Related Research Articles
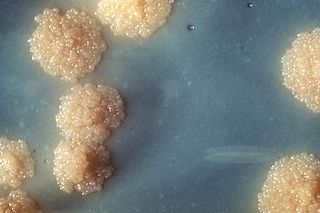
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.

Mycobacterium is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with a waxy lipid-rich outer layer containing high concentrations of mycolic acid, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types.
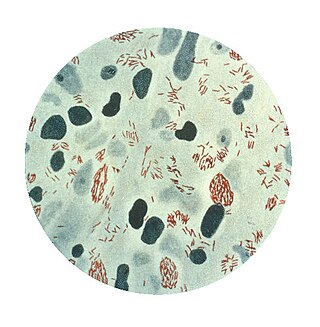
Mycobacterium leprae is one of the two species of bacteria that cause Hansen's disease (leprosy), a chronic but curable infectious disease that damages the peripheral nerves and targets the skin, eyes, nose, and muscles.

Mycobacterium bovis is a slow-growing aerobic bacterium and the causative agent of tuberculosis in cattle. It is related to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium which causes tuberculosis in humans. M. bovis can jump the species barrier and cause tuberculosis-like infection in humans and other mammals.
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM), also known as environmental mycobacteria, atypical mycobacteria and mycobacteria other than tuberculosis (MOTT), are mycobacteria which do not cause tuberculosis or leprosy/Hansen's disease. NTM can cause pulmonary diseases that resemble tuberculosis. Mycobacteriosis is any of these illnesses, usually meant to exclude tuberculosis. They occur in many animals, including humans, and are commonly found in soil and water.

Buruli ulcer is an infectious disease characterized by the development of painless open wounds. The disease is limited to certain areas of the world, with most cases occurring in Sub-Saharan Africa and Australia. The first sign of infection is a small painless nodule or area of swelling, typically on the arms or legs. The nodule grows larger over days to weeks, eventually forming an open ulcer. Deep ulcers can cause scarring of muscles and tendons, resulting in permanent disability.
Mycobacterium africanum is a species of Mycobacterium that is most commonly found in West African countries, where it is estimated to cause up to 40% of pulmonary tuberculosis. The symptoms of infection resemble those of M. tuberculosis.
The Royal Society Africa Prize has been awarded by the Royal Society since 2006 to African-based researchers at the start of their career who are making innovative contributions to the biological sciences in Africa. £60,000 is awarded as a grant for the recipient to carry out a research project that is linked to an African centre of scientific excellence, normally a University or equivalent research centre, and a further £5,000 is given directly to the prizewinner.
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex is a genetically related group of Mycobacterium species that can cause tuberculosis in humans or other animals.
Barry R. Bloom is Joan L. and Julius H. Jacobson Professor of Public Health, Emeritus in the Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases and Department of Global Health and Population in the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, where he served as dean of the faculty from 1998 through December 31, 2008.

Lalita Ramakrishnan is an Indian-born American microbiologist who is known for her contributions to the understanding of the biological mechanism of tuberculosis. As of 2019 she serves as a professor of Immunology and Infectious Diseases at the University of Cambridge, where she is also a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow and a practicing physician. Her research is conducted at the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, where she serves as the Head of the Molecular Immunity Unit of the Department of Medicine embedded at the MRC LMB. Working with Stanley Falkow at Stanford, she developed the strategy of using Mycobacterium marinum infection as a model for tuberculosis. Her work has appeared in a number of journals, including Science, Nature, and Cell. In 2018 and 2019 Ramakrishnan coauthored two influential papers in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) arguing that the widely accepted estimates of the prevalence of latent tuberculosis—estimates used as a basis for allocation of research funds—are far too high. She is married to Mark Troll, a physical chemist.
Sangita Mukhopadhyay is an Indian molecular cell biologist, immunologist and the head of the molecular biology group at the Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics. Known for her studies on immunosuppression and infection biology, Mukhopadhyay is an elected fellow of all the three major Indian science academies namely the Indian National Science Academy, the Indian Academy of Sciences and the National Academy of Sciences, India. The Department of Biotechnology of the Government of India awarded her the National Bioscience Award for Career Development, one of the highest Indian science awards, for her contributions to biosciences in 2008.

Judith Glynn is a Professor of Epidemiology at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine. She worked on the Karonga Prevention Study on HIV and Tuberculosis in Malawi. She is also a sculptor.

