
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.

A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term workstation has been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP, NeXT, and IBM which powered the 3D computer graphics revolution of the late 1990s.

A framebuffer is a portion of random-access memory (RAM) containing a bitmap that drives a video display. It is a memory buffer containing data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame. Modern video cards contain framebuffer circuitry in their cores. This circuitry converts an in-memory bitmap into a video signal that can be displayed on a computer monitor.

Low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS), also known as TIA/EIA-644, is a technical standard that specifies electrical characteristics of a differential, serial signaling standard. LVDS operates at low power and can run at very high speeds using inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables. LVDS is a physical layer specification only; many data communication standards and applications use it and add a data link layer as defined in the OSI model on top of it.
A music workstation is an electronic musical instrument providing the facilities of:
Display Data Channel (DDC) is a collection of protocols for digital communication between a computer display and a graphics adapter that enable the display to communicate its supported display modes to the adapter and that enable the computer host to adjust monitor parameters, such as brightness and contrast.
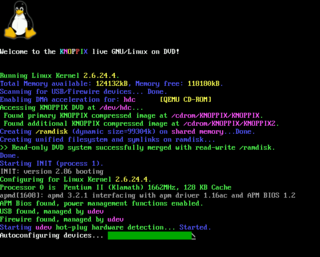
One meaning of system console, computer console, root console, operator's console, or simply console is the text entry and display device for system administration messages, particularly those from the BIOS or boot loader, the kernel, from the init system and from the system logger. It is a physical device consisting of a keyboard and a printer or screen, and traditionally is a text terminal, but may also be a graphical terminal. System consoles are generalized to computer terminals, which are abstracted respectively by virtual consoles and terminal emulators. Today communication with system consoles is generally done abstractly, via the standard streams, but there may be system-specific interfaces, for example those used by the system kernel.
Apple Inc. has sold a variety of LCD and CRT computer displays since introducing their first display in 1980. Apple paused production of their own standalone displays in 2016 and partnered with LG to design displays for Macs. In June 2019, the Pro Display XDR was introduced, however it was expensive and targeted for professionals. In March 2022, the Studio Display was launched as a consumer-targeted counterpart. These are currently the only Apple-branded displays available.

A digital audio workstation is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integrated stand-alone unit, all the way to a highly complex configuration of numerous components controlled by a central computer. Regardless of configuration, modern DAWs have a central interface that allows the user to alter and mix multiple recordings and tracks into a final produced piece.
An output device is any piece of computer hardware that converts information or data into a human-perceptible form or, historically, into a physical machine-readable form for use with other non-computerized equipment. It can be text, graphics, tactile, audio, or video. Examples include monitors, printers, speakers, headphones, projectors, GPS devices, optical mark readers, and braille readers.

A KVM switch is a hardware device that allows a user to control multiple computers from one or more sets of keyboards, video monitors, and mouse.

DB13W3 (13W3) is a style of D-subminiature connector used for analog video interfaces. The 13 refers to the total number of pins, the W refers to workstation and the 3 refers to the number of high-frequency pins. The connector was something of a pseudo-standard for high-end graphical workstations from the early 1990s to the early 2000s.

An audio/video receiver (AVR) is a consumer electronics component used in a home theater. Its purpose is to receive audio and video signals from a number of sources, and to process them and provide power amplifiers to drive loudspeakers and route the video to displays such as a television, monitor or video projector. Inputs may come from a satellite receiver, radio, DVD players, Blu-ray Disc players, VCRs or video game consoles, among others. The AVR source selection and settings such as volume, are typically set by a remote controller.
In computing, the term remote desktop refers to a software- or operating system feature that allows a personal computer's desktop environment to be run remotely from one system, while being displayed on a separate client device. Remote desktop applications have varying features. Some allow attaching to an existing user's session and "remote controlling", either displaying the remote control session or blanking the screen. Taking over a desktop remotely is a form of remote administration.
Torch Computers Ltd was a computer hardware company with origins in a 1982 joint venture between Acorn Computers and Climar Group that led to the development of the Communicator or C-series computer, a system based on the BBC Micro with a Z80 second processor and integral modem, intended as a viewdata terminal.

Dynamic device mapping is a technology for USB KVM switches which is sometimes implemented as an alternative to standard USB keyboard and mouse emulation.
Digital model railway control systems are an alternative to control a layout and simplify the wiring and add more flexibility in operations. A number of control systems are available to operate locomotives on model railways. Analog systems where the speed and the direction of a train is controlled by adjusting the voltage on the track are still popular while they have recently given way to control systems based on computer technology.

HDBaseT is a consumer electronic (CE) and commercial connectivity standard for transmission of uncompressed ultra-high-definition video, digital audio, DC power, Ethernet, USB 2.0, and other control communication over a single category cable up to 100 m (328 ft) in length, terminated using 8P8C modular connectors. The conductors, cable, and connectors are as used in Ethernet networks, but are not otherwise exchangeable. HDBaseT technology is promoted and advanced by the HDBaseT Alliance.

A KVM is a computer input/output device offering the combination of a keyboard, video monitor and mouse. They are typically constructed to fit into a 19-inch rack although there are manufacturers who offer a KVM that can be mounted to a flat surface such as a control console.

A KVMSplitter, also known as a Reverse KVM switch, is a hardware device that allows users to control a single computer from one or more sets of keyboards, video monitors, and mice. With a KVM splitter, users access the connected computer consecutively rather than simultaneously. It differs from a KVM Switch which allows multiple computers to be controlled, usually, by a single keyboard, monitor and mouse.












