Related Research Articles
Educational psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the scientific study of human learning. The study of learning processes, from both cognitive and behavioral perspectives, allows researchers to understand individual differences in intelligence, cognitive development, affect, motivation, self-regulation, and self-concept, as well as their role in learning. The field of educational psychology relies heavily on quantitative methods, including testing and measurement, to enhance educational activities related to instructional design, classroom management, and assessment, which serve to facilitate learning processes in various educational settings across the lifespan.

Lev Semyonovich Vygotsky was a Soviet psychologist, best known for his work on psychological development in children and creating the framework known as cultural-historical activity theory. After his early death, his books and research were banned in the Soviet Union until Joseph Stalin's death in 1953, with a first collection of major texts published in 1956.
Bloom's taxonomy is a framework for categorizing educational goals, developed by a committee of educators chaired by Benjamin Bloom in 1956. It was first introduced in the publication Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals. The taxonomy divides learning objectives into three broad domains: cognitive (knowledge-based), affective (emotion-based), and psychomotor (action-based), each with a hierarchy of skills and abilities. These domains are used by educators to structure curricula, assessments, and teaching methods to foster different types of learning.

Jerome Seymour Bruner was an American psychologist who made significant contributions to human cognitive psychology and cognitive learning theory in educational psychology. Bruner was a senior research fellow at the New York University School of Law. He received a BA in 1937 from Duke University and a PhD from Harvard University in 1941. He taught and did research at Harvard University, the University of Oxford, and New York University. A Review of General Psychology survey, published in 2002, ranked Bruner as the 28th most cited psychologist of the 20th century.
Instructional scaffolding is the support given to a student by an instructor throughout the learning process. This support is specifically tailored to each student; this instructional approach allows students to experience student-centered learning, which tends to facilitate more efficient learning than teacher-centered learning. This learning process promotes a deeper level of learning than many other common teaching strategies.
The psychology of learning refers to theories and research on how individuals learn. There are many theories of learning. Some take on a more behaviorist approach which focuses on inputs and reinforcements. Other approaches, such as neuroscience and social cognition, focus more on how the brain's organization and structure influence learning. Some psychological approaches, such as social constructivism, focus more on one's interaction with the environment and with others. Other theories, such as those related to motivation, like the growth mindset, focus more on individuals' perceptions of ability.

Constructivism in education is a theory that suggests that learners do not passively acquire knowledge through direct instruction. Instead, they construct their understanding through experiences and social interaction, integrating new information with their existing knowledge. This theory originates from Swiss developmental psychologist Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development.
A learning management system (LMS) or virtual learning environment (VLE) is a software application for the administration, documentation, tracking, reporting, automation, and delivery of educational courses, training programs, materials or learning and development programs. The learning management system concept emerged directly from e-Learning. Learning management systems make up the largest segment of the learning system market. The first introduction of the LMS was in the late 1990s. LMSs have been adopted by almost all higher education institutions in the English-speaking world. Learning management systems have faced a massive growth in usage due to the emphasis on remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.

The zone of proximal development (ZPD) is a concept in educational psychology that represents the space between what a learner is capable of doing unsupported and what the learner cannot do even with support. It is the range where the learner is able to perform, but only with support from a teacher or a peer with more knowledge or expertise. This person is known as the "more knowledgable other." The concept was introduced, but not fully developed, by psychologist Lev Vygotsky (1896–1934) during the last three years of his life. Vygotsky argued that a child gets involved in a dialogue with the "more knowledgeable other" and gradually, through social interaction and sense-making, develops the ability to solve problems independently and do certain tasks without help. Following Vygotsky, some educators believe that the role of education is to give children experiences that are within their zones of proximal development, thereby encouraging and advancing their individual learning skills and strategies.
Computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL) is a pedagogical approach wherein learning takes place via social interaction using a computer or through the Internet. This kind of learning is characterized by the sharing and construction of knowledge among participants using technology as their primary means of communication or as a common resource. CSCL can be implemented in online and classroom learning environments and can take place synchronously or asynchronously.

