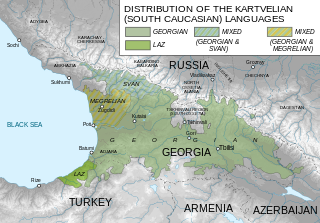
Georgian is the most widely spoken Kartvelian language; it serves as the literary language or lingua franca for speakers of related languages. It is the official language of Georgia and the native or primary language of 88% of its population. Its speakers today amount to approximately 3.8 million. Georgian is written with its own unique Georgian scripts, alphabetical systems of unclear origin.
The Albanian alphabet is a variant of the Latin alphabet used to write the Albanian language. It consists of 36 letters:
Vernacular is the ordinary, informal, spoken form of language, particularly when perceived as having lower social status or less prestige in contrast to standard language, which is more codified, institutionally promoted, literary, or formal. More narrowly, a particular language variety that does not hold a widespread high-status perception, and sometimes even carries social stigma, is also called a vernacular, vernacular dialect, nonstandard dialect, etc. and is typically its speakers' native variety. Regardless of any such stigma, modern linguistics regards all nonstandard dialects as full-fledged varieties of language with their own consistent grammatical structure, sound system, body of vocabulary, etc.

The Georgian scripts are the three writing systems used to write the Georgian language: Asomtavruli, Nuskhuri and Mkhedruli. Although the systems differ in appearance, their letters share the same names and alphabetical order and are written horizontally from left to right. Of the three scripts, Mkhedruli, once the civilian royal script of the Kingdom of Georgia and mostly used for the royal charters, is now the standard script for modern Georgian and its related Kartvelian languages, whereas Asomtavruli and Nuskhuri are used only by the Georgian Orthodox Church, in ceremonial religious texts and iconography.
Judeo-Italian is a groups of endangered and extinct Jewish dialects, with only about 200 speakers in Italy and 250 total speakers today. The dialects are one of the Italian languages and are a subgrouping of the Judeo-Romance Languages. Some words have Italian prefixes and suffixes added to Hebrew words as well as Aramaic roots. All of the dialects except Judeo-Roman are now extinct.
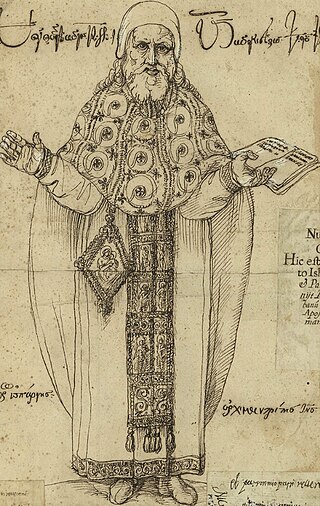
Nikoloz Cholokashvili, known in Europe as Niceforo Irbachi, (1585–1658), was a Georgian Orthodox priest, politician and diplomat.

(Italian: Pietro Bogdano; 1627 – 6 December 1689) was the most original writer of Old Albanian literature. He was author of the Cuneus Prophetarum, 1685, the first prose work of substance written originally in (Gheg) Albanian. He organized a resistance against the Ottomans and a pro-Austrian movement in Kosovo in 1689 that included Muslim and Christian Albanians.
Alphabetum grandonico-malabaricum sive samscrudonicum is a book on the grammar of the South Indian Malayalam language, published in 1772 at the printing press of the Congregatio de Propaganda Fide in Rome. It is believed to be the first book on Malayalam printed in Europe. The Alphabetum grandonico-malabaricum focuses on the pronunciation of the Malayalam alphabet, with many examples in Malayalam characters. It also made use of devanagari fonts. It also includes some remarks on the general characteristics of the grammar. At the end, there are also some short Malayalam sentences of a religious nature, such as the Ten Commandments.

The Segugio Italiano is either of two Italian breeds of dog of scent hound type, the wire-haired Segugio Italiano a Pelo Forte or the short-haired Segugio Italiano a Pelo Raso. Apart from the coat type, they are closely similar, and in some sources may be treated as a single breed; the Fédération Cynologique Internationale and the Ente Nazionale della Cinofilia Italiana treat them as separate. They are also genetically close to the other two Italian scent hound breeds, the Segugio Maremmano and the Segugio dell'Appennino. They are traditionally used for hunting hare, but may also be used in boar hunts.

Italian profanity are profanities that are blasphemous or inflammatory in the Italian language.

The global spread of the printing press began with the invention of the printing press with movable type by Johannes Gutenberg in Mainz, Germany c. 1439. Western printing technology was adopted in all world regions by the end of the 19th century, displacing the manuscript and block printing.

Pietro Paolini, called il Lucchese was an Italian painter of the Baroque period. Working in Rome, Venice and finally his native Lucca, he was a follower of Caravaggio to whose work he responded in a very personal manner. He founded an Academy in his hometown, which formed the next generation of painters of Lucca.

Teimuraz I (1589–1663), of the Bagrationi dynasty, was a Georgian monarch (mepe) who ruled, with intermissions, as King of Kakheti from 1605 to 1648 and also of Kartli from 1625 to 1633. The eldest son of David I and Ketevan, Teimuraz spent most of his childhood at the court of Shah of Iran, where he came to be known as Tahmuras Khan. He was made king of Kakheti following a revolt against his reigning uncle, Constantine I, in 1605. From 1614 on, he waged a five-decade long struggle against the Safavid Iranian domination of Georgia in the course of which he lost several members of his family and ended his life as the Shah's prisoner at Astarabad at the age of 74.

Paulinus of St. Bartholomew was an Austrian Carmelite missionary and Orientalist of Croatian origin. He is known by several names as Paulinus S. Bartholomaeo, Paolino da San Bartolomeo, Paulinus Paathiri, Paulin de St Barthelemi, Paulinus A S. Bartholomaeo, Johann Philipp Wesdin, or Johann Philipp Werdin.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Genoa, Liguria, Italy.

Alphabetum Ibericum sive Georgianum cum Oratione is the first book printed in the Georgian language using movable type in 1629 at Palazzo di Propaganda Fide. The book was printed along with Dittionario giorgiano e italiano by Nikoloz Cholokashvili, the ambassador of the Georgian king Teimuraz I, in Rome. It includes a guide for Latin speakers on reading and pronouncing Georgian written in Mkhedruli script.
The Maronite Catholic Archeparchy of Tripoli is a non-Metropolitan Archeparchy of the Maronite Church in the north-west of Lebanon.
Isabella Piccini was an Italian artist and nun. She worked in the mediums of etching, engraving, and illustration.
Ignatius of Jesus was an Italian Roman Catholic friar of the Order of the Discalced Carmelites who served as a missionary in Persia, Basra, and Lebanon for 35 years. He is best known for writing the first Western scholarly work on Mandaeism, Narratio originis, rituum, & errorum christianorum Sancti Ioannis (1652).
Adriano Politi was an Italian translator, philologist and classical scholar. He belonged to the Sienese School of philologists.











