Related Research Articles

The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocalisation including speech possible.

The thoracic cavity is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall. The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There are two openings of the thoracic cavity, a superior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic inlet and a lower inferior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic outlet.

The pleural cavity, or pleural space, is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient.

The pleural cavity, or pleural space, is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication between the membranes, and also to create a pressure gradient.

A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as fourth order, fifth order, and sixth order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.

A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli.

The mediastinum is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is a region that contains vital organs and structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the vagus, phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest.

A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.
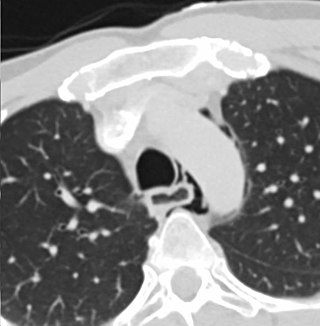
Esophageal rupture, also known as Boerhaave syndrome, is a rupture of the esophageal wall. Iatrogenic causes account for approximately 56% of esophageal perforations, usually due to medical instrumentation such as an endoscopy or paraesophageal surgery. The 10% of esophageal perforations caused specifically by vomiting are termed Boerhaave syndrome.
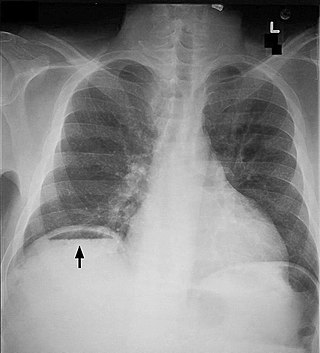
Pneumoperitoneum is pneumatosis in the peritoneal cavity, a potential space within the abdominal cavity. The most common cause is a perforated abdominal organ, generally from a perforated peptic ulcer, although any part of the bowel may perforate from a benign ulcer, tumor or abdominal trauma. A perforated appendix seldom causes a pneumoperitoneum.

Mediastinitis is inflammation of the tissues in the mid-chest, or mediastinum. It can be either acute or chronic. It is thought to be due to four different etiologies:

Pneumomediastinum is pneumatosis in the mediastinum, the central part of the chest cavity. First described in 1819 by René Laennec, the condition can result from physical trauma or other situations that lead to air escaping from the lungs, airways, or bowel into the chest cavity. In underwater divers it is usually the result of pulmonary barotrauma.

Hamman's syndrome, also known as Macklin's syndrome, is a syndrome of spontaneous subcutaneous emphysema and pneumomediastinum, sometimes associated with pain and, less commonly, dyspnea, dysphonia, and a low-grade fever.
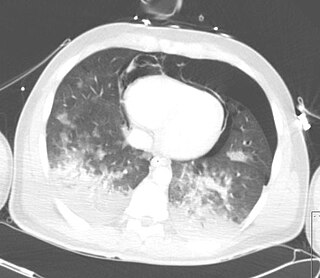
Pneumopericardium is a medical condition where air enters the pericardial cavity. This condition has been recognized in preterm neonates, in which it is associated with severe lung pathology, after vigorous resuscitation, or in the presence of assisted ventilation. This is a serious complication, which if untreated may lead to cardiac tamponade and death. Pneumomediastinum, which is the presence of air in the mediastinum, may mimic and also coexist with pneumopericardium.

Subcutaneous emphysema occurs when gas or air accumulates and seeps under the skin, where normally no gas should be present. Subcutaneous refers to the subcutaneous tissue, and emphysema refers to trapped air pockets. Since the air generally comes from the chest cavity, subcutaneous emphysema usually occurs around the upper torso, such as on the chest, neck, face, axillae and arms, where it is able to travel with little resistance along the loose connective tissue within the superficial fascia. Subcutaneous emphysema has a characteristic crackling-feel to the touch, a sensation that has been described as similar to touching warm Rice Krispies. This sensation of air under the skin is known as subcutaneous crepitation, a form of crepitus.

Tracheobronchial injury is damage to the tracheobronchial tree. It can result from blunt or penetrating trauma to the neck or chest, inhalation of harmful fumes or smoke, or aspiration of liquids or objects.

The pleurae are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the mediastinum, the inside surfaces of the surrounding chest walls and the diaphragm. Although wrapped onto itself resulting in an apparent double layer, each lung is surrounded by a single, continuous pleural membrane.

Pneumatosis is the abnormal presence of air or other gas within tissues.

Mediastinal shift is an abnormal movement of the mediastinal structures toward one side of the chest cavity. A shift indicates a severe imbalance of pressures inside the chest. Mediastinal shifts are generally caused by increased lung volume, decreased lung volume, or abnormalities in the pleural space. Additionally, masses inside the mediastinum or musculoskeletal abnormalities can also lead to abnormal mediastinal arrangement. Typically, these shifts are observed on x-ray but also on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). On chest x-ray, tracheal deviation, or movement of the trachea away from its midline position can be used as a sign of a shift. Other structures, like the heart, can also be used as reference points. Below are examples of pathologies that can cause a mediastinal shift and their appearance.

An air bronchogram is defined as a pattern of air-filled bronchi on a background of airless lung.
References
- ↑ Zylak, Christopher M.; Standen, James R.; Barnes, George R.; Zylak, Carl J. (July 2000). "Pneumomediastinum Revisited". RadioGraphics. 20 (4): 1043–1057. doi:10.1148/radiographics.20.4.g00jl131043. ISSN 0271-5333. PMID 10903694 . Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ↑ Kouritas, Vasileios K.; Papagiannopoulos, Konstantinos; Lazaridis, George; Baka, Sofia; Mpoukovinas, Ioannis; Karavasilis, Vasilis; Lampaki, Sofia; Kioumis, Ioannis; Pitsiou, Georgia; Papaiwannou, Antonis; Karavergou, Anastasia; Kipourou, Maria; Lada, Martha; Organtzis, John; Katsikogiannis, Nikolaos; Tsakiridis, Kosmas; Zarogoulidis, Konstantinos; Zarogoulidis, Paul (February 2015). "Pneumomediastinum". Journal of Thoracic Disease. 7 (Suppl 1): S44-9. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2015.01.11. ISSN 2077-6624. PMC 4332083 . PMID 25774307 . Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ↑ Yudin, Andrey (2023). "Ring Around Artery Sign, Double Bronchial Wall Sign". Metaphorical Signs in Computed Tomography of Chest and Abdomen. Springer International Publishing. p. 83. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-24494-0_42. ISBN 978-3-031-24493-3 . Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ↑ Dixit, R; George, J (July 2012). "Spontaneous pneumomediastinum with a classical radiological sign". Lung India. 29 (3): 295–6. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.99126 . PMC 3424876 . PMID 22919176.