Discovery learning is a technique of inquiry-based learning and is considered a constructivist based approach to education. It is also referred to as problem-based learning, experiential learning and 21st century learning. It is supported by the work of learning theorists and psychologists Jean Piaget, Jerome Bruner, and Seymour Papert.
English-language learner is a term used in some English-speaking countries such as the United States and Canada to describe a person who is learning the English language and has a native language that is not English. Some educational advocates, especially in the United States, classify these students as non-native English speakers or emergent bilinguals. Various other terms are also used to refer to students who are not proficient in English, such as English as a second language (ESL), English as an additional language (EAL), limited English proficient (LEP), culturally and linguistically diverse (CLD), non-native English speaker, bilingual students, heritage language, emergent bilingual, and language-minority students. The legal term that is used in federal legislation is 'limited English proficient'.
An edublog is a blog created for educational purposes. Edublogs archive and support teacher learning by facilitating reflection, questioning by self and others, collaboration and by providing contexts for engaging in higher-order thinking. Edublogs proliferated when blogging architecture became more simplified and teachers perceived the instructional potential of blogs as an online resource. The use of blogs has become popular in education institutions including public schools and colleges. Blogs can be useful tools for sharing information and tips among co-workers, providing information for students, or keeping in contact with parents. Common examples include blogs written by or for teachers, blogs maintained for the purpose of classroom instruction, or blogs written about educational policy. Educators who blog are sometimes called edubloggers.
Inquiry-based learning is a form of active learning that starts by posing questions, problems or scenarios. It contrasts with traditional education, which generally relies on the teacher presenting facts and their knowledge about the subject. Inquiry-based learning is often assisted by a facilitator rather than a lecturer. Inquirers will identify and research issues and questions to develop knowledge or solutions. Inquiry-based learning includes problem-based learning, and is generally used in small-scale investigations and projects, as well as research. The inquiry-based instruction is principally very closely related to the development and practice of thinking and problem-solving skills.
Reciprocal teaching is a powerful instructional method designed to foster reading comprehension through collaborative dialogue between educators and students. Rooted in the work of Annemarie Palincsar, this approach aims to empower students with specific reading strategies, such as Questioning, Clarifying, Summarizing, and Predicting, to actively construct meaning from text.
Online tutoring is the process of tutoring in an online, virtual, or networked, environment, in which teachers and learners participate from separate physical locations. Aside from space, participants can also be separated by time.
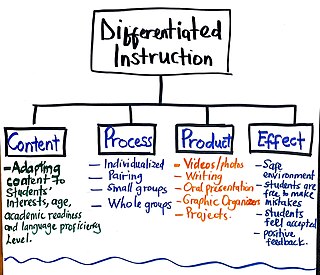
Differentiated instruction and assessment, also known as differentiated learning or, in education, simply, differentiation, is a framework or philosophy for effective teaching that involves providing all students within their diverse classroom community of learners a range of different avenues for understanding new information in terms of: acquiring content; processing, constructing, or making sense of ideas; and developing teaching materials and assessment measures so that all students within a classroom can learn effectively, regardless of differences in their ability. Differentiated instruction means using different tools, content, and due process in order to successfully reach all individuals. Differentiated instruction, according to Carol Ann Tomlinson, is the process of "ensuring that what a student learns, how he or she learns it, and how the student demonstrates what he or she has learned is a match for that student's readiness level, interests, and preferred mode of learning." According to Boelens et al. (2018), differentiation can be on two different levels: the administration level and the classroom level. The administration level takes the socioeconomic status and gender of students into consideration. At the classroom level, differentiation revolves around content, processing, product, and effects. On the content level, teachers adapt what they are teaching to meet the needs of students. This can mean making content more challenging or simplified for students based on their levels. The process of learning can be differentiated as well. Teachers may choose to teach individually at a time, assign problems to small groups, partners or the whole group depending on the needs of the students. By differentiating product, teachers decide how students will present what they have learned. This may take the form of videos, graphic organizers, photo presentations, writing, and oral presentations. All these take place in a safe classroom environment where students feel respected and valued—effects.
The gradual release of responsibility (GRR) model is a structured method of pedagogy centred on devolving responsibility within the learning process from the teacher to the learner. This approach requires the teacher to initially take on all the responsibility for a task, transitioning in stages to the students assuming full independence in carrying it out. The goal is to cultivate confident learners and thinkers who are capable of handling tasks even in areas where they have not yet gained expertise.

