A disk image, in computing, is a computer file containing the contents and structure of a disk volume or of an entire data storage device, such as a hard disk drive, tape drive, floppy disk, optical disc, or USB flash drive. A disk image is usually made by creating a sector-by-sector copy of the source medium, thereby perfectly replicating the structure and contents of a storage device independent of the file system. Depending on the disk image format, a disk image may span one or more computer files.
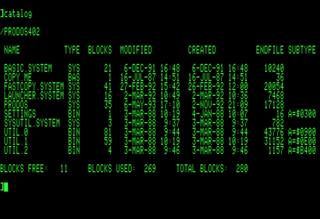
ProDOS is the name of two similar operating systems for the Apple II series of personal computers. The original ProDOS, renamed ProDOS 8 in version 1.2, is the last official operating system usable by all 8-bit Apple II series computers, and was distributed from 1983 to 1993. The other, ProDOS 16, was a stop-gap solution for the 16-bit Apple IIGS that was replaced by GS/OS within two years.

System 7, codenamed "Big Bang", and also known as Mac OS 7, is a graphical user interface-based operating system for Macintosh computers and is part of the classic Mac OS series of operating systems. It was introduced on May 13, 1991, by Apple Computer It succeeded System 6, and was the main Macintosh operating system until it was succeeded by Mac OS 8 in 1997. Current for more than six years, System 7 was the longest-lived major version series of the classic Macintosh operating system. Features added with the System 7 release included virtual memory, personal file sharing, QuickTime, QuickDraw 3D, and an improved user interface.
StuffIt is a discontinued family of computer software utilities for archiving and compressing files. Originally produced for the Macintosh, versions for Microsoft Windows, Linux (x86), and Sun Solaris were later created. The proprietary compression format used by the StuffIt utilities is also termed StuffIt.

Mac OS 8 is an operating system that was released by Apple Computer on July 26, 1997. It includes the largest overhaul of the classic Mac OS experience since the release of System 7, approximately six years before. It places a greater emphasis on color than prior versions. Released over a series of updates, Mac OS 8 represents an incremental integration of many of the technologies which had been developed from 1988 to 1996 for Apple's overly ambitious OS named Copland. Mac OS 8 helped modernize the Mac OS while Apple developed its next-generation operating system, Mac OS X.
HFS Plus or HFS+ is a journaling file system developed by Apple Inc. It replaced the Hierarchical File System (HFS) as the primary file system of Apple computers with the 1998 release of Mac OS 8.1. HFS+ continued as the primary Mac OS X file system until it was itself replaced with the Apple File System (APFS), released with macOS High Sierra in 2017. HFS+ is also one of the formats supported by the iPod digital music player.

Norton Utilities was a utility software suite designed to help analyze, configure, optimize and maintain a computer. The latest version of Norton Utilities is Norton Utilities 16 for Windows XP/Vista/7/8 was released 26 October 2012.

Disk Utility is a system utility for performing disk and disk volume-related tasks on the macOS operating system by Apple Inc.
Distribution Media Format (DMF) is a format for floppy disks that Microsoft used to distribute software. It allowed the disk to contain 1680 KB of data on a 31⁄2-inch disk, instead of the standard 1440 KB. As a side effect, utilities had to specially support the format in order to read and write the disks, which made copying of products distributed on this medium more difficult. An Apple Macintosh computer running Disk Copy 6.3.3 on the Mac OS 7.6 or later operating system can copy and make DMF disks. The first Microsoft software product that uses DMF for distribution were the "c" revisions of Office 4.x. It also was the first software product to use CAB files, then called "Diamond".
Amiga software is computer software engineered to run on the Amiga personal computer. Amiga software covers many applications, including productivity, digital art, games, commercial, freeware and hobbyist products. The market was active in the late 1980s and early 1990s but then dwindled. Most Amiga products were originally created directly for the Amiga computer, and were not ported from other platforms.

Time Machine is the backup mechanism of macOS, the desktop operating system developed by Apple. The software is designed to work with both local storage devices and network-attached disks, and is most commonly used with external disk drives connected using either USB or Thunderbolt. It was first introduced in Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard, which appeared in October 2007 and incrementally refined in subsequent releases of macOS. Time Machine was revamped in macOS 11 Big Sur to support APFS, thereby enabling "faster, more compact, and more reliable backups" than were possible previously.
A sparse image is a type of disk image file used on macOS that grows in size as the user adds data to the image, taking up only as much disk space as stored in it. Encrypted sparse image files are used to secure a user's home directory by the FileVault feature in Mac OS X Snow Leopard and earlier. Sparse images can be created using Disk Utility.
Apple Software Restore or asr is a command line utility in Mac OS X used to apply a DMG disk image to a selected partition or mount point on a file system. It is often used for cloning large numbers of Macintosh computers. Apple Software Restore can read an image locally or from a server via HTTP or its own multicast asr:// URI.
Amiga support and maintenance software performs service functions such as formatting media for a specific filesystem, diagnosing failures that occur on formatted media, data recovery after media failure, and installation of new software for the Amiga family of personal computers—as opposed to application software, which performs business, education, and recreation functions.
VHD and its successor VHDX are file formats representing a virtual hard disk drive (HDD). They may contain what is found on a physical HDD, such as disk partitions and a file system, which in turn can contain files and folders. They are typically used as the hard disk of a virtual machine, are built into modern versions of Windows, and are the native file format for Microsoft's hypervisor, Hyper-V.
This article is a comparison of notable software applications that can access or manipulate disk image files. It compares their disk image handling features.

AppleDisk Image is a disk image format commonly used by the macOS operating system. When opened, an Apple Disk Image is mounted as a volume within the Finder.

Mac OS is the series of operating systems developed for the Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Computer from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The Macintosh operating system is credited with having popularized the graphical user interface concept. It was included with every Macintosh that was sold during the era in which it was developed, and many updates to the system software were done in conjunction with the introduction of new Macintosh systems.
Apple File System (APFS) is a proprietary file system developed and deployed by Apple Inc. for macOS Sierra (10.12.4) and later, iOS 10.3 and later, tvOS 10.2 and later, watchOS 3.2 and later, and all versions of iPadOS. It aims to fix core problems of HFS+, APFS's predecessor on these operating systems. APFS is optimized for solid-state drive storage and supports encryption, snapshots, and increased data integrity, among other capabilities.







