Related Research Articles
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
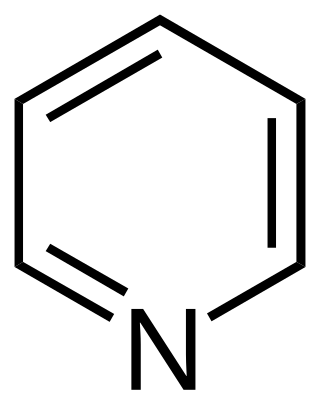
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles.

Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

Glutamic acid is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons.
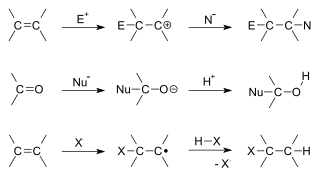
In organic chemistry, an addition reaction is an organic reaction in which two or more molecules combine to form a larger molecule called the adduct.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.
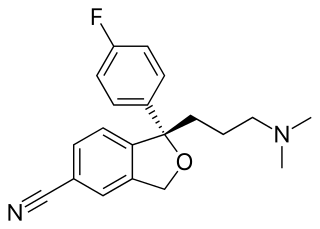
The skeletal formula, line-angle formula, bond-line formula or shorthand formula of an organic compound is a type of molecular structural formula that serves as a shorthand representation of a molecule's bonding and some details of its molecular geometry. A skeletal formula shows the skeletal structure or skeleton of a molecule, which is composed of the skeletal atoms that make up the molecule. It is represented in two dimensions, as on a piece of paper. It employs certain conventions to represent carbon and hydrogen atoms, which are the most common in organic chemistry.

In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula −CH2−HC=CH2. It consists of a methylene bridge attached to a vinyl group. The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, Allium sativum. In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "Schwefelallyl". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to H2C=CH−CH2, some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride.
Cyclopropene is an organic compound with the formula C3H4. It is the simplest cycloalkene. Because the ring is highly strained, cyclopropene is difficult to prepare and highly reactive. This colorless gas has been the subject for many fundamental studies of bonding and reactivity. It does not occur naturally, but derivatives are known in some fatty acids. Derivatives of cyclopropene are used commercially to control ripening of some fruit.
The International Chemical Identifier is a textual identifier for chemical substances, designed to provide a standard way to encode molecular information and to facilitate the search for such information in databases and on the web. Initially developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) from 2000 to 2005, the format and algorithms are non-proprietary. Since May 2009, it has been developed by the InChI Trust, a nonprofit charity from the United Kingdom which works to implement and promote the use of InChI.
Propanamide has the chemical formula CH3CH2C=O(NH2). It is the amide of propanoic acid.
In chemistry, the carbon–hydrogen bond is a chemical bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms that can be found in many organic compounds. This bond is a covalent, single bond, meaning that carbon shares its outer valence electrons with up to four hydrogens. This completes both of their outer shells, making them stable.

Non-stoichiometric compounds are chemical compounds, almost always solid inorganic compounds, having elemental composition whose proportions cannot be represented by a ratio of small natural numbers ; most often, in such materials, some small percentage of atoms are missing or too many atoms are packed into an otherwise perfect lattice work.
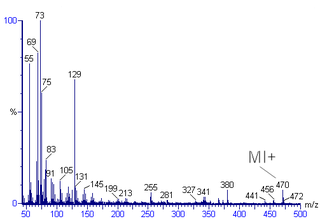
Mass spectral interpretation is the method employed to identify the chemical formula, characteristic fragment patterns and possible fragment ions from the mass spectra. Mass spectra is a plot of relative abundance against mass-to-charge ratio. It is commonly used for the identification of organic compounds from electron ionization mass spectrometry. Organic chemists obtain mass spectra of chemical compounds as part of structure elucidation and the analysis is part of many organic chemistry curricula.
Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005 is the 2005 version of Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. It is a collection of rules for naming inorganic compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).

1-Methylimidazole or N-methylimidazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula CH3C3H3N2. It is a colourless liquid that is used as a specialty solvent, a base, and as a precursor to some ionic liquids. It is a fundamental nitrogen heterocycle and as such mimics for various nucleoside bases as well as histidine and histamine.

Stannole is an organotin compound with the formula (CH)4SnH2. It is classified as a metallole, i.e. an unsaturated five-membered ring containing a heteroatom. It is a structural analog of cyclopentadiene, with tin replacing the saturated carbon atom. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, are also called stannoles.
Heteroatom-promoted lateral lithiation is the site-selective replacement of a benzylic hydrogen atom for lithium for the purpose of further functionalization. Heteroatom-containing substituents may direct metalation to the benzylic site closest to the heteroatom or increase the acidity of the ring carbons via an inductive effect.

Imidogen is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NH. Like other simple radicals, it is highly reactive and consequently short-lived except as a dilute gas. Its behavior depends on its spin multiplicity.

Trifluoroperacetic acid is an organofluorine compound, the peroxy acid analog of trifluoroacetic acid, with the condensed structural formula CF
3COOOH. It is a strong oxidizing agent for organic oxidation reactions, such as in Baeyer–Villiger oxidations of ketones. It is the most reactive of the organic peroxy acids, allowing it to successfully oxidise relatively unreactive alkenes to epoxides where other peroxy acids are ineffective. It can also oxidise the chalcogens in some functional groups, such as by transforming selenoethers to selones. It is a potentially explosive material and is not commercially available, but it can be quickly prepared as needed. Its use as a laboratory reagent was pioneered and developed by William D. Emmons.