Related Research Articles

Kolmogorov–Smirnov test is a nonparametric test of the equality of continuous, one-dimensional probability distributions that can be used to test whether a sample came from a given reference probability distribution, or to test whether two samples came from the same distribution. Intuitively, the test provides a method to qualitatively answer the question "How likely is it that we would see a collection of samples like this if they were drawn from that probability distribution?" or, in the second case, "How likely is it that we would see two sets of samples like this if they were drawn from the same probability distribution?". It is named after Andrey Kolmogorov and Nikolai Smirnov.
Nonparametric statistics is a type of statistical analysis that makes minimal assumptions about the underlying distribution of the data being studied. Often these models are infinite-dimensional, rather than finite dimensional, as is parametric statistics. Nonparametric statistics can be used for descriptive statistics or statistical inference. Nonparametric tests are often used when the assumptions of parametric tests are evidently violated.
The Mann–Whitney test is a nonparametric statistical test of the null hypothesis that, for randomly selected values X and Y from two populations, the probability of X being greater than Y is equal to the probability of Y being greater than X.

Walter Andrew Shewhart was an American physicist, engineer and statistician. He is sometimes also known as the grandfather of statistical quality control and also related to the Shewhart cycle.

Control charts are graphical plots used in production control to determine whether quality and manufacturing processes are being controlled under stable conditions. The hourly status is arranged on the graph, and the occurrence of abnormalities is judged based on the presence of data that differs from the conventional trend or deviates from the control limit line. Control charts are classified into Shewhart individuals control chart and CUSUM(CUsUM)(or cumulative sum control chart)(ISO 7870-4).

Statistical process control (SPC) or statistical quality control (SQC) is the application of statistical methods to monitor and control the quality of a production process. This helps to ensure that the process operates efficiently, producing more specification-conforming products with less waste scrap. SPC can be applied to any process where the "conforming product" output can be measured. Key tools used in SPC include run charts, control charts, a focus on continuous improvement, and the design of experiments. An example of a process where SPC is applied is manufacturing lines.

Mathematical statistics is the application of probability theory and other mathematical concepts to statistics, as opposed to techniques for collecting statistical data. Specific mathematical techniques that are commonly used in statistics include mathematical analysis, linear algebra, stochastic analysis, differential equations, and measure theory.
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric rank test for statistical hypothesis testing used either to test the location of a population based on a sample of data, or to compare the locations of two populations using two matched samples. The one-sample version serves a purpose similar to that of the one-sample Student's t-test. For two matched samples, it is a paired difference test like the paired Student's t-test. The Wilcoxon test is a good alternative to the t-test when the normal distribution of the differences between paired individuals cannot be assumed. Instead, it assumes a weaker hypothesis that the distribution of this difference is symmetric around a central value and it aims to test whether this center value differs significantly from zero. The Wilcoxon test is a more powerful alternative to the sign test because it considers the magnitude of the differences, but it requires this moderately strong assumption of symmetry.

In statistical process control (SPC), the and R chart is a type of scheme, popularly known as control chart, used to monitor the mean and range of a normally distributed variables simultaneously, when samples are collected at regular intervals from a business or industrial process. It is often used to monitor the variables data but the performance of the and R chart may suffer when the normality assumption is not valid.

