Ahmose was an Ancient Egyptian queen in the Eighteenth Dynasty. She was the Great Royal Wife of the dynasty's third pharaoh, Thutmose I, and the mother of the queen and pharaoh Hatshepsut. Her name means "Born of the Moon".

Amenhotep I or Amenophis I, was the second Pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt. His reign is generally dated from 1526 to 1506 BC.

God's Wife of Amun was the highest-ranking priestess of the Amun cult, an important religious institution in ancient Egypt. The cult was centered in Thebes in Upper Egypt during the Twenty-fifth and Twenty-sixth dynasties. The office had political importance as well as religious, since the two were closely related in ancient Egypt.

The necropolis of Draʻ Abu el-Naga' is located on the West Bank of the Nile at Thebes, Egypt, just by the entrance of the dry bay that leads up to Deir el-Bahari and north of the necropolis of el-Assasif. The necropolis is located near the Valley of the Kings.

The necropolis of Sheikh Abd el-Qurna is located on the West Bank at Thebes in Upper Egypt. It is part of the archaeological area of Deir el-Bahari, and named after the domed tomb of the local saint. This is the most frequently visited cemetery on the Theban west bank, with the largest concentration of private tombs.

Heqakheperre Shoshenq II or Shoshenq IIa was a pharaoh of the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt. He was the only ruler of this dynasty whose tomb was not plundered by tomb robbers. His final resting place was discovered within an antechamber of Psusennes I's tomb at Tanis by Pierre Montet in 1939. Montet removed the coffin lid of Shoshenq II on March 20, 1939, in the presence of king Farouk of Egypt himself. It proved to contain many jewel-encrusted bracelets and pectorals, along with a beautiful hawkheaded silver coffin and a gold funerary mask. The facemask had been placed upon the head of the king. Montet later discovered the intact tombs of two Twenty-first Dynasty kings a year later in February and April 1940 respectively. Shoshenq II's prenomen, Heqakheperre Setepenre, means "The manifestation of Ra rules, the chosen one of Ra."

Shoshenq VI is known to be Pedubast I's immediate successor at Thebes based upon the career of the Letter Writer to Pharaoh Hor IX, who served under Osorkon II and Pedubast I. Since Shoshenq VI's prenomen is inscribed on Hor IX's funerary cones, this indicates that Hor IX outlived Pedubast I and made his funeral arrangements under Shoshenq VI instead. His prenomen or royal name was "Usermaatre Meryamun Shoshenq" which is unusual because it is the only known example where the epithet "Meryamun" appears within a king's cartouche. Shoshenq VI's High Priest of Amun was a certain Takelot who first appears in office in Year 23 of Pedubast I.

Ahmose-Meritamun was a Queen of Egypt during the early Eighteenth Dynasty. She was both the older sister and the wife of Pharaoh Amenhotep I. She died fairly young and was buried in tomb TT358 in Deir el-Bahari.

Hapuseneb was the High Priest of Amun during the reign of Hatshepsut.

The High Priest of Amun or First Prophet of Amun was the highest-ranking priest in the priesthood of the ancient Egyptian god Amun. The first high priests of Amun appear in the New Kingdom of Egypt, at the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty.
Bas-relief carvings in the ancient Egyptian temple of Deir el-Bahari depict events in the life of the pharaoh or monarch Hatshepsut of the Eighteenth Dynasty. They show the Egyptian gods, in particular Amun, presiding over her creation, and describe the ceremonies of her coronation. Their purpose was to confirm the legitimacy of her status as a woman pharaoh. Later rulers attempted to erase the inscriptions.
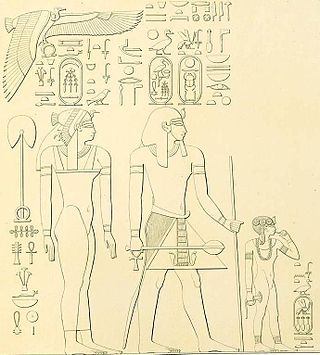
Minmontu(mn.w-mnṯ.w) was a High Priest of Amun from the time of Ahmose I.
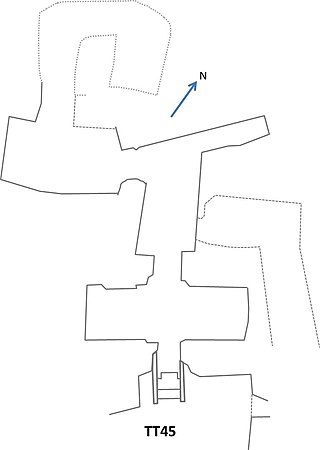
The Theban Tomb TT45 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite modern Luxor. It was originally the burial place of the ancient Egyptian named Djehuty (Thoth), who was a scribe of the offering-table of Mery, high-priest of Amun, head of all the weavers of Amun, and steward of Mery, high priest of Amun. Djehuty lived during the reign of Amenhotep II. He was the son of a lady also named Djehuty.

The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty spanned the period from 1550/1549 to 1292 BC. This dynasty is also known as the Thutmoside Dynasty) for the four pharaohs named Thutmose.
This page list topics related to ancient Egypt.

The Department of Egyptian Antiquities of the Louvre is a department of the Louvre that is responsible for artifacts from the Nile civilizations which date from 4,000 BC to the 4th century. The collection, comprising over 50,000 pieces, is among the world's largest, overviews Egyptian life spanning Ancient Egypt, the Middle Kingdom, the New Kingdom, Coptic art, and the Roman, Ptolemaic, and Byzantine periods.
The Second Prophet of Amun, also called the Second Priest of Amun, was a high ranking priestly official in the cult of the ancient Egyptian god Amun. The Second Prophet of Amun office was created in the New Kingdom, at the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty.
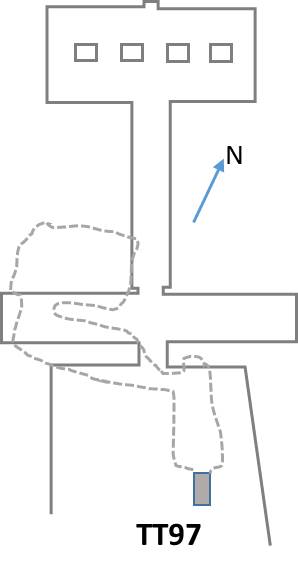
The Theban Tomb TT97 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. The tomb belongs to an ancient Egyptian named Amenemhat, who was the High Priest of Amun at Karnak, during the reign of pharaoh Amenhotep II of the 18th Dynasty. Amenemhat was the son of the wab-priest and "Overseer of the sandal makers of Amun", Djehutyhotep.

The Theban Tomb TT358 is located in Deir el-Bahari, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. The tomb belongs to the king's wife Ahmose-Meritamun, the sister and the wife of Pharaoh Amenhotep I. The tomb was later used for the additional burial of the King's daughter Nany, who was a daughter of Pharaoh Pinedjem I.

The Theban Tomb TT120 is located in Sheikh Abd el-Qurna. It forms part of the Theban Necropolis, situated on the west bank of the Nile opposite Luxor. The tomb is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian official Ahmose, who was the second prophet of Amun-Ra at Karnak and later the first prophet of Amun at Henqet-Ankh, the mortuary temple of Tuthmosis III at Qurnah during the reign of the Tuthmosis III.

