Styles of children’s learning across various indigenous communities in the Americas have been practiced for centuries prior to European colonization and persist today. Despite extensive anthropological research, efforts made towards studying children’s learning and development in Indigenous communities of the Americas as its own discipline within Developmental Psychology, has remained rudimentary. However, studies that have been conducted reveal several larger thematic commonalities, which create a paradigm of children’s learning that is fundamentally consistent across differing cultural communities.
Annemarie Sullivan Palincsar is a scholar of education known for her research on literacy instruction, reciprocal teaching, and cognitive apprenticeships. Her involvement in the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Research Council on the Prevention of Reading Difficulty in Young Children, the National Research Council's Panel on Teacher Preparation, and the International Literacy Association's Literacy Research Panel, attests to her dedication to advancing educational research and improving teacher training. Palincsar is the Ann L. Brown Distinguished University Professor Emerita at the Marsal Family School of Education at the University of Michigan.
References
- ↑ Puntambekar, S., & Kolodner, J.L. (1998). Distributed scaffolding: Helping students learning by design. In A. S. Bruckman, M. Guzdial, J. L. Kolodner, & A. Ram (Eds.), Proceedings of the Third International Conference of the Learning Sciences (ICLS’98)(pp. 35–41). Atlanta, GA: Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education.
- 1 2 Wood, Bruner & Ross 1976.
- 1 2 3 Puntambekar & Hubscher 2005.
- 1 2 3 4 Tabak 2004.
- ↑ Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. (M. Cole, V. John-Steiner, S. Scribner, & E. Souberman, Eds.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 86.
- ↑ Palincsar, Annemarie Sullivan (1998). "Keeping the Metaphor of Scaffolding Fresh—A Response to C. Addison Stone's 'The Metaphor of Scaffolding: Its Utility for the Field of Learning Disabilities'". Journal of Learning Disabilities. 31 (4). SAGE Publications: 370–373. doi:10.1177/002221949803100406. hdl: 2027.42/68637 . ISSN 0022-2194. PMID 9666613. S2CID 26881323.
- 1 2 3 Stone 1998.
- 1 2 Rogoff 1990.
- 1 2 3 Puntambekar & Kolodner 2005.
- ↑ Palinscar, A.S., & Brown, A.L. (1984). Reciprocal teaching of comprehension-fostering and comprehension-monitoring activities. Cognition and Instruction, 1(2), 117–175.
- ↑ Stone 1998, p. 349.
- 1 2 Tabak & Kyza 2018, p. 193.
- 1 2 Tabak 2004, p. 307.
- ↑ Tabak 2004, p. 319.
Bibliography
- Puntambekar, Sadhana; Hubscher, Roland (2005). "Tools for Scaffolding Students in a Complex Learning Environment: What Have We Gained and What Have We Missed?". Educational Psychologist. 40 (1). Informa UK Limited: 1–12. doi:10.1207/s15326985ep4001_1. ISSN 0046-1520. S2CID 39373429.
- Puntambekar, Sadhana; Kolodner, Janet L. (2005). "Toward implementing distributed scaffolding: Helping students learn science from design". Journal of Research in Science Teaching. 42 (2). Wiley: 185–217. doi:10.1002/tea.20048. ISSN 0022-4308.
- Rogoff, B. (1990), Apprenticeship in thinking: Cognitive development in social context, Oxford: Oxford University Press
- Tabak, Iris (2004). "Synergy: A Complement to Emerging Patterns of Distributed Scaffolding". Journal of the Learning Sciences. 13 (3). Informa UK Limited: 305–335. doi:10.1207/s15327809jls1303_3. ISSN 1050-8406. S2CID 62714877.
- Tabak, I.; Kyza, E.A. (2018). "Research on scaffolding in the learning sciences: A methodological perspective". In F. Fischer; C.E. Hmelo-Silver; S.R. Goldman; P. Reimann (eds.). International Handbook of the Learning Sciences. New York: Routledge. pp. 191–200).
- Stone, C. Addison (1998). "The Metaphor of Scaffolding". Journal of Learning Disabilities. 31 (4). SAGE Publications: 344–364. doi:10.1177/002221949803100404. ISSN 0022-2194. PMID 9666611. S2CID 44706306.
- Wood, David; Bruner, Jerome S.; Ross, Gail (1976). "The role of tutoring in problem solving". Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 17 (2). Wiley: 89–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1976.tb00381.x . ISSN 0021-9630. PMID 932126. S2CID 27949621.