Related Research Articles

Anatomy is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science which deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine.

The labia majora are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the labia of the vulva.

A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water and excretes carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia is the zoologists' name for gills.

The spleen is an organ found in virtually all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes from Ancient Greek σπλήν (splḗn).

The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.

A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at various body openings such as the eyes, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lip, vagina, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated.

In biology, tissue is a cellular organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is an ensemble of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.

An organ is a group of tissues with similar functions. Plant life and animal life rely on many organs that coexist in organ systems.

Standard anatomical terms of location deal unambiguously with the anatomy of animals, including humans. Terms used generally derive from Latin or Greek roots and used to describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes.

Fish anatomy is the study of the form or morphology of fishes. It can be contrasted with fish physiology, which is the study of how the component parts of fish function together in the living fish. In practice, fish anatomy and fish physiology complement each other, the former dealing with the structure of a fish, its organs or component parts and how they are put together, such as might be observed on the dissecting table or under the microscope, and the latter dealing with how those components function together in living fish.

The Archaeognatha are an order of apterygotes, known by various common names such as jumping bristletails. Among extant insect taxa they are some of the most evolutionarily primitive; they appeared in the Middle Devonian period at about the same time as the arachnids. Specimens that closely resemble extant species have been found as both body and trace fossils in strata from the remainder of the Paleozoic Era and more recent periods. For historical reasons an alternative name for the order is Microcoryphia.
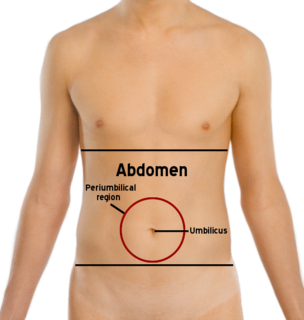
The abdomen is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the trunk. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax.
The "body without organs" is a concept used by French philosophers Gilles Deleuze and Félix Guattari. It is a "body without an image", a structure or zone without imposed organization that can be sentient or inanimate. In Deleuze and Guattari's Capitalism and Schizophrenia, it is the raw product of social alienation and destabilization, and a surface on which repressed and uncontrollable desires flow without organization, but with consistency.

Fish are gill-bearing aquatic craniate animals that lack limbs with digits. They form a sister group to the tunicates, together forming the olfactores. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Around 99% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with over 95% belonging to the teleost subgrouping.

The anatomy of spiders includes many characteristics shared with other arachnids. These characteristics include bodies divided into two tagmata, eight jointed legs, no wings or antennae, the presence of chelicerae and pedipalps, simple eyes, and an exoskeleton, which is periodically shed.

A nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which receive and expel air for respiration alongside the mouth. Behind the nose are the olfactory mucosa and the sinuses. Behind the nasal cavity, air next passes through the pharynx, shared with the digestive system, and then into the rest of the respiratory system. In humans, the nose is located centrally on the face and serves as an alternative respiratory passage especially during suckling for infants.
This glossary describes the terms used in formal descriptions of spiders; where applicable these terms are used in describing other arachnids.

A sucker in zoology refers to specialised attachment organ of an animal. It acts as an adhesion device in parasitic worms, several flatworms, cephalopods, certain fishes, amphibians, and bats. It is a muscular structure for suction on a host or substrate. In parasitic annelids, flatworms and roundworms, suckers are the organs of attachment to the host tissues. In tapeworms and flukes, they are a parasitic adaptation for attachment on the internal tissues of the host, such as intestines and blood vessels. In roundworms and flatworms they serve as attachment between individuals particularly during mating. In annelids, a sucker can be both a functional mouth and a locomotory organ. The structure and number of suckers are often used as basic taxonomic diagnosis between different species, since they are unique in each species. In tapeworms there are two distinct classes of suckers, namely "bothridia" for true suckers, and "bothria" for false suckers. In digeneal flukes there are usually an oral sucker at the mouth and a ventral sucker posterior to the mouth. Roundworms have their sucker just in front of the anus; hence it is often called a pre-anal sucker.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors.

Anatomical terminology is used to describe microanatomical structures. This helps describe precisely the structure, layout and position of an object, and minimises ambiguity. An internationally accepted lexicon is Terminologia Histologica.
References
- ↑
 One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Dorsiventral". Encyclopædia Britannica . 8 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 436.
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Dorsiventral". Encyclopædia Britannica . 8 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 436. - ↑ Oldeman, Roelof. Forests: Elements of Silvology. p. 151.
| | This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |