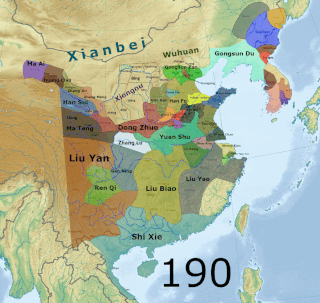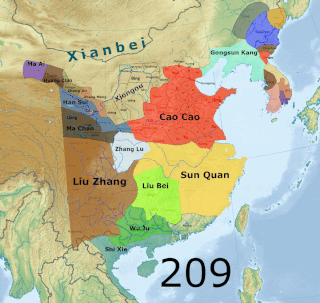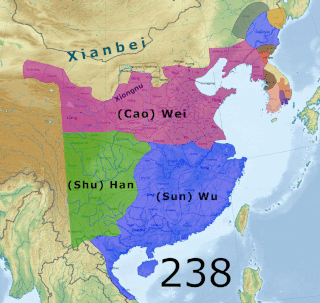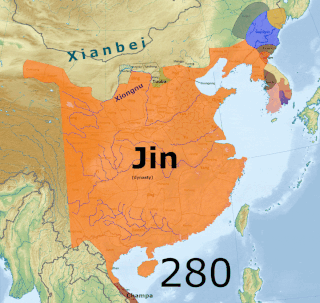
The Three Kingdoms of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu dominated China from 220 to 280 AD following the end of the Han dynasty. This period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and followed by the Western Jin dynasty. Academically, the periodisation begins with the establishment of Cao Wei in 220 and ends with the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280. The period immediately preceding the Three Kingdoms from 184 to 220 was marked by chaotic infighting among warlords across China as Han authority collapsed. The period from 220 to 263 was marked by a comparatively stable arrangement between Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. This stability broke down with the conquest of Shu by Wei in 263, followed by the usurpation of Cao Wei by Jin in 266, and ultimately the conquest of Wu by Jin in 280.

Throughout Chinese history, "Emperor" was the superlative title held by the monarchs who ruled various imperial dynasties or Chinese empires. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was the "Son of Heaven", an autocrat with the divine mandate right to rule all under Heaven. Emperors were worshiped posthumously under an imperial cult. The lineage of emperors descended from a paternal family line constituted a dynasty, and succession in most cases theoretically followed agnatic primogeniture.

Romance of the Three Kingdoms is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD and ending with the reunification of the land in 280 by the Western Jin. The novel is based primarily on the Records of the Three Kingdoms, written by Chen Shou in the 3rd century.

Emperor Xiaowen of Northern Wei ( 魏孝文帝), personal name né Tuoba Hong (拓拔宏), later Yuan Hong (元宏), was an emperor of China's Northern Wei dynasty, reigning from September 20, 471 to April 26, 499.

He Jin, courtesy name Suigao, was a Chinese military general and politician. He was the military Grand Marshal and regent of the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was an elder half-brother of Empress He, and a maternal uncle of Emperor Shao. In 189, he and his sister shared power as regents when the young Emperor Shao was put on the throne following Emperor Ling's death. During the time, the conflict between He Jin and the influential eunuch faction intensified. After they overheard a conversation between He Jin and the empress dowager, the eunuch faction lured him into a trap in the imperial palace and assassinated him. While He Jin's subordinates, led by the warlord Yuan Shao, slaughtered the eunuch faction in revenge, the warlord Dong Zhuo took advantage of the power vacuum to enter the imperial capital Luoyang and seize control of the Han central government. Dong Zhuo's seizure of control and the subsequent breakdown of central command that followed brought forth the beginning of massive civil wars that lasted for nearly a century, during which time the Han dynasty came to an end and the Three Kingdoms period began in its place.

Zaifeng, also known as Tsai Feng, Prince of Ch'ün, formally known by his title Prince Chun, was a Manchu prince and regent of the late Qing dynasty. He was a son of Yixuan, the seventh son of the Daoguang Emperor, and the father of Puyi, the Last Emperor. He served as prince regent from 1908 to 1911 during the reign of his son until the Qing dynasty was overthrown by the Xinhai Revolution in 1911.

Emperor Gong of Song, personal name Zhao Xian, was the 16th emperor of the Song dynasty of China and the seventh emperor of the Southern Song dynasty. The sixth son of his predecessor, Emperor Duzong, Zhao Xian came to the throne around the age of four, and reigned for less than two years before he was forced to abdicate in 1276. He was succeeded by his fifth brother, Zhao Shi.

The end of the Han dynasty was the period of Chinese history from 189 to 220 CE, roughly coinciding with the tumultuous reign of the Han dynasty's last ruler, Emperor Xian. It was followed by the Three Kingdoms era. During the end of the Han dynasty, the country was thrown into turmoil by the Yellow Turban Rebellion (184–205). Meanwhile, the Han Empire's institutions were destroyed by the warlord Dong Zhuo and fractured into regional regimes ruled by various warlords, some of whom were nobles and officials of the Han imperial court. The warlord Cao Cao took control of Emperor Xian and his court in 196 and began gradually reunifying the empire. Cao Cao ostensibly operated under Emperor Xian's rule, though in reality the emperor was a hostage.

The Heirloom Seal of the Realm, also known in English as the Imperial Seal of China, was a Chinese jade seal allegedly carved out of the Heshibi, a sacred piece of jade. The Seal was created in 221 BC, shortly after Qin Shi Huang unified China and established the Qin dynasty, China's first imperial dynasty. The Heirloom Seal served as the imperial Chinese seal throughout the next millennium of Chinese history, and its possession was seen as a physical symbol of the Mandate of Heaven.

Liu Cong (died 31 August 318), courtesy name Xuanming, nickname Zai, also known by his posthumous name as the Emperor Zhaowu of Han (Zhao), was an emperor of the Xiongnu-led Chinese Han-Zhao dynasty. He captured the Emperor Huai of Jin and the Emperor Min of Jin, and executed them back in Pingyang after forcing them to act as cupbearers. These raids finally forced the Jin dynasty to move its capital from Luoyang to Nanjing.

Wang Dao, courtesy name Maohong (茂弘), formally Duke Wenxian of Shixing (始興文獻公), was a Chinese politician during the Jin dynasty who played an important role in the administrations of Emperor Yuan, Emperor Ming, and Emperor Cheng, including as Emperor Cheng's regent. In these capacities, he served as a crucial governing figure of the Eastern Jin Dynasty during its first decades, as well as the leading member of the prominent Wang clan of Langya. His governance style was to be lenient with the laws, and he handed out few punishments—which stabilized the Jin regime greatly, but which also led to extensive, if moderate, corruption and incompetence in the Jin regime, making it difficult for Jin armies to recapture northern China.
Yu Liang, courtesy name Yuangui (元規), formally Marquess Wenkang of Duting (都亭文康侯), was a Chinese military general and politician of the Jin dynasty who impressed many with his knowledge but whose inability to tolerate dissent and overly high evaluation of his own abilities led to the disastrous revolt of Su Jun, weakening Jin's military capability for years.
Emperor Xiaoming of (Northern) Wei ( 魏孝明帝), personal name Yuan Xu (元詡), was an emperor of the Xianbei-led Chinese Northern Wei dynasty. He ascended the throne in 515 at the age of five, and governmental matters were dominated by his mother Empress Dowager Hu. In 528, Emperor Xiaoming tried to curb his mother's powers and kill her lover Zheng Yan (鄭儼) by conspiring with the general Erzhu Rong. As a result, the 18-year-old emperor was poisoned by his mother, who was soon overthrown by Erzhu. From that point on, Northern Wei royal lineage had no actual power. The next ruler, Emperor Xiaozhuang (507–531) was established by Erzhu. Since Erzhu's rival, general Gao Huan, enthroned another royal offspring, the country was soon split in two rival polities, Eastern and Western Wei, both of which did not hold long on the political map of the Southern and Northern Dynasties.

Emperor Xiaozhuang of Northern Wei, personal name Yuan Ziyou, courtesy name Yanda (彥達), was an emperor of China's Northern Wei dynasty. He was placed on the throne by General Erzhu Rong, who refused to recognize the young emperor, Yuan Zhao, who Empress Dowager Hu had placed on the throne after she poisoned her son Emperor Xiaoming.
Yuan Hao (元顥), courtesy name Ziming (子明) was an imperial prince and pretender to the throne of the Chinese/Xianbei dynasty Northern Wei, who briefly received allegiance from most of the provinces south of the Yellow River after he captured the capital Luoyang with support of neighboring Liang dynasty. He became complacent after capturing Luoyang, however, and when the general Erzhu Rong, who supported Emperor Xiaozhuang, counterattacked later that year, Yuan Hao fled Luoyang and was killed in flight.
Yuan Qin, known in historiography as Emperor Fei of Western Wei, was an emperor of China's Xianbei-led Western Wei dynasty. He, even more so than his father Emperor Wen, held little actual power in the face of overwhelming control of power by the paramount general Yuwen Tai. In 554, he tried to plot to have Yuwen killed, but his plot was discovered, and Yuwen deposed him, and soon had him killed.
Empress Yuan was an empress of the Chinese Northern Qi dynasty. known at times semi-formally as Empress Shuncheng (順成皇后). Her husband was Emperor Xiaozhao.
Shulü Ping, nickname Yueliduo (月里朵), formally Empress Yingtian also known as Empress Di (地皇后) during the reign of her husband Emperor Taizu of Liao, posthumous name initially EmpressZhenlie then Empress Chunqin was an empress of the Khitan-led Liao dynasty of China. After Emperor Taizu's death in 926, she served as empress dowager until her death in 953. She was directly involved in two imperial successions and is credited with changing expectations of widows in Khitan society.
Empress Yuan, personal name unknown, was briefly an emperor of the Xianbei-led Chinese Northern Wei dynasty. She bore the surname Yuan, originally Tuoba. Yuan was the only child of Emperor Xiaoming, born to his concubine Consort Pan. Soon after her birth, her grandmother the Empress Dowager Hu, who was also Xiaoming's regent, falsely declared that she was a boy and ordered a general pardon. Emperor Xiaoming died soon afterwards. On 1 April 528, Empress Dowager Hu installed the infant on the throne for a matter of hours before replacing her with Yuan Zhao the next day. Emperor Xiaoming's daughter was not recognised as a legitimate emperor (huangdi) by later generations. No further information about her or her mother is available.

Cao Cao is a Chinese television series based on the life of Cao Cao, a warlord who rose to power towards the end of the Eastern Han dynasty and laid the foundation for the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period. Directed by Hu Mei, the series aimed to portray a more historically accurate image of Cao Cao, who is traditionally depicted as a villain in Chinese culture. Starring Zhao Lixin as the eponymous character, the series was filmed at the Xiangshan Film City in Ningbo, Zhejiang between 1 November 2011 and 15 March 2012.












