In music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps, depending on their position in the scale. This pattern ensures that, in a diatonic scale spanning more than one octave, all the half steps are maximally separated from each other.
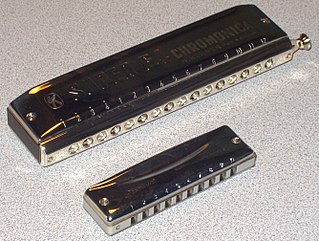
The harmonica, also known as a French harp or mouth organ, is a free reed wind instrument used worldwide in many musical genres, notably in blues, American folk music, classical music, jazz, country, and rock. The many types of harmonica include diatonic, chromatic, tremolo, octave, orchestral, and bass versions. A harmonica is played by using the mouth to direct air into or out of one holes along a mouthpiece. Behind each hole is a chamber containing at least one reed. The most common is the diatonic Richter-tuned with ten air passages and twenty reeds, often called the blues harp. A harmonica reed is a flat, elongated spring typically made of brass, stainless steel, or bronze, which is secured at one end over a slot that serves as an airway. When the free end is made to vibrate by the player's air, it alternately blocks and unblocks the airway to produce sound.
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord.
In music theory, the tritone is defined as a musical interval composed of three adjacent whole tones. For instance, the interval from F up to the B above it is a tritone as it can be decomposed into the three adjacent whole tones F–G, G–A, and A–B. According to this definition, within a diatonic scale there is only one tritone for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned interval F–B is the only tritone formed from the notes of the C major scale. A tritone is also commonly defined as an interval spanning six semitones. According to this definition, a diatonic scale contains two tritones for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned C major scale contains the tritones F–B and B–F. In twelve-equal temperament, the tritone divides the octave exactly in half as 6 of 12 semitones or 600 of 1,200 cents.
A seventh chord is a chord consisting of a triad plus a note forming an interval of a seventh above the chord's root. When not otherwise specified, a "seventh chord" usually means a dominant seventh chord: a major triad together with a minor seventh. However, a variety of sevenths may be added to a variety of triads, resulting in many different types of seventh chords.

In music theory, the circle of fifths is a way of organizing the 12 chromatic pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths. If C is chosen as a starting point, the sequence is: C, G, D, A, E, B, F♯, C♯, A♭, E♭, B♭, F. Continuing the pattern from F returns the sequence to its starting point of C. This order places the most closely related key signatures adjacent to one another. It is usually illustrated in the form of a circle.

In music theory, a comma is a very small interval, the difference resulting from tuning one note two different ways. Strictly speaking, there are only two kinds of comma, the syntonic comma, "the difference between a just major 3rd and four just perfect 5ths less two octaves", and the Pythagorean comma, "the difference between twelve 5ths and seven octaves". The word comma used without qualification refers to the syntonic comma, which can be defined, for instance, as the difference between an F♯ tuned using the D-based Pythagorean tuning system, and another F♯ tuned using the D-based quarter-comma meantone tuning system. Intervals separated by the ratio 81:80 are considered the same note because the 12-note Western chromatic scale does not distinguish Pythagorean intervals from 5-limit intervals in its notation. Other intervals are considered commas because of the enharmonic equivalences of a tuning system. For example, in 53TET, B♭ and A♯ are both approximated by the same interval although they are a septimal kleisma apart.

In music, a guitar chord is a set of notes played on a guitar. A chord's notes are often played simultaneously, but they can be played sequentially in an arpeggio. The implementation of guitar chords depends on the guitar tuning. Most guitars used in popular music have six strings with the "standard" tuning of the Spanish classical guitar, namely E–A–D–G–B–E' ; in standard tuning, the intervals present among adjacent strings are perfect fourths except for the major third (G,B). Standard tuning requires four chord-shapes for the major triads.

The Richter-tuned harmonica, or 10-hole harmonica or blues harp, is the most widely known type of harmonica. It is a variety of diatonic harmonica, with ten holes which offer the player 19 notes in a three-octave range.
There are numerous techniques available for playing the harmonica, including bending, overbending, and tongue blocking.

In music theory, the harmonic major scale is a musical scale found in some music from the common practice era and now used occasionally, most often in jazz. In George Russell's Lydian Chromatic Concept it is the fifth mode (V) of the Lydian Diminished scale. It corresponds to the Raga Sarasangi in Indian Carnatic music.

In classical music from Western culture, a diminished seventh is an interval produced by narrowing a minor seventh by a chromatic semitone. For instance, the interval from A to G is a minor seventh, ten semitones wide, and both the intervals from A♯ to G, and from A to G♭ are diminished sevenths, spanning nine semitones. Being diminished, it is considered a dissonant interval.
The chromatic harmonica is a type of harmonica that uses a button-activated sliding bar to redirect air from the hole in the mouthpiece to the selected reed-plate desired. When the button is not pressed, an altered diatonic major scale of the key of the harmonica is available, while depressing the button accesses the same scale a semitone higher in each hole. Thus, the instrument is capable of playing the 12 notes of the Western chromatic scale. The chromatic harmonica can thus be contrasted with a standard harmonica, which can play only the notes in a given musical key.
Quarter-comma meantone, or 1⁄4-comma meantone, was the most common meantone temperament in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, and was sometimes used later. In this system the perfect fifth is flattened by one quarter of a syntonic comma (81:80), with respect to its just intonation used in Pythagorean tuning ; the result is 3/2 × 1⁄4 = 4√5 ≈ 1.49535, or a fifth of 696.578 cents. This fifth is then iterated to generate the diatonic scale and other notes of the temperament. The purpose is to obtain justly intoned major thirds. It was described by Pietro Aron in his Toscanello de la Musica of 1523, by saying the major thirds should be tuned to be "sonorous and just, as united as possible." Later theorists Gioseffo Zarlino and Francisco de Salinas described the tuning with mathematical exactitude.

Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the common practice music of the period 1600–1900.
Richter tuning is a system of choosing the reeds for a diatonic wind instrument. It is named after Joseph Richter, a Bohemian instrument maker who adopted the tuning for his harmonicas in the early 19th century and is credited with inventing the blow/draw mechanism that allows the harmonica to play different notes when the air is drawn instead of blown.
Solo tuning is a system of choosing the reeds for a diatonic wind instrument to fit a pattern where blow notes repeat a sequence of
An augmented tuning is a musical tuning system for musical instruments that is associated with augmented triads, that is a root note, a major third, and an augmented fifth. The augmented fifth is constructed by stacking the major third with another major third. Consequently, all of the intervals are major thirds.

Five-limit tuning, 5-limit tuning, or 5-prime-limit tuning (not to be confused with 5-odd-limit tuning), is any system for tuning a musical instrument that obtains the frequency of each note by multiplying the frequency of a given reference note (the base note) by products of integer powers of 2, 3, or 5 (prime numbers limited to 5 or lower), such as 2−3·31·51 = 15/8.








