
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled auto-loading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles are typically designed more for firing short bursts rather than continuous firepower and are not considered true machine guns. Submachine guns fire handgun cartridges rather than rifle cartridges, therefore they are not considered machine guns, while automatic firearms of 20 mm (0.79 in) caliber or more are classified as autocannons rather than machine guns.

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:

The Sentinels are a group of mutant-hunting robots appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. They are typically depicted as antagonists to the X-Men.
The Star Trek fictional universe contains a variety of weapons, ranging from missiles to melee. The Star Trek franchise consists mainly of several multi-season television shows and a dozen movies, as well as various video games and inspired merchandise. Many aspects of the Star Trek universe impact modern popular culture, especially its fictitious terminology and the concept of weaponry on spacecraft. The franchise has had a widespread influence on its audiences from the late 20th to early 21st century. Notably, Star Trek's science fiction concepts have been studied by real scientists; NASA described it in relation to the real world as "entertaining combination of real science, imaginary science gathered from lots of earlier stories, and stuff the writers make up week-by-week to give each new episode novelty." For example, NASA noted that the Star Trek "phasers" were a fictional extrapolation of real-life lasers, and compared them to real-life microwave based weapons that have a stunning effect.
Star Destroyers are capital ships in the fictional Star Wars universe. Star Destroyers were produced by Kuat Drive Yards, later Kuat-Entralla Engineering, and serve as "the signature vessel of the fleet" for the Galactic Republic, Galactic Empire, the First Order, and the Sith Eternal in numerous published works including film, television, novels, comics, and video games.

An autocannon, automatic cannon or machine cannon is a fully automatic gun that is capable of rapid-firing large-caliber armour-piercing, explosive or incendiary shells, as opposed to the smaller-caliber kinetic projectiles (bullets) fired by a machine gun. Autocannons have a longer effective range and greater terminal performance than machine guns, due to the use of larger/heavier munitions, but are usually smaller than tank guns, howitzers, field guns, or other artillery. When used on its own, the word "autocannon" typically indicates a non-rotary weapon with a single barrel. When multiple rotating barrels are involved, such a weapon is referred to as a "rotary autocannon" or occasionally "rotary cannon", for short.
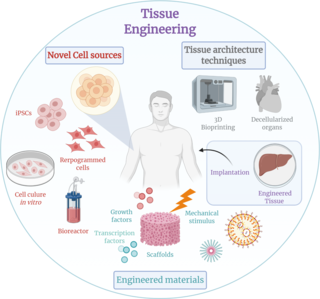
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of cells, engineering, materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field of its own.
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. The term "tissue culture" was coined by American pathologist Montrose Thomas Burrows. This technique is also called micropropagation. After the cells of interest have been isolated from living tissue, they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions. They need to be kept at body temperature (37 °C) in an incubator. These conditions vary for each cell type, but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or rich medium that supplies the essential nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), growth factors, hormones, and gases (CO2, O2), and regulates the physio-chemical environment (pH buffer, osmotic pressure, temperature). Most cells require a surface or an artificial substrate to form an adherent culture as a monolayer (one single-cell thick), whereas others can be grown free floating in a medium as a suspension culture. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-solid, or solid growth medium, such as broth or agar. Tissue culture commonly refers to the culture of animal cells and tissues, with the more specific term plant tissue culture being used for plants. The lifespan of most cells is genetically determined, but some cell-culturing cells have been “transformed” into immortal cells which will reproduce indefinitely if the optimal conditions are provided.

Loose connective tissue, also known as areolar tissue, is a cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers. They have a semi-fluid matrix with lesser proportions of fibers. Its ground substance occupies more volume than the fibers do. It has a viscous to gel-like consistency and plays an important role in the diffusion of oxygen and nutrients from the capillaries that course through this connective tissue as well as in the diffusion of carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes back to the vessels. Moreover, loose connective tissue is primarily located beneath the epithelia that cover the body surfaces and line the internal surfaces of the body. It is also associated with the epithelium of glands and surrounds the smallest blood vessels. This tissue is thus the initial site where pathogenic agents, such as bacteria that have breached an epithelial surface, are challenged and destroyed by cells of the immune system.

Cell disruption is a method or process for releasing biological molecules from inside a cell.
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size. Examples of granulation tissue can be seen in pyogenic granulomas and pulp polyps. Its histological appearance is characterized by proliferation of fibroblasts and thin-walled, delicate capillaries (angiogenesis), and infiltrated inflammatory cells in a loose extracellular matrix.

Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3D printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3D object is produced. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The biocompatible plastic forms a scaffold that acts as the skeleton for the organ that is being printed. As the plastic is being laid down, it is also seeded with human cells from the patient's organ that is being printed for. After printing, the organ is transferred to an incubation chamber to give the cells time to grow. After a sufficient amount of time, the organ is implanted into the patient.

Strontium-90 is a radioactive isotope of strontium produced by nuclear fission, with a half-life of 28.8 years. It undergoes β− decay into yttrium-90, with a decay energy of 0.546 MeV. Strontium-90 has applications in medicine and industry and is an isotope of concern in fallout from nuclear weapons, nuclear weapons testing, and nuclear accidents.
Cardiomyoplasty is a surgical procedure in which healthy muscle from another part of the body is wrapped around the heart to provide support for the failing heart. Most often the latissimus dorsi muscle is used for this purpose. A special pacemaker is implanted to make the skeletal muscle contract. If cardiomyoplasty is successful and increased cardiac output is achieved, it usually acts as a bridging therapy, giving time for damaged myocardium to be treated in other ways, such as remodeling by cellular therapies.
The internal environment was a concept developed by Claude Bernard, a French physiologist in the 19th century, to describe the interstitial fluid and its physiological capacity to ensure protective stability for the tissues and organs of multicellular organisms.
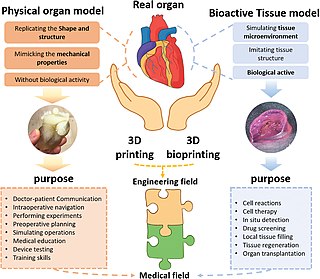
Three dimensional (3D) bioprinting is the utilization of 3D printing–like techniques to combine cells, growth factors, and/or biomaterials to fabricate biomedical parts, often with the aim of imitating natural tissue characteristics. Generally, 3D bioprinting can utilize a layer-by-layer method to deposit materials known as bio-inks to create tissue-like structures that are later used in various medical and tissue engineering fields. 3D bioprinting covers a broad range of bioprinting techniques and biomaterials. Currently, bioprinting can be used to print tissue and organ models to help research drugs and potential treatments. Nonetheless, translation of bioprinted living cellular constructs into clinical application is met with several issues due to the complexity and cell number needed to create functional organs. However, innovations span from bioprinting of extracellular matrix to mixing cells with hydrogels deposited layer by layer to produce the desired tissue. In addition, 3D bioprinting has begun to incorporate the printing of scaffolds which can be used to regenerate joints and ligaments.
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions from sub-disciplines and related fields, see Glossary of cell biology, Glossary of genetics, Glossary of evolutionary biology, Glossary of ecology, Glossary of environmental science and Glossary of scientific naming, or any of the organism-specific glossaries in Category:Glossaries of biology.
Invasion is the process by which cancer cells directly extend and penetrate into neighboring tissues in cancer. It is generally distinguished from metastasis, which is the spread of cancer cells through the circulatory system or the lymphatic system to more distant locations. Yet, lymphovascular invasion is generally the first step of metastasis.
Tissue engineered heart valves (TEHV) offer a new and advancing proposed treatment of creating a living heart valve for people who are in need of either a full or partial heart valve replacement. Currently, there are over a quarter of a million prosthetic heart valves implanted annually, and the number of patients requiring replacement surgeries is only suspected to rise and even triple over the next fifty years. While current treatments offered such as mechanical valves or biological valves are not deleterious to one's health, they both have their own limitations in that mechanical valves necessitate the lifelong use of anticoagulants while biological valves are susceptible to structural degradation and reoperation. Thus, in situ (in its original position or place) tissue engineering of heart valves serves as a novel approach that explores the use creating a living heart valve composed of the host's own cells that is capable of growing, adapting, and interacting within the human body's biological system.










