External links
- LIBRARIAN VERSUS DOCUMENTALIST 1953 Article by Eugene Garfield
A documentalist is a professional, trained in documentation science and specializing in assisting researchers in their search for scientific and technical documentation. With the development of bibliographical databases such as MEDLINE, documentalists were professionals who searched such databases on the behalf of users.
When the field of documentation changed its name to information science, the terms information specialist or information professional often replaced the term documentalist.
Information science is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information. Practitioners within and outside the field study the application and the usage of knowledge in organizations in addition to the interaction between people, organizations, and any existing information systems with the aim of creating, replacing, improving, or understanding the information systems.

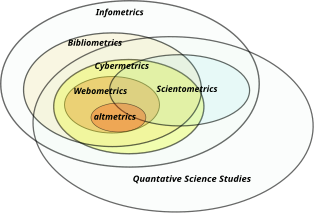
Eugene Eli Garfield was an American linguist and businessman, one of the founders of bibliometrics and scientometrics. He helped to create Current Contents, Science Citation Index (SCI), Journal Citation Reports, and Index Chemicus, among others, and founded the magazine The Scientist.

An index is a list of words or phrases ('headings') and associated pointers ('locators') to where useful material relating to that heading can be found in a document or collection of documents. Examples are an index in the back matter of a book and an index that serves as a library catalog. An index differs from a word index, or concordance, in focusing on the subject of the text rather than the exact words in a text, and it differs from a table of contents because the index is ordered by subject, regardless of whether it is early or late in the book, while the listed items in a table of contents is placed in the same order as the book.

Jesse Hauk Shera was an American librarian and information scientist who pioneered the use of information technology in libraries and played a role in the expansion of its use in other areas throughout the 1950s, 60s, and 70s.

Edge-notched cards or edge-punched cards are a system used to store a small amount of binary or logical data on paper index cards, encoded via the presence or absence of notches in the edges of the cards. The notches allowed efficient sorting and selecting of specific cards matching multiple desired criteria, from a larger number of cards in a paper-based database of information. In the mid-20th century they were sold under names such as Cope-Chat cards, E-Z Sort cards, McBee Keysort cards, and Indecks cards. They are also informally called needle cards since they can be sorted with long knitting needles.
Music librarianship is the area of librarianship that pertains to music collections and their development, cataloging, preservation and maintenance, as well as reference issues connected with musical works and music literature. Music librarians often have degrees in both music and librarianship. Music librarians deal with standard librarianship duties such as cataloging and reference, which become more complicated when music scores and recordings are involved. Therefore, music librarians generally read music and have at least a basic understanding of both music theory and music history to aid in their duties.

Foster Edward Mohrhardt was a United States librarian. He had a long and illustrious career in library and information science as a scholar, organizer and diplomat, and was listed by American Libraries among "100 Leaders we had in the 20th Century". Mohrhardt is also known for his work to have the United States Department of Agriculture Library re-designated as a national library.
The term information scientist developed in the latter part of the twentieth century by Wm. Hovey Smith to describe an individual, usually with a relevant subject degree or high level of subject knowledge, providing focused information to scientific and technical research staff in industry. It is a role quite distinct from and complementary to that of a librarian. Developments in end-user searching, together with some convergence between the roles of librarian and information scientist, have led to a diminution in its use in this context, and the term information officer or information professional are also now used.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to information science:
Roderick Samson Mabomba was a library leader in Malawi. He worked to make information science an important subject in Malawi and to bring libraries to the attention of the Malawi government. He spoke at numerous conferences, where he presented his papers giving exposure to libraries from Africa.
Herman Howe Fussler was an American librarian, library administrator, teacher, writer and editor, who was a pioneer in the use of microphotography. Fussler was ranked as one of the "100 of the Most Important Leaders we had in the 20th Century" by American Libraries. Fussler served as director of the University of Chicago libraries from 1948 to 1971, was Dean of the University of Chicago Graduate Library School, from 1961 to 1963, and was instrumental in the founding of the Regenstein Library. He helped create the Center for Research Libraries. He was an elected fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
ProCite, a commercial reference management software program, was designed in the early 1980s by Victor Rosenberg, associate professor in the School of Library and Information Studies at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. ProCite was published in 1983 by Personal Bibliographic Software of Ann Arbor, Michigan. In 1996, ProCite was purchased by the Institute for Scientific Information, a division of Thomson Reuters. Thomson Reuters discontinued sales and support of Procite in May 2013.
Samuel Clement Bradford was a British mathematician, librarian and documentalist at the Science Museum in London. He developed "Bradford's law" regarding differences in demand for scientific journals. This work influences bibliometrics and citation analysis of scientific publications. Bradford founded the British Society for International Bibliography (BSIB) and he was elected president of International Federation for Information and Documentation (FID) in 1945. Bradford was a strong proponent of the UDC and of establishing abstracts of the scientific literature.

Documentation science is the study of the recording and retrieval of information. Documentation science gradually developed into the broader field of information science.
A library and information scientist, also known as a library scholar, is a researcher or academic who specializes in the field of library and information science and often participates in scholarly writing about and related to library and information science. A library and information scientist is neither limited to any one subfield of library and information science nor any one particular type of library. These scientists come from all information-related sectors.

Information history may refer to the history of each of the categories listed below. It should be recognized that the understanding of, for example, libraries as information systems only goes back to about 1950. The application of the term information for earlier systems or societies is a retronym.
The Classification Research Group (CRG) was a significant contributor to classification research and theory in the field of library and information science in the latter half of the 20th century. It was formed in England in 1952 and was active until 1968. Informal meetings continued until 1990. Among its members were Derek Austin, Eric Coates, Jason Farradane, Robert Fairthorne, Douglas Foskett, Barbara Kyle, Derek Langridge, Jack Mills, Pauline Atherton Cochrane,Phyllis Richmond, Bernard Palmer, Jack Wells, and Brian Campbell Vickery. The group formed important principles on faceted classification and also worked on the theory of integrative levels.

Claire Kelly Schultz was an American computer consultant and academic. She was a leading figure in the early development of automated information retrieval systems and information science. A "documentalist", she was particularly known for her work in thesaurus construction and machine-aided indexing, innovating techniques for punch card information retrieval.

The Award of Merit is bestowed by the Association for Information Science and Technology. It is an annual prize to an individual for a lifetime of achievement that recognizes sustained contributions to and/or achievements in the field of information science and/or the professions in which it is practiced. The Award of Merit was first given in 1964.