Gordon Akanzuwine Awandare is a Ghanaian parasitologist and the Pro-Vice Chancellor in charge of Academic and Student Affairs at the University of Ghana. Prior to his appointment in January 2022, He was the founding Director of the West African Center for Cell Biology of Infectious Pathogens (WACCBIP). He is the current chairman of the CKT-UTAS governing council and the Africa Global Editor of the Experimental Biology and Medicine (EBM) journal.
Amit Singh is an Indian microbiologist and an associate professor at the Department of Microbiology & Cell Biology of the Indian Institute of Science. A Wellcome-DBT Senior Fellow, Singh is known for his research on the pathogenesis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. His research focuses on exploring the mechanisms behind the persistence of human pathogens, such as those responsible for tuberculosis and HIV.

Henry Charles Mwandumba is an African Professor of Medicine and the Director of the Malawi-Liverpool-Wellcome Programme. He works on the tuberculosis phagosome in the University of Malawi College of Medicine, and serves as President of the Federation of African Immunological Societies. In 2019 Mwandumba was awarded the Royal Society Africa Prize.
Hazel Marguerite Dockrell is an Irish-born microbiologist and immunologist whose research has focused on immunity to the human mycobacterial diseases, leprosy and tuberculosis. She has spent most of her career at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, where as of 2020 she is a professor of immunology. She was the first female president of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. Jimmy Whitworth of the Wellcome Trust describes her as "a marvellous ambassador for global health and research."

Ayesha Jennifer Verrall is a New Zealand politician, infectious-diseases physician and researcher with expertise in tuberculosis and international health. Since 2020 she has been a Member of the New Zealand House of Representatives for the Labour Party.

Christian Happi is a Professor of Molecular Biology and Genomics in the Department of Biological Sciences and the Director of the African Centre of Excellence for Genomics of Infectious Diseases, both at Redeemer’s University. He is known for leading the team of scientists that used genomic sequencing to identify a single point of infection from an animal reservoir to a human in the Ebola outbreak in West Africa. His research focus is on infectious diseases, including malaria, Lassa fever, Ebola virus disease, HIV, and SARS-CoV-2.
Martin Antonio is a Ghanaian biologist who is Principal Investigator at the Medical Research Council Unit at London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. He is Director of the World Health Organization Centre for New Vaccines Surveillance and leads the West and Central Africa Regional Reference Laboratory for Invasive Bacterial Diseases.
References
- ↑ Sill, Ulrike (2010). Encounters in Quest of Christian Womanhood: The Basel Mission in Pre- and Early Colonial Ghana. BRILL. ISBN 978-9004188884.
- 1 2 3 "FAIS Africa". www.faisafrica.com. Archived from the original on 2018-07-19. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "Dishing the dirt on street food safety in Accra, Ghana | Eldis". eldis.org. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ Mensah, Patience; Yeboah-Manu, Dorothy; Owusu-Darko, Kwaku; Ablordey, Anthony (2002). "Street foods in Accra, Ghana: how safe are they?". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 80 (7): 546–554. ISSN 0042-9686. PMC 2567559 . PMID 12163918.
- ↑ Yeleliere, Enoch; Cobbina, Samuel Jerry; Abubakari, Zarouk Imoro (2017-10-23). "Review of microbial food contamination and food hygiene in selected capital cities of Ghana". Cogent Food & Agriculture. 3 (1). doi: 10.1080/23311932.2017.1395102 . ISSN 2331-1932.
- ↑ Yeboah-Manu, Dorothy; Röltgen, Katharina; Opare, William; Asan-Ampah, Kobina; Quenin-Fosu, Kwabena; Asante-Poku, Adwoa; Ampadu, Edwin; Fyfe, Janet; Koram, Kwadwo (2012-01-10). "Sero-Epidemiology as a Tool to Screen Populations for Exposure to Mycobacterium ulcerans". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 6 (1): e1460. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001460 . ISSN 1935-2735. PMC 3254650 . PMID 22253937.
- 1 2 3 4 "Members". GUIDE Africa. 2017-03-15. Archived from the original on 2018-07-19. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "Search". Swiss TPH (in German). Archived from the original on 2018-07-19. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "ORID Research Report -printed". www.orid.ug.edu.gh. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "Intermediate Fellowships in Public Health and Tropical Medicine: people we've funded | Wellcome". wellcome.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2018-07-19. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "Study Reveals Tuberculosis On The Increase". Modern Ghana. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "NATIONAL FACULTY – West African Centre for Cell Biology of Infectious Pathogens". www.waccbip.org. Archived from the original on 2018-07-19. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "Cell Biology Hits the Big Time in West Africa - ASCB". ASCB. 2016-04-01. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "African Books Collective: Dorothy Yeboah-Manu". www.africanbookscollective.com. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "African Books Collective: Towards Effective Disease Control in Ghana: Research and Policy Implications". www.africanbookscollective.com. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- ↑ "Recipients of Royal Society medals and awards in 2018 announced | Royal Society". royalsociety.org. Retrieved 2018-07-19.