Digallate may refer to:
- a salt of digallic acid
- a molecule containing two gallic acid moieties, like Theaflavin digallate
Digallate may refer to:
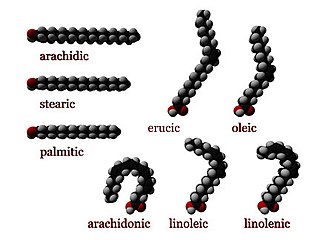
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually not found in organisms in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and they are important structural components for cells.

In nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such compounds; most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.

In biology and biochemistry, a lipid is a macrobiomolecule that is soluble in nonpolar solvents. Non-polar solvents are typically hydrocarbons used to dissolve other naturally occurring hydrocarbon lipid molecules that do not dissolve in water, including fatty acids, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, and phospholipids.
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:

Monosodium glutamate (MSG), also known as sodium glutamate, is the sodium salt of glutamic acid. MSG is found naturally in some foods including tomatoes and cheese. MSG is used in cooking as a flavor enhancer with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty, savory flavor of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in foods such as stews and meat soups.
Synthesis or synthesize may also refer to:
Coumaric acid is a phenolic derivative of cinnamic acid having a hydroxy group as substituent at one of the aromatic positions:
Linolenic acid is a type of fatty acid. It can refer to either of two octadecatrienoic acids, or a mixture of the two. Linolenate is often found in vegetable oils; traditionally, such fatty acylates are reported as the fatty acids:
Monohydroxybenzoic acid may refer to any of three isomeric phenolic acids:
Gaa may refer to:

Theaflavin (TF) and its derivatives, known collectively as theaflavins, are antioxidant polyphenols that are formed from the condensation of flavan-3-ols in tea leaves during the enzymatic oxidation of black tea. Theaflavin-3-gallate, theaflavin-3'-gallate, and theaflavin-3-3'-digallate are the main theaflavins. Theaflavins are types of thearubigins, and are therefore reddish in color. Those molecules contain a tropolone moiety.

Theaflavin digallate (TFDG) is an antioxidant natural phenol found in black tea, and a theaflavin derivative.
In enzymology, a tannase (EC 3.1.1.20) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Dihydroxybenzoic acids (DHBA) are a type of phenolic acids.
Aminosalicylic acid can refer to any amino derivative of salicylic acid, such as:
TF3 may refer to:
Trihydroxybenzoic acid may refer to the following phenolic acids :
Dihydroxycinnamic acid may refer to several molecules with the molecular formula C9H8O4 including:
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid.
The hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor (abbreviated HCA receptor and HCAR) family includes the following human proteins: