Douglas Little is an American historian specializing in American diplomatic history, twentieth century America, and United States relations with the Middle East. Currently, his research focuses on the U.S. response to radical Islam between the 1967 Six-Day War and the 1979 Iranian Revolution. He teaches at Clark University in Worcester, Massachusetts, where he was also the Dean of the College.
His published books include American Orientalism: The United States and the Middle East since 1945, and Malevolent Neutrality: The United States, Great Britain and the origins of the Spanish Civil War.

In art history, literature and cultural studies, Orientalism is the imitation or depiction of aspects in the Eastern world. These depictions are usually done by writers, designers, and artists from the Western world. In particular, Orientalist painting, depicting more specifically the Middle East, was one of the many specialisms of 19th-century academic art, and the literature of Western countries took a similar interest in Oriental themes.

The Truman Doctrine is an American foreign policy that pledges American "support for democracies against authoritarian threats." The doctrine originated with the primary goal of containing Soviet geopolitical expansion during the Cold War. It was announced to Congress by President Harry S. Truman on March 12, 1947, and further developed on July 4, 1948, when he pledged to contain the communist uprisings in Greece and Turkey. More generally, the Truman Doctrine implied American support for other nations threatened by Moscow. It became the foundation of American foreign policy, and led, in 1949, to the formation of NATO, a military alliance that still exists. Historians often use Truman's speech to date the start of the Cold War.

Bernard Lewis, was a British American historian specialized in Oriental studies. He was also known as a public intellectual and political commentator. Lewis was the Cleveland E. Dodge Professor Emeritus of Near Eastern Studies at Princeton University. Lewis's expertise was in the history of Islam and the interaction between Islam and the West.
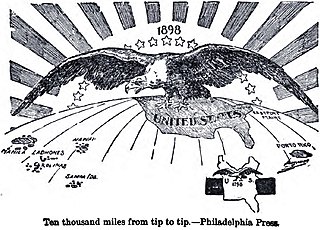
American imperialism refers to the expansion of American political, economic, cultural, media and military influence beyond the boundaries of the United States. Depending on the commentator, it may include imperialism through outright military conquest; gunboat diplomacy; unequal treaties; subsidization of preferred factions; regime change; or economic penetration through private companies, potentially followed by diplomatic or forceful intervention when those interests are threatened.

Harry St John Bridger Philby, CIE, also known as Jack Philby or Sheikh Abdullah, was a British Arabist, adviser, explorer, writer, and a colonial intelligence officer who served as an advisor to King Abdulaziz al-Saud, the founder of Saudi Arabia.

Sir Antony James Beevor, is a British military historian. He has published several popular historical works on the Second World War and the Spanish Civil War.

In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939, the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relatively short, yet featured many significant social, political, and economic changes throughout the world. Petroleum-based energy production and associated mechanisation led to the prosperous Roaring Twenties, a time of both social mobility and economic mobility for the middle class. Automobiles, electric lighting, radio, and more became common among populations in the developed world. The indulgences of the era subsequently were followed by the Great Depression, an unprecedented worldwide economic downturn that severely damaged many of the world's largest economies.

The European Civil War is a concept meant to characterize a series of 19th- and 20th-century conflicts in Europe as segments of an overarching civil war within a supposed European society. The timeframes associated with this European Civil War vary among historians. Some descriptions range from 1914 to 1945, thus including World War I, World War II, and many lesser conflicts of the interwar period. Others argue that this period started in 1870 with the Franco-Prussian War, or in 1905. Sometimes, the notion also serves to explain or justify the process of European integration and the creation of the European Union as a "solution" to this conflict.

