
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulations to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry incorporated into computer programs to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. The importance of this subject stems from the fact that, with the exception of some relatively recent findings related to the hydrogen molecular ion, achieving an accurate quantum mechanical depiction of chemical systems analytically, or in a closed form, is not feasible. The complexity inherent in the many-body problem exacerbates the challenge of providing detailed descriptions of quantum mechanical systems. While computational results normally complement information obtained by chemical experiments, it can occasionally predict unobserved chemical phenomena.
Quantum chemistry, also called molecular quantum mechanics, is a branch of physical chemistry focused on the application of quantum mechanics to chemical systems, particularly towards the quantum-mechanical calculation of electronic contributions to physical and chemical properties of molecules, materials, and solutions at the atomic level. These calculations include systematically applied approximations intended to make calculations computationally feasible while still capturing as much information about important contributions to the computed wave functions as well as to observable properties such as structures, spectra, and thermodynamic properties. Quantum chemistry is also concerned with the computation of quantum effects on molecular dynamics and chemical kinetics.

Theoretical chemistry is the branch of chemistry which develops theoretical generalizations that are part of the theoretical arsenal of modern chemistry: for example, the concepts of chemical bonding, chemical reaction, valence, the surface of potential energy, molecular orbitals, orbital interactions, and molecule activation.
In quantum chemistry and molecular physics, the Born–Oppenheimer (BO) approximation is the best-known mathematical approximation in molecular dynamics. Specifically, it is the assumption that the wave functions of atomic nuclei and electrons in a molecule can be treated separately, based on the fact that the nuclei are much heavier than the electrons. Due to the larger relative mass of a nucleus compared to an electron, the coordinates of the nuclei in a system are approximated as fixed, while the coordinates of the electrons are dynamic. The approach is named after Max Born and his 23-year-old graduate student J. Robert Oppenheimer, the latter of whom proposed it in 1927 during a period of intense ferment in the development of quantum mechanics.
In classical and quantum mechanics, geometric phase is a phase difference acquired over the course of a cycle, when a system is subjected to cyclic adiabatic processes, which results from the geometrical properties of the parameter space of the Hamiltonian. The phenomenon was independently discovered by S. Pancharatnam (1956), in classical optics and by H. C. Longuet-Higgins (1958) in molecular physics; it was generalized by Michael Berry in (1984). It is also known as the Pancharatnam–Berry phase, Pancharatnam phase, or Berry phase. It can be seen in the conical intersection of potential energy surfaces and in the Aharonov–Bohm effect. Geometric phase around the conical intersection involving the ground electronic state of the C6H3F3+ molecular ion is discussed on pages 385–386 of the textbook by Bunker and Jensen. In the case of the Aharonov–Bohm effect, the adiabatic parameter is the magnetic field enclosed by two interference paths, and it is cyclic in the sense that these two paths form a loop. In the case of the conical intersection, the adiabatic parameters are the molecular coordinates. Apart from quantum mechanics, it arises in a variety of other wave systems, such as classical optics. As a rule of thumb, it can occur whenever there are at least two parameters characterizing a wave in the vicinity of some sort of singularity or hole in the topology; two parameters are required because either the set of nonsingular states will not be simply connected, or there will be nonzero holonomy.

In quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers are quantities that characterize the possible states of the system. To fully specify the state of the electron in a hydrogen atom, four quantum numbers are needed. The traditional set of quantum numbers includes the principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum numbers. To describe other systems, different quantum numbers are required. For subatomic particles, one needs to introduce new quantum numbers, such as the flavour of quarks, which have no classical correspondence.
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory (MO theory or MOT) is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. It was proposed early in the 20th century. The MOT explains the paramagnetic nature of O2, which valence bond theory cannot explain.
Vibronic coupling in a molecule involves the interaction between electronic and nuclear vibrational motion. The term "vibronic" originates from the combination of the terms "vibrational" and "electronic", denoting the idea that in a molecule, vibrational and electronic interactions are interrelated and influence each other. The magnitude of vibronic coupling reflects the degree of such interrelation.
Per-Olov Löwdin was a Swedish physicist, professor at the University of Uppsala from 1960 to 1983, and in parallel at the University of Florida until 1993.
The diabatic representation as a mathematical tool for theoretical calculations of atomic collisions and of molecular interactions.
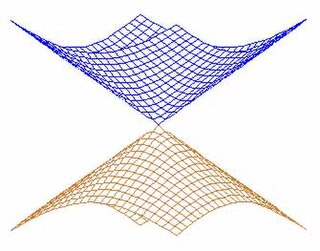
In quantum chemistry, a conical intersection of two or more potential energy surfaces is the set of molecular geometry points where the potential energy surfaces are degenerate (intersect) and the non-adiabatic couplings between these states are non-vanishing. In the vicinity of conical intersections, the Born–Oppenheimer approximation breaks down and the coupling between electronic and nuclear motion becomes important, allowing non-adiabatic processes to take place. The location and characterization of conical intersections are therefore essential to the understanding of a wide range of important phenomena governed by non-adiabatic events, such as photoisomerization, photosynthesis, vision and the photostability of DNA.
Car–Parrinello molecular dynamics or CPMD refers to either a method used in molecular dynamics or the computational chemistry software package used to implement this method.
In atomic, molecular, and optical physics and quantum chemistry, the molecular Hamiltonian is the Hamiltonian operator representing the energy of the electrons and nuclei in a molecule. This operator and the associated Schrödinger equation play a central role in computational chemistry and physics for computing properties of molecules and aggregates of molecules, such as thermal conductivity, specific heat, electrical conductivity, optical, and magnetic properties, and reactivity.