In statistics, a Q–Q plot (quantile–quantile plot) is a probability plot, a graphical method for comparing two probability distributions by plotting their quantiles against each other. A point (x, y) on the plot corresponds to one of the quantiles of the second distribution (y-coordinate) plotted against the same quantile of the first distribution (x-coordinate). This defines a parametric curve where the parameter is the index of the quantile interval.
Nonparametric regression is a category of regression analysis in which the predictor does not take a predetermined form but is constructed according to information derived from the data. That is, no parametric equation is assumed for the relationship between predictors and dependent variable. Nonparametric regression requires larger sample sizes than regression based on parametric models because the data must supply the model structure as well as the parameter estimates.
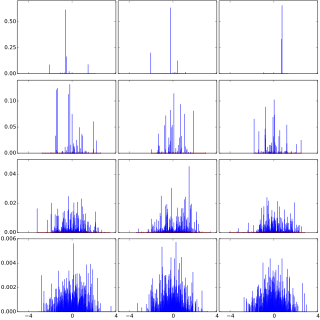
In probability theory, Dirichlet processes are a family of stochastic processes whose realizations are probability distributions. In other words, a Dirichlet process is a probability distribution whose range is itself a set of probability distributions. It is often used in Bayesian inference to describe the prior knowledge about the distribution of random variables—how likely it is that the random variables are distributed according to one or another particular distribution.
In statistics, the Hodges–Lehmann estimator is a robust and nonparametric estimator of a population's location parameter. For populations that are symmetric about one median, such as the Gaussian or normal distribution or the Student t-distribution, the Hodges–Lehmann estimator is a consistent and median-unbiased estimate of the population median. For non-symmetric populations, the Hodges–Lehmann estimator estimates the "pseudo–median", which is closely related to the population median.
In industrial statistics, the X-bar chart is a type of variable control chart that is used to monitor the arithmetic means of successive samples of constant size, n. This type of control chart is used for characteristics that can be measured on a continuous scale, such as weight, temperature, thickness etc. For example, one might take a sample of 5 shafts from production every hour, measure the diameter of each, and then plot, for each sample, the average of the five diameter values on the chart.
Siegel–Tukey test, named after Sidney Siegel and John Tukey, is a non-parametric test which may be applied to data measured at least on an ordinal scale. It tests for differences in scale between two groups.
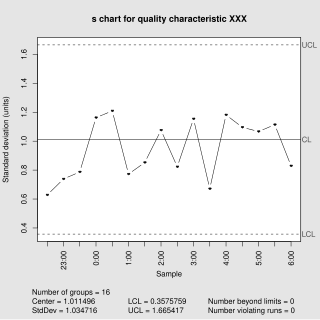
In statistical quality control, the and s chart is a type of control chart used to monitor variables data when samples are collected at regular intervals from a business or industrial process. This is connected to traditional statistical quality control (SQC) and statistical process control (SPC). However, Woodall noted that "I believe that the use of control charts and other monitoring methods should be referred to as “statistical process monitoring,” not “statistical process control (SPC).”"

In statistical quality control, an EWMA chart is a type of control chart used to monitor either variables or attributes-type data using the monitored business or industrial process's entire history of output. While other control charts treat rational subgroups of samples individually, the EWMA chart tracks the exponentially-weighted moving average of all prior sample means. EWMA weights samples in geometrically decreasing order so that the most recent samples are weighted most highly while the most distant samples contribute very little.
In statistics, the Cucconi test is a nonparametric test for jointly comparing central tendency and variability in two samples. Many rank tests have been proposed for the two-sample location-scale problem. Nearly all of them are Lepage-type tests, that is a combination of a location test and a scale test. The Cucconi test was first proposed by Odoardo Cucconi in 1968.
In statistics, the Lepage test is an exact distribution-free test for jointly monitoring the location and scale (variability) in two-sample treatment versus control comparisons. It is a rank test for the two-sample location-scale problem. The Lepage test statistic is the squared Euclidean distance of the standardized Wilcoxon rank-sum test for location and the standardized Ansari–Bradley test for scale. The Lepage test was first introduced by Yves Lepage in 1971 in a paper in Biometrika. A large number of Lepage-type tests exists in statistical literature for simultaneously testing location and scale shifts in case-control studies. The details may be found in the book: Nonparametric statistical tests: A computational approach. Wolfgang Kössler in 2006 also introduced various Lepage type tests using some alternative score functions optimal for various distributions. Amitava Mukherjee and Marco Marozzi introduced a class of percentile modified versions of the Lepage test. An alternative to the Lepage-type tests is known as the Cucconi test proposed by Odoardo Cucconi in 1968.
References
- ↑ Bhattacharya, P. K.; Frierson, Dargan (May 1981). "A Nonparametric Control Chart for Detecting Small Disorders". The Annals of Statistics. 9 (3): 544–554. doi: 10.1214/aos/1176345458 . ISSN 0090-5364.
- ↑ Amin, Raid W.; Reynolds, Marion R.; Saad, Bakir (January 1995). "Nonparametric quality control charts based on the sign statistic". Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods. 24 (6): 1597–1623. doi:10.1080/03610929508831574. ISSN 0361-0926.
- ↑ Balakrishnan, N.; Triantafyllou, I.S.; Koutras, M.V. (September 2009). "Nonparametric control charts based on runs and Wilcoxon-type rank-sum statistics". Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference. 139 (9): 3177–3192. doi:10.1016/j.jspi.2009.02.013. ISSN 0378-3758.
- ↑ Mukherjee, A.; Chakraborti, S. (2011-09-26). "A Distribution-free Control Chart for the Joint Monitoring of Location and Scale". Quality and Reliability Engineering International. 28 (3): 335–352. doi:10.1002/qre.1249. ISSN 0748-8017.
- ↑ Chowdhury, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chakraborti, S. (2013-02-19). "A New Distribution-free Control Chart for Joint Monitoring of Unknown Location and Scale Parameters of Continuous Distributions". Quality and Reliability Engineering International. 30 (2): 191–204. doi:10.1002/qre.1488. ISSN 0748-8017.