This article does not cite any sources .(October 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Doume | |
|---|---|
| Country | |
| Province | Ogooué-Lolo |
| Department | Mouloundou |
Doume is a small town in central Gabon.
This article does not cite any sources .(October 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Doume | |
|---|---|
| Country | |
| Province | Ogooué-Lolo |
| Department | Mouloundou |
Doume is a small town in central Gabon.
It has a small station on the Trans-Gabon Railway.

Gabon, officially the Gabonese Republic, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, Gabon is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo on the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of nearly 270,000 square kilometres (100,000 sq mi) and its population is estimated at 2 million people. Its capital and largest city is Libreville.
Little is known of the history of Gabon prior to European contact. Bantu migrants settled the area beginning in the 14th century. Portuguese explorers and traders arrived in the area in the late 15th century. The coast subsequently became a center of the slave trade with Dutch, English, and French traders arriving in the 16th century. In 1839 and 1841, France established a protectorate over the coast.

Gabon enjoys a per capita income four times that of most nations of sub-Saharan Africa, its reliance on resource extraction industry releasing much of the population from extreme poverty.

The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean between Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian is in the gulf.

The mandrill is a primate of the Old World monkey (Cercopithecidae) family. It is one of two species assigned to the genus Mandrillus, along with the drill. Both the mandrill and the drill were once classified as baboons in the genus Papio, but they now have their own genus, Mandrillus. Although they look superficially like baboons, they are more closely related to Cercocebus mangabeys. Mandrills are found in southern Cameroon, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, and Congo. Mandrills mostly live in tropical rainforests. They live in very large groups. Mandrills have an omnivorous diet consisting mostly of fruits and insects. Their mating season peaks in July to September, with a corresponding birth peak in December to April.

The African palm civet, also known as the two-spotted palm civet, is a small feliform mammal widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.

The Gabon national football team, nicknamed Les Panthères or Les Brésiliens, is the national team of Gabon and is controlled by the Gabonese Football Federation. They have never qualified for the World Cup, but have qualified seven times for the Africa Cup of Nations.
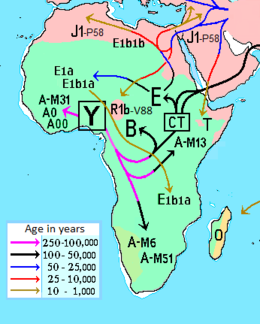
Haplogroup B (B-M60) is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup common to paternal lineages in Africa. It is a primary branch of the haplogroup BT.

The Ngounié River is a river flowing through southwest-central Gabon. It is the last and second most important tributary of the Ogooué River, the first being the Ivindo River. It initially flows down from the Chaillu Mountains, along the border with Congo, and then turns northwest, flowing through the towns of Fougamou, Sindara and Mouila before flowing into the Ogooué.

The Central African oyan, also called Central African linsang, is a linsang species native to Central Africa.

The Benito roundleaf bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae found in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, and Togo. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The Gabon talapoin, also known as the northern talapoin, is a small species of African monkey in the family Cercopithecidae. It is found in riparian habitats in Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and western Republic of the Congo and far western Democratic Republic of Congo. It may have been introduced to Fernando Poo and the Canary Islands. Unlike the related Angolan talapoin, the Gabon talapoin has flesh-coloured ears and facial skin.

Mayoko District is a district in the Niari Department of south-western Republic of the Congo. The capital lies at Mayoko. It has a northern border with Gabon. As of 2007, the population is 5,147.

Komo-Mondah is a department of Estuaire Province in western Gabon. The capital lies at Ntoum.

Sebe-Brikolo is a department of Haut-Ogooué Province in eastern Gabon. The capital lies at Okondja.

Bendje is a department of Ogooué-Maritime Province in western Gabon. The capital lies at Port-Gentil.

Haut-Komo is a department of Woleu-Ntem Province in northern Gabon. The capital lies at Ndindi. The department borders with Equatorial Guinea.

Okano is a department of Woleu-Ntem Province in northern Gabon. The capital lies at Mitzic.
Elections to the French National Assembly were held in Gabon and Moyen Congo as part of the wider French elections election on 10 November 1946.
The Stade de Port-Gentil is a stadium in Port-Gentil, Gabon. This 20,000 capacity stadium opened in time for its use in the 2017 Africa Cup of Nations.
Coordinates: 0°50′47″S12°57′47″E / 0.8464212°S 12.96300°E

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.
| This Gabon location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |