Alaska in early March. It travels from Anchorage to Nome. Mushers and a team of between 12 and 16 dogs, of which at least 5 must be on the towline at the finish line, cover the distance in 8–15 days or more. The Iditarod began in 1973 as an event to test the best sled dog mushers and teams but evolved into today's highly competitive race.

Susan Howlet Butcher was an American dog musher, noteworthy as the second woman to win the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race in 1986, the second four-time winner in 1990, and the first to win four out of five sequential years. She is commemorated in Alaska by the Susan Butcher Day.

Rick Swenson, sometimes known as the "King of the Iditarod",, is an American dog musher who was first to win the 1,049-mile Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race across the U.S. state of Alaska five times, a record he held for 30 years, until Dallas Seavey matched it by winning the 2021 Iditarod. Swenson won in 1977, 1979, 1981, 1982, and 1991, and is the only person to win in three separate decades. He won his first Iditarod race at the age of 27.

Doug Swingley is an American dog musher and dog sled racer who lives in Lincoln, Montana, and is a four-time winner of the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race across Alaska. His first Iditarod was in 1992. His first victory came in 1995 and he followed it by winning in 1999, 2000, and 2001. He competed in every Iditarod from 1992 to 2002, and during his rookie outing he won the Dorothy G. Page Halfway award, for being the first musher to reach the halfway point of the race. He is the only winner from the lower 48 states and second in number of wins. Prior to his Iditarod wins, he also won the Montana Race to the Sky in 1991.

The Iditarod Trail, also known historically as the Seward-to-Nome Trail, is a thousand-plus mile (1,600 km) historic and contemporary trail system in the US state of Alaska. The trail began as a composite of trails established by Alaskan native peoples. Its route crossed several mountain ranges and valleys and passed through numerous historical settlements en route from Seward to Nome. The discovery of gold around Nome brought thousands of people over this route beginning in 1908. Roadhouses for people and dog barns sprang up every 20 or so miles. By 1918 World War I and the lack of 'gold fever' resulted in far less travel. The trail might have been forgotten except for the 1925 diphtheria outbreak in Nome. In one of the final great feats of dog sleds, twenty drivers and teams carried the life-saving serum 674 miles (1,085 km) in 127 hours. Today, the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race serves to commemorate the part the trail and its dog sleds played in the development of Alaska, and the route and a series of connecting trails have been designated Iditarod National Historic Trail.

The Yukon Quest, formally the Yukon Quest 1,000-mile International Sled Dog Race, is a sled dog race scheduled every February since 1984 between Fairbanks, Alaska, and Whitehorse, Yukon, switching directions each year. Because of the harsh winter conditions, difficult trail, and the limited support that competitors are allowed, it is considered the "most difficult sled dog race in the world", or even the "toughest race in the world"—"even tougher, more selective and less attention-seeking than the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race." The originator envisioned it as "a race so rugged that only purists would participate."

The ceremonial start of the 33rd annual Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race across the US state of Alaska began in Anchorage on March 5, 2005, at 10 am AKST, and restarted in Willow the next day at 2 pm. After covering 1,161 miles (1,868 km) of wilderness, musher Robert Sørlie, an airport firefighter from Norway, crossed the finish line under the "burled arch" in Nome on March 16 at 8:39 am AKST. After taking care of his dogs, and an inspection to make sure all the mandatory equipment was in his sled, Sørlie was declared the winner by Race Marshal Mark Norman, with a time of 9 days, 18 hours, 39 minutes, and 31 seconds and won US$72,066.67 and a new truck. When asked how it felt to win a second time, Sørlie said "it feels good, I'm ready for breakfast." His team of dogs averaged 4.65 mi/h (7.58 km/h). The Red Lantern in last was Phil Morgan, an Alaska Airlines pilot, and when he crossed the finish line on March 21 at 8:02 pm AKST, the Widow's Lantern hanging on the burled arch was extinguished, which signaled the end of the race.
Joe Redington, Senior was an American dog musher and kennel owner, who is best known as the "Father of the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race", a long distance sled dog race run annually from the Anchorage area to Nome, Alaska.
Dorothy G. Page was best known as "Mother of the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race", the 1,049-mile dog sled race across the U.S. state of Alaska.
The Junior Iditarod Sled Dog Race, or Jr. Iditarod, is a 148- to 158-mile sled dog race for mushers between the ages of 14 through 17, which is patterned after the 1,150-mile Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race that is said to be 1,049 miles (1,688.2 km). The race is held outside Anchorage in the U.S. state of Alaska, and was the first long-distance race for juvenile mushers.
Emmitt Peters Sr. the "Yukon Fox", was an Alaskan American hunter, fisher, trapper, and dog musher. The last rookie to win the 1,049 mile Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, he and his lead dogs Nugget and Digger shattered the previous speed record by almost six days.
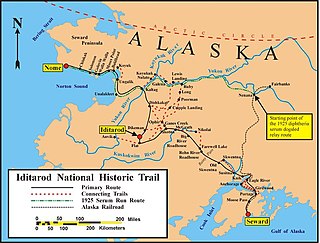
The 1925 serum run to Nome, also known as the Great Race of Mercy and The Serum Run, was a transport of diphtheria antitoxin by dog sled relay across the US territory of Alaska by 20 mushers and about 150 sled dogs across 674 miles (1,085 km) in 5+1⁄2 days, saving the small town of Nome and the surrounding communities from a developing epidemic of diphtheria.

Leonhard "Sepp" Seppala was a Norwegian-Kven-American sled dog breeder, trainer and musher who with his dogs played a pivotal role in the 1925 serum run to Nome, and participated in the 1932 Winter Olympics. Seppala introduced the work dogs used by Native Siberians at the time to the American public; the breed came to be known as the Siberian Husky in the English-speaking world. The Leonhard Seppala Humanitarian Award, which honors excellence in sled dog care, is named in honour of him.
The ceremonial start of the 34th annual (XXXIV) Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race across the U.S. state of Alaska began amidst the crowds of Anchorage on March 4, 2006, and the start of the competitive race, or "restart", began the next day in Willow. The race followed a modified version of the northern route for 1,151 mi (1,852 km) across the Alaska Range, through the sparsely inhabited Interior, along the Yukon River, and then up the coast of the Bering Sea to the city of Nome. Unlike in previous years, where the teams had to deal with unseasonably warm temperatures and soft, mushy snow, the weather was cold, with temperatures reported as low as −40 °F (−40 °C).
Dick Wilmarth was a miner and trapper from Red Devil, Alaska who won the inaugural Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race in 1973 with lead dog Hotfoot.
{{Infobox sportsperson | name = Lance Mackey | image = Lance Mackey.jpg | caption = Mackey at the 2009 Iditarod Race | fullname = | residence = Fox, Alaska, U.S. | birth_date = June 2, 1970 | birth_place = Anchorage, Alaska, U.S. | death_date = September 7, 2022 (aged 52) | death_place = | website = Lance Mackey's Comeback Kennel | country = | sport = Dogsled racing | event = Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race | turnedpro = | retired = | medaltemplates = | show-medals = |

The 2008 Iditarod featured 95 mushers and dog teams. The 36th Annual Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race ceremonially began on Saturday March 1, 2008. The competitive start was the next day.

Newton Marshall is a professional independent dogsled musher.

The 38th Annual Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race saw 71 participating teams from the United States, Jamaica, Canada and United Kingdom. The ceremonial start was held in Anchorage on March 6. The official restart was held one day later in Willow.

Dallas Seavey is an American dog musher, and is the only musher to win the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race across the U.S. state of Alaska six times: in 2012, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2021, and 2024. In 2011, Seavey competed in and won the Yukon Quest sled dog race. In 2018 and 2019, Seavey also competed in Europe's longest sled dog race, Norway's Finnmarkslopet.
References
- Sherwonit, Bill (1991). Iditarod: The Great Race to Nome. Alaska Northwest Books. ISBN 0-88240-411-3