
Justus Freiherr von Liebig was a German scientist who made major contributions to the theory, practice, and pedagogy of chemistry, as well as to agricultural and biological chemistry; he is considered one of the principal founders of organic chemistry. As a professor at the University of Giessen, he devised the modern laboratory-oriented teaching method, and for such innovations, he is regarded as one of the most outstanding chemistry teachers of all time. He has been described as the "father of the fertilizer industry" for his emphasis on nitrogen and minerals as essential plant nutrients, and his popularization of the law of the minimum, which states that plant growth is limited by the scarcest nutrient resource, rather than the total amount of resources available. He also developed a manufacturing process for beef extracts, and with his consent a company, called Liebig Extract of Meat Company, was founded to exploit the concept; it later introduced the Oxo brand beef bouillon cube. He popularized an earlier invention for condensing vapors, which came to be known as the Liebig condenser.

A Petri dish is a shallow transparent lidded dish that biologists use to hold growth medium in which cells can be cultured, originally, cells of bacteria, fungi and small mosses. The container is named after its inventor, German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri. It is the most common type of culture plate. The Petri dish is one of the most common items in biology laboratories and has entered popular culture. The term is sometimes written in lower case, especially in non-technical literature.

Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engineering is the field dedicated to controlling and preventing corrosion.

August Wilhelm von Hofmann was a German chemist who made considerable contributions to organic chemistry. His research on aniline helped lay the basis of the aniline-dye industry, and his research on coal tar laid the groundwork for his student Charles Mansfield's practical methods for extracting benzene and toluene and converting them into nitro compounds and amines. Hofmann's discoveries include formaldehyde, hydrazobenzene, the isonitriles, and allyl alcohol. He prepared three ethylamines and tetraethylammonium compounds and established their structural relationship to ammonia.
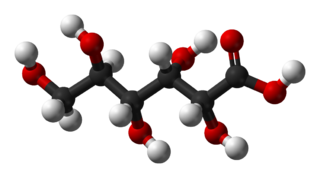
Gluconic acid is an organic compound with molecular formula C6H12O7 and condensed structural formula HOCH2(CHOH)4CO2H. A white solid, it forms the gluconate anion in neutral aqueous solution. The salts of gluconic acid are known as "gluconates". Gluconic acid, gluconate salts, and gluconate esters occur widely in nature because such species arise from the oxidation of glucose. Some drugs are injected in the form of gluconates.
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the general subject of organic synthesis, there are many different types of synthetic routes that can be completed including total synthesis, stereoselective synthesis, automated synthesis, and many more. Additionally, in understanding organic synthesis it is necessary to be familiar with the methodology, techniques, and applications of the subject.

In chemistry, the CPK coloring is a popular color convention for distinguishing atoms of different chemical elements in molecular models.

The Kunstakademie Düsseldorf is the academy of fine arts of the state of North Rhine Westphalia at the city of Düsseldorf, Germany. Notable artists who studied or taught at the academy include Joseph Beuys, Gerhard Richter, Magdalena Jetelová, Gotthard Graubner, Nam June Paik, Nan Hoover, Katharina Fritsch, Tony Cragg, Ruth Rogers-Altmann, Sigmar Polke, Anselm Kiefer, Rosemarie Trockel, Thomas Schütte, Katharina Grosse, Michael Krebber and photographers Thomas Ruff, Thomas Demand, Christopher Williams, Thomas Struth, Andreas Gursky and Candida Höfer. In the stairway of its main entrance are engraved the Words: "Für unsere Studenten nur das Beste".

The Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize, or Leibniz Prize, is awarded by the German Research Foundation to "exceptional scientists and academics for their outstanding achievements in the field of research". Since 1986, up to ten prizes have been awarded annually to individuals or research groups working at a research institution in Germany or at a German research institution abroad. It is considered the most important research award in Germany.

In chemistry, a condenser is laboratory apparatus used to condense vapors – that is, turn them into liquids – by cooling them down.

Underground is a 1941 American war thriller film directed by Vincent Sherman and starring Jeffrey Lynn, Philip Dorn and Kaaren Verne. Focusing on the German Nazi Resistance opposing the Nazis in World War II, Lynn and Dorn play two brothers initially on opposite sides. It was produced and distributed by Warner Brothers.

The Villa Romana Prize, German: Villa-Romana-Preis, is an art prize awarded by the Deutscher Künstlerbund. It was established in 1905 and is the oldest German art award. The prize consists of a one-year artistic residence in the Villa Romana, a nineteenth-century villa on the Via Senese in the southern outskirts of Florence, in Tuscany in central Italy.

Hermann Levinson was a German biologist and physiologist. He lived with his wife Anna Levinson in Starnberg and has worked at the Max Planck Institute for Behavioral Physiology since 1971, and at the Max Planck Institute for Ornithology since 2004, in Seewiesen and Erling.

Copper(II) carbonate or cupric carbonate is a chemical compound with formula CuCO
3. At ambient temperatures, it is an ionic solid consisting of copper(II) cations Cu2+
and carbonate anions CO2−
3.

In microbiology, a cell spreader or plate spreader is a tool used to smoothly spread cells and bacteria on a culture plate, such as a petri dish.

A Babcock bottle is a clear glass flask with a long graduated neck, used in the Babcock test to evaluate the cream contents of milk. It is also called a Babcock milk test bottle, milk test bottle, cream test bottle, and other similar names.
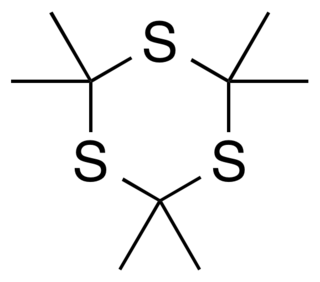
Trithioacetone (2,2,4,4,6,6-hexamethyl-1,3,5-trithiane) is an organic chemical with formula C
9H
18S
3. Its covalent structure is [–C(CH
3)
2–S–]
3, that is, a six-membered ring of alternating carbon and sulfur atoms, with two methyl groups attached to each carbon. It can be viewed as a derivative of 1,3,5-trithiane, with methyl-group substituents for all of the hydrogen atoms in that parent structure.

The Hütte - Das Ingenieurwissen is a reference work for engineers of various disciplines. It was compiled for the first time in 1857 by the Akademischer Verein Hütte of the Königliches Gewerbe-Institut in Berlin, from which the association of German engineers Verein Deutscher Ingenieure (VDI) emerged. The authors were members of the association. The technical illustrations were created in woodcut technique by Otto Ebel. It is published in constantly revised editions to this day and is therefore the oldest German reference work still available today.


