Debashis Mukherjee is a theoretical chemist, well known for his research in the fields of molecular many body theory, theoretical spectroscopy, finite temperature non-perturbative many body theories. Mukherjee has been the first to develop and implement a class of many-body methods for electronic structure which are now standard works in the field. These methods, collectively called multireference coupled cluster formalisms, are versatile and powerful methods for predicting with quantitative accuracy the energetics and cross-sections of a vast range of molecular excitations and ionization. A long-standing problem of guaranteeing proper scaling of energy for many electron wave-functions of arbitrary complexity has also been first resolved by him. He has also been the first to develop a rigorously size-extensive state-specific multi-reference coupled cluster formalism, and its perturbative counterpart which is getting increasingly recognized as a very promising methodological advance.

William Hughes Miller is an American professor at the University of California, Berkeley and a leading researcher in the field of theoretical chemistry.

CP2K is a freely available (GPL) quantum chemistry and solid state physics program package, written in Fortran 2008, to perform atomistic simulations of solid state, liquid, molecular, periodic, material, crystal, and biological systems. It provides a general framework for different methods: density functional theory (DFT) using a mixed Gaussian and plane waves approach (GPW) via LDA, GGA, MP2, or RPA levels of theory, classical pair and many-body potentials, semi-empirical and tight-binding Hamiltonians, as well as Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) hybrid schemes relying on the Gaussian Expansion of the Electrostatic Potential (GEEP). The Gaussian and Augmented Plane Waves method (GAPW) as an extension of the GPW method allows for all-electron calculations. CP2K can do simulations of molecular dynamics, metadynamics, Monte Carlo, Ehrenfest dynamics, vibrational analysis, core level spectroscopy, energy minimization, and transition state optimization using NEB or dimer method.
Path integral molecular dynamics (PIMD) is a method of incorporating quantum mechanics into molecular dynamics simulations using Feynman path integrals. In PIMD, one uses the Born–Oppenheimer approximation to separate the wavefunction into a nuclear part and an electronic part. The nuclei are treated quantum mechanically by mapping each quantum nucleus onto a classical system of several fictitious particles connected by springs governed by an effective Hamiltonian, which is derived from Feynman's path integral. The resulting classical system, although complex, can be solved relatively quickly. There are now a number of commonly used condensed matter computer simulation techniques that make use of the path integral formulation including Centroid Molecular Dynamics (CMD), Ring Polymer Molecular Dynamics (RPMD), and the Feynman-Kleinert Quasi-Classical Wigner (FK-QCW) method. The same techniques are also used in path integral Monte Carlo (PIMC).
Sharon Hammes-Schiffer is a physical chemist who has contributed to theoretical and computational chemistry. She is currently a Sterling Professor of Chemistry at Yale University. She has served as senior editor and deputy editor of the Journal of Physical Chemistry and advisory editor for Theoretical Chemistry Accounts. As of 1 January 2015 she is editor-in-chief of Chemical Reviews.
Surface hopping is a mixed quantum-classical technique that incorporates quantum mechanical effects into molecular dynamics simulations. Traditional molecular dynamics assume the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, where the lighter electrons adjust instantaneously to the motion of the nuclei. Though the Born-Oppenheimer approximation is applicable to a wide range of problems, there are several applications, such as photoexcited dynamics, electron transfer, and surface chemistry where this approximation falls apart. Surface hopping partially incorporates the non-adiabatic effects by including excited adiabatic surfaces in the calculations, and allowing for 'hops' between these surfaces, subject to certain criteria.
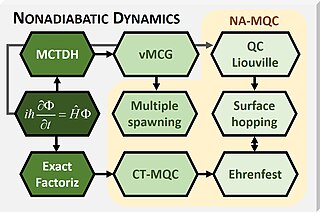
Mixed quantum-classical (MQC) dynamics is a class of computational theoretical chemistry methods tailored to simulate non-adiabatic (NA) processes in molecular and supramolecular chemistry. Such methods are characterized by:
- Propagation of nuclear dynamics through classical trajectories;
- Propagation of the electrons through quantum methods;
- A feedback algorithm between the electronic and nuclear subsystems to recover nonadiabatic information.







