Distinguished Public Service Medal may be one of the following decorations of the United States:

The Defense Superior Service Medal (DSSM) is a military decoration of the United States Department of Defense, which is presented to United States Armed Forces servicemembers who perform superior meritorious service in a position of significant responsibility.
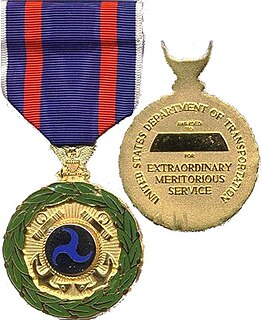
The Transportation Distinguished Service Medal was the highest decoration which could be bestowed by the Secretary of Transportation for exceptional service to the United States government in a position of great responsibility to a member of the United States Coast Guard. In 2003 it was replaced by the Homeland Security Distinguished Service Medal.

Norman (Norm) Ralph Augustine is a U.S. aerospace businessman who served as United States Under Secretary of the Army from 1975 to 1977. Augustine served as chairman and CEO of the Lockheed Martin Corporation. He was chairman of the Review of United States Human Space Flight Plans Committee.

The Coast Guard Distinguished Service Medal (CGDSM) is a military decoration of the United States Coast Guard that was established 4 August 1949 and is presented to coast guardsmen for "Exceptionally meritorious service to the government in a duty of great responsibility." Prior to this date, members of the Coast Guard were eligible to receive the Navy Distinguished Service Medal. The Homeland Security Distinguished Service Medal, which replaced the Transportation Distinguished Service Medal in 2002, is another higher precedence Distinguished Service Medal that may be awarded to Coast Guardsmen. The Coast Guard Distinguished Service Medal is equivalent to the Army's Army Distinguished Service Medal, Navy and Marine Corps' Navy Distinguished Service Medal, and the Air Force and Space Force's Air Force Distinguished Service Medal.

The Certificate of Merit Medal was a military decoration of the United States Army that was issued between the years of 1905 and 1918. The Certificate of Merit Medal replaced the much older Certificate of Merit which was authorized by the United States Congress on March 3, 1847.

The Congressional Gold Medal is an award bestowed by the United States Congress. It is Congress's highest expression of national appreciation for distinguished achievements and contributions by individuals or institutions. The congressional practice of issuing gold medals to occasionally honor recipients from the military began during the American Revolution. Later the practice extended to individuals in all walks of life and in the late 20th century also to groups. The Congressional Gold Medal and the Presidential Medal of Freedom are the highest civilian awards in the United States. The congressional medal seeks to honor those, individually or as a group, "who have performed an achievement that has an impact on American history and culture that is likely to be recognized as a major achievement in the recipient's field long after the achievement." However, "There are no permanent statutory provisions specifically relating to the creation of Congressional Gold Medals. When a Congressional Gold Medal has been deemed appropriate, Congress has, by legislative action, provided for the creation of a medal on an ad hoc basis." Thus, there are generally fewer gold medals than presidential medals. U.S. citizenship is not a requirement.

The Public Safety Officer Medal of Valor is the highest decoration for bravery exhibited by public safety officers in the United States, comparable to the military's Medal of Honor.
The United States military inter-service awards and decorations are those medals and ribbons which may be awarded to all members of the six military branches of the U.S. Armed Forces. Each military department awards inter-service awards under the same criteria.
Awards and decorations of the United States Army are those military awards including decorations which are issued to members of the United States Army under the authority of the Secretary of the Army. Together with military badges such awards provide an outward display of a service member's accomplishments.
Awards and decorations of the United States Department of the Air Force are military decorations which are issued by the Department of the Air Force to airmen of the United States Air Force and guardians of the United States Space Force and members of other military branches serving under Air Force and Space Force commands.
Awards and decorations of the United States government are civilian awards of the U.S. federal government which are typically issued for sustained meritorious service, in a civilian capacity, while serving in the U.S. federal government. Certain U.S. government awards may also be issued to military personnel of the United States Armed Forces and be worn in conjunction with awards and decorations of the United States military. In order of precedence, those U.S. non-military awards and decorations authorized for wear are worn after U.S. military personal decorations and unit awards and before U.S. military campaign and service awards.
The United States Department of the Army offers a variety of awards, decorations and incentive programs to honor and recognize the contribution and efforts of its civilian workforce. Department of the Army civilian awards are governed by Army Regulation 672–20 Decorations, Awards, and Honors Incentive Awards.
Distinguished Service Award is a term for an organization's award for services and contributions. It may refer to:
The United States Department of State, like other agencies of the U.S. federal government, gives civilian decorations for outstanding service, sacrifice, or heroism. The criteria for the awards are set down in 3 FAM 4820 - Foreign Affairs Manual, 3 FAM - Personnel, section 3 FAM 4800 Department Awards Program.

The Distinguished Honor Award is an award of the United States Department of State. Similar versions of the same award exist for the former U.S. Information Agency, Arms Control and Disarmament Agency, and USAID. It is presented to groups or individuals in recognition of exceptionally outstanding service or achievements of marked national or international significance.

The Superior Public Service Medal formerly the Secretary of the Army Public Service Award consists of a silver medal, lapel button, and citation certificate. The United States Secretary of the Army awards this decoration to those who provide exceptional service that makes a substantial contribution to the accomplishment of the Army's missions. These include any individual.

The Distinguished Public Service Medal, formerly the Department of the Army Decoration for Distinguished Civilian Service was established by directive of the Secretary of the Army in May 1956. This award consists of a gold medal, lapel button and certificate. This award recognizes distinguished service toward the accomplishment of the Army's mission.

The Secretary’s Distinguished Service Award is an award of the United States Department of State. It is presented at the discretion of the Secretary of State in recognition of exceptionally outstanding leadership, professional competence, and significant accomplishment over a sustained period of time in the field of foreign affairs. Such achievements must be of notable national or international significance and have made an important contribution to the advancement of U.S. national interests.

The Department of the Army Distinguished Civilian Service Award formerly the Department of the Army Decoration for Exceptional Civilian Service is the highest award that may be bestowed by or on behalf of the Secretary of the Army to Army civilian employees. The medal was approved by the War Department 29 December 1945. This award consists of a gold medal, lapel button and certificate. A ribbon bar and miniature medal is also available for private purchase.

The Department of Defense Medal for Distinguished Public Service is the highest award that is presented by the Secretary of Defense, to a private citizen, politician, non-career federal employee, or foreign national. It is presented for exceptionally distinguished service of significance to the Department of Defense as a whole, or a DoD Component or function, where recognition at the component level would not be sufficient for the service rendered.