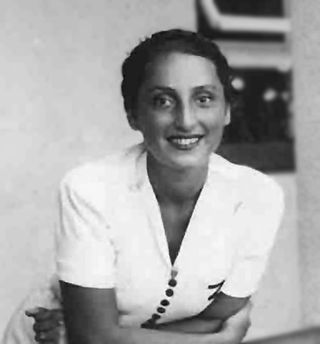Alexandria is the second largest city in Egypt and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile River delta. Founded in c. 331 BC by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilization, eventually replacing Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" internationally, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and oil pipelines from Suez.

Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic coast of northern Poland. With a population of 486,492, Gdańsk is the capital and largest city of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. It is Poland's principal seaport and the country's fourth-largest metropolitan area.

Szczecin is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major seaport and Poland's seventh-largest city. As of December 2021, the population was 395,513.

Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.1 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures 517 km2 (200 sq mi) and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers 6,100 km2 (2,355 sq mi). Warsaw is an alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also capital of the Masovian Voivodeship.

Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the Sudeten Mountains to the south. As of 2023, the official population of Wrocław is 674,132 making it the third largest city in Poland. Population of the Wrocław metropolitan area is around 1.25 million.

Bolesław I the Brave, less often known as Bolesław the Great, was Duke of Poland from 992 to 1025, and the first King of Poland in 1025. He was also Duke of Bohemia between 1003 and 1004 as Boleslaus IV. A member of the ancient Piast dynasty, Bolesław was a capable monarch and a strong mediator in Central European affairs. He continued to proselytise Western Christianity among his subjects and raised Poland to the rank of a kingdom, thus becoming the first Polish ruler to hold the title of rex, Latin for king.

Bolesław III Wrymouth, also known as Boleslaus the Wry-mouthed, was the duke of Lesser Poland, Silesia and Sandomierz between 1102 and 1107 and over the whole of Poland between 1107 and 1138. He was the only child of Duke Władysław I Herman and his first wife, Judith of Bohemia.

Częstochowa is a city in southern Poland on the Warta River with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship. However, Częstochowa is historically part of the Lesser Poland region, not of Silesia, and before 1795, it belonged to the Kraków Voivodeship. Częstochowa is located in the Kraków-Częstochowa Upland. It is the largest economic, cultural and administrative hub in the northern part of the Silesian Voivodeship.

Grudziądz is a city in northern Poland, with 92,552 inhabitants (2021). Located on the Vistula River, it lies within the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship and is the fourth-largest city in its province. The Old Town of Grudziądz and 14th-century granaries were declared National Historic Monuments of Poland.
The Poles come from different West Slavic tribes living on territories belonging later to Poland in the early Middle Ages.

The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, or simply Poland–Lithuania, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost 1,000,000 km2 (400,000 sq mi) and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages.

Gdańsk is one of the oldest cities in Poland. Founded by the Polish ruler Mieszko I in the 10th century, the city was for a long time part of Piast state either directly or as a fief. In 1308 the city became part of the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights until 1454. Thereafter it became part of Poland again, although with increasing autonomy. A vital naval city for Polish grain trade, it attracted people from all over the European continent. The city was taken over by Prussia during the Second Partition of Poland in 1793 and subsequently lost its importance as a trading port. Briefly becoming a free city during Napoleonic Wars, it was again Prussian after Napoleon's defeat, and later became part of the newly created German Empire.

In the second half of the 2nd millennium B.C., Silesia belonged to the Lusatian culture. About 500 BC Scyths arrived, and later Celts in the South and Southwest. During the 1st century BC Silingi and other Germanic people settled in Silesia. For this period we have written reports of antique authors who included the area. Slavs arrived in this territory around the 6th century. The first known states in Silesia were those of Greater Moravia and Bohemia. In the 10th century, Mieszko I incorporated Silesia into Civitas Schinesghe, a Polish state. It remained part of Poland until the Fragmentation of Poland. Afterwards it was divided between Piast dukes, descendants of Władysław II the Exile, High Duke of Poland.

The Warsaw National Museum, also known as the National Museum in Warsaw, is a national museum in Warsaw, one of the largest museums in Poland and the largest in the capital. It comprises a rich collection of ancient art, counting about 11,000 pieces, an extensive gallery of Polish painting since the 16th century and a collection of foreign painting including some paintings from Adolf Hitler's private collection, ceded to the museum by the American authorities in post-war Germany. The museum is also home to numismatic collections, a gallery of applied arts and a department of oriental art, with the largest collection of Chinese art in Poland, comprising some 5,000 objects.
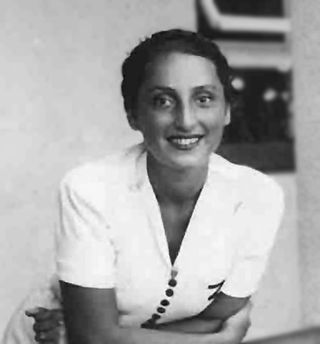
Zuzanna Ginczanka, pen nameZuzanna Polina Gincburg was a Polish-Jewish poet of the interwar period. Although she published only a single collection of poetry in her lifetime, the book O centaurach created a sensation in Poland's literary circles. She was arrested and executed in Kraków shortly before the end of World War II.

The most important phenomenon that took place within the lands of Poland in the Early Middle Ages, as well as other parts of Central Europe was the arrival and permanent settlement of the West Slavic or Lechitic peoples. The Slavic migrations to the area of contemporary Poland started in the second half of the 5th century AD, about a half century after these territories were vacated by Germanic tribes fleeing from the Huns. The first waves of the incoming Slavs settled the vicinity of the upper Vistula River and elsewhere in the lands of present southeastern Poland and southern Masovia. Coming from the east, from the upper and middle regions of the Dnieper River, the immigrants would have had come primarily from the western branch of the early Slavs known as Sclaveni, and since their arrival are classified as West Slavs and Lechites, who are the closest ancestors of Poles.

The bilateral relations between Poland and Germany have been marked by an extensive and complicated history.

Jesuit College in Khyriv, formerly Jesuit College in Chyrów, was a purpose-built Polish secondary boys college, owned by the Society of Jesus, in the occupied Austro-Hungarian partition of Poland in the late 19th century. The vast estate, comprising the college, has the rare distinction of having existed in at least five separate national Jurisdictions in the last century and a half. From 1918 the college was in independent Poland until 1939 when it ceased to exist as an institution, although not as an asset, due to foreign invasions, first by the Red Army till 1941, then by the German Wehrmacht until 1943, before being re-taken by the Soviet Union. Since 1944 the site and its entire estate was in the USSR and since 1991 has been in present-day Ukraine.
The Samir Shamma Prize for Islamic Numismatics is a bi-annual award for the best book or article in the field of Islamic Numismatics.

Clan Ostoja (Moscics) is one of the largest and oldest knightly and heraldic families in Europe, belonging to the Polish nobility. The family is sealed with the Ostoja coat of arms.