Western civilization traces its roots back to Europe and the Mediterranean. It is linked to ancient Greece, the Roman Empire and with Medieval Western Christendom which emerged from the Middle Ages to experience such transformative episodes as Scholasticism, the Renaissance, the Reformation, the Enlightenment, the Industrial Revolution, the Scientific Revolution, and the development of liberal democracy. The civilizations of Classical Greece and Ancient Rome are considered seminal periods in Western history. Major cultural contributions also came from the Christianized Germanic peoples, such as the Franks, Goths, and Burgundians. Charlemagne founded the Carolingian Empire and is referred to as the "Father of Europe." Contributions also emerged from pagan peoples of pre-Christian Europe, such as the Celts and Germanic pagans as well as some significant religious contributions derived from Judaism and Hellenistic Judaism stemming back to Second Temple Judea, Galilee, and the early Jewish diaspora; and some other Middle Eastern influences. Western Christianity has played a prominent role in the shaping of Western civilization, which throughout most of its history, has been nearly equivalent to Christian culture.. Western civilization has spread to produce the dominant cultures of modern Americas and Oceania, and has had immense global influence in recent centuries in many ways.

Oriental studies is the academic field that studies Near Eastern and Far Eastern societies and cultures, languages, peoples, history and archaeology. In recent years, the subject has often been turned into the newer terms of Middle Eastern studies and Asian studies. Traditional Oriental studies in Europe is today generally focused on the discipline of Islamic studies, and the study of China, especially traditional China, is often called Sinology. The study of East Asia in general, especially in the United States, is often called East Asian studies.

The history of the Philippines from 1898 to 1946 began with the outbreak of the Spanish–American War in April 1898, when the Philippines was still a colony of the Spanish East Indies, and concluded when the United States formally recognized the independence of the Republic of the Philippines on July 4, 1946.
Jeffrey C. Herf is an American historian of Modern European, in particular, modern German history. He is Distinguished University Professor of modern European at the University of Maryland, College Park.

John Bullock Clark Jr. was a general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War and a postbellum five-term U.S. Congressman from Missouri.

United States foreign policy in the Middle East has its roots in the 19th-century Barbary Wars that occurred shortly after the 1776 establishment of the United States as an independent sovereign state, but became much more expansive in the aftermath of World War II. With the goal of preventing the Soviet Union from gaining influence in the region during the Cold War, American foreign policy saw the deliverance of extensive support in various forms to anti-communist and anti-Soviet regimes; among the top priorities for the U.S. with regards to this goal was its support for the State of Israel against its Soviet-backed neighbouring Arab countries during the peak of the Arab–Israeli conflict. The U.S. also came to replace the United Kingdom as the main security patron for Saudi Arabia as well as the other Arab states of the Persian Gulf in the 1960s and 1970s in order to ensure, among other goals, a stable flow of oil from the Persian Gulf. As of 2023, the U.S. has diplomatic relations with every country in the Middle East except for Iran, with whom relations were severed after the 1979 Islamic Revolution, and Syria, with whom relations were suspended in 2012 following the outbreak of the Syrian Civil War.

Wolfgang G. Schwanitz is a German-American Middle East historian. He is a specialist in comparative studies of modern international relations between the United States, the Middle East, and Europe. Schwanitz is known for his research on relations between Arabs, Jews, and Germans, and on the history of German relations with the Middle East.

Edward Wadie Said was a Palestinian American professor of literature at Columbia University, a public intellectual, and a founder of the academic field of postcolonial studies. Born in Mandatory Palestine, he was a citizen of the United States by way of his father, a U.S. Army veteran.

Thomas Campbell Clark was an American lawyer who served as the 59th United States Attorney General from 1945 to 1949 and as Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1949 to 1967.

Since the 19th century, the United States government has participated and interfered, both overtly and covertly, in the replacement of many foreign governments. In the latter half of the 19th century, the U.S. government initiated actions for regime change mainly in Latin America and the southwest Pacific, including the Spanish–American and Philippine–American wars. At the onset of the 20th century, the United States shaped or installed governments in many countries around the world, including neighbors Panama, Honduras, Nicaragua, Mexico, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic.
Steven Fred Lawson is a noted historian of the Civil Rights Movement in the United States. Born in the Bronx, New York, he is the son of Ceil Parker Lawson, a housewife, and Murray Lawson, a retail hardware clerk. He had a sister, Lona Lawson Mirchin, who died in 2004. After teaching at various colleges and universities for forty years, he is now retired, works as an independent scholar, and shares a home in New Jersey with his wife Nancy A. Hewitt and their miniature poodle, Scooter.
After 1780, the United States began relations with North African countries and with the Ottoman Empire.