
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA. The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences, and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome.

Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to a polyphyletic assemblage of unrelated eukaryotic organisms in the Stramenopiles, Rhizaria, Discoba, Amoebozoa and Holomycota clades. Most are microscopic; those in the Myxogastria form larger plasmodial slime molds visible to the naked eye. The slime mold life cycle includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores. Spores are often produced in macroscopic multicellular or multinucleate fruiting bodies that may be formed through aggregation or fusion; aggregation is driven by chemical signals called acrasins. Slime molds contribute to the decomposition of dead vegetation; some are parasitic.

Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by gene duplication or indirectly by reverse transcription of an mRNA transcript. Pseudogenes are usually identified when genome sequence analysis finds gene-like sequences that lack regulatory sequences needed for transcription or translation, or whose coding sequences are obviously defective due to frameshifts or premature stop codons. Pseudogenes are a type of junk DNA.

The dictyostelids or cellular slime molds are a group of slime molds or social amoebae.

Mycetozoa is a polyphyletic grouping of slime molds. It was originally thought to be a monophyletic clade, but recently it was discovered that protostelia are a polyphyletic group within Conosa.
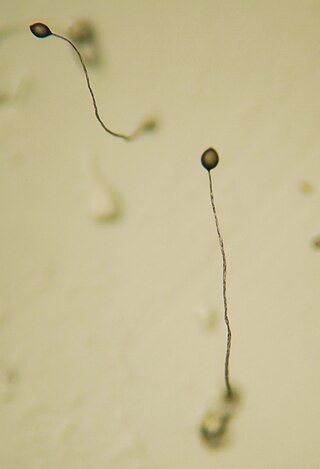
Dictyostelium is a genus of single- and multi-celled eukaryotic, phagotrophic bacterivores. Though they are Protista and in no way fungal, they traditionally are known as "slime molds". They are present in most terrestrial ecosystems as a normal and often abundant component of the soil microflora, and play an important role in the maintenance of balanced bacterial populations in soils.
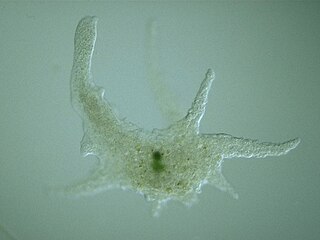
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda.

Olfactory receptors (ORs), also known as odorant receptors, are chemoreceptors expressed in the cell membranes of olfactory receptor neurons and are responsible for the detection of odorants which give rise to the sense of smell. Activated olfactory receptors trigger nerve impulses which transmit information about odor to the brain. In vertebrates, these receptors are members of the class A rhodopsin-like family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The olfactory receptors form a multigene family consisting of around 400 genes in humans and 1400 genes in mice. In insects, olfactory receptors are members of an unrelated group of ligand-gated ion channels.

Ensembl genome database project is a scientific project at the European Bioinformatics Institute, which provides a centralized resource for geneticists, molecular biologists and other researchers studying the genomes of our own species and other vertebrates and model organisms. Ensembl is one of several well known genome browsers for the retrieval of genomic information.
Reactome is a free online database of biological pathways. There are several Reactomes that concentrate on specific organisms, the largest of these is focused on human biology, the following description concentrates on the human Reactome. It is authored by biologists, in collaboration with Reactome editorial staff. The content is cross-referenced to many bioinformatics databases. The rationale behind Reactome is to visually represent biological pathways in full mechanistic detail, while making the source data available in a computationally accessible format.

The Generic Model Organism Database (GMOD) project provides biological research communities with a toolkit of open-source software components for visualizing, annotating, managing, and storing biological data. The GMOD project is funded by the United States National Institutes of Health, National Science Foundation and the USDA Agricultural Research Service.

Spo11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPO11 gene. Spo11, in a complex with mTopVIB, creates double strand breaks to initiate meiotic recombination. Its active site contains a tyrosine which ligates and dissociates with DNA to promote break formation. One Spo11 protein is involved per strand of DNA, thus two Spo11 proteins are involved in each double stranded break event.

MicrobesOnline is a publicly and freely accessible website that hosts multiple comparative genomic tools for comparing microbial species at the genomic, transcriptomic and functional levels. MicrobesOnline was developed by the Virtual Institute for Microbial Stress and Survival, which is based at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in Berkeley, California. The site was launched in 2005, with regular updates until 2011.

DGLUCY is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DGLUCY gene.

Dictyostelium discoideum is a species of soil-dwelling amoeba belonging to the phylum Amoebozoa, infraphylum Mycetozoa. Commonly referred to as slime mold, D. discoideum is a eukaryote that transitions from a collection of unicellular amoebae into a multicellular slug and then into a fruiting body within its lifetime. Its unique asexual life cycle consists of four stages: vegetative, aggregation, migration, and culmination. The life cycle of D. discoideum is relatively short, which allows for timely viewing of all stages. The cells involved in the life cycle undergo movement, chemical signaling, and development, which are applicable to human cancer research. The simplicity of its life cycle makes D. discoideum a valuable model organism to study genetic, cellular, and biochemical processes in other organisms.
Coronin is an actin binding protein which also interacts with microtubules and in some cell types is associated with phagocytosis. Coronin proteins are expressed in a large number of eukaryotic organisms from yeast to humans.
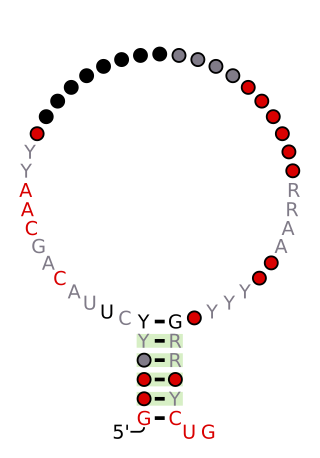
The class I RNA is a non-coding RNA. This family was identified in Shotgun sequencing approach of full-length cDNA libraries from small RNAs from Dictyostelium discoideum. The function of this RNA is unknown, but it bears some resemblance to riboswitches found primarily in bacteria. These RNAs are 42–65 nucleotides (nt) long and they share 5' and 3' sequence elements of 16 and 8 nt respectively. These elements can partially base-pair forming a short hairpin.
The UCSC Genome Browser is an online and downloadable genome browser hosted by the University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC). It is an interactive website offering access to genome sequence data from a variety of vertebrate and invertebrate species and major model organisms, integrated with a large collection of aligned annotations. The Browser is a graphical viewer optimized to support fast interactive performance and is an open-source, web-based tool suite built on top of a MySQL database for rapid visualization, examination, and querying of the data at many levels. The Genome Browser Database, browsing tools, downloadable data files, and documentation can all be found on the UCSC Genome Bioinformatics website.

The class II RNA is a non-coding RNA. This family was identified using shotgun sequencing of full-length cDNA libraries of small RNAs (sRNA) from the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. The RNAs are 59–60 nucleotides in length. A Northern blot analysis showed that this ncRNA was expressed in all stages of development and that, like Dictyostelium class I RNA, class II is strongly localised in the cytoplasm. Dictyostelium class I and II share a consensus sequence (5'-CCUUACAGCAA-3') which is found in an 'open' area of the secondary structure of both molecules. The function of this RNA is unknown.
Model organism databases (MODs) are biological databases, or knowledgebases, dedicated to the provision of in-depth biological data for intensively studied model organisms. MODs allow researchers to easily find background information on large sets of genes, plan experiments efficiently, combine their data with existing knowledge, and construct novel hypotheses. They allow users to analyse results and interpret datasets, and the data they generate are increasingly used to describe less well studied species. Where possible, MODs share common approaches to collect and represent biological information. For example, all MODs use the Gene Ontology (GO) to describe functions, processes and cellular locations of specific gene products. Projects also exist to enable software sharing for curation, visualization and querying between different MODs. Organismal diversity and varying user requirements however mean that MODs are often required to customize capture, display, and provision of data.














