
Oliver Cromwell was an English statesman, politician, and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in the history of the British Isles. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially as a senior commander in the Parliamentarian army and latterly as a politician. A leading advocate of the execution of Charles I in January 1649, which led to the establishment of The Protectorate, he ruled as Lord Protector from December 1653 until his death in September 1658. Cromwell remains a controversial figure due to his use of the army to acquire political power, and the brutality of his 1649 campaign in Ireland.

Thomas Carlyle was a Scottish essayist, historian, and philosopher from the Scottish Lowlands. A leading writer of the Victorian era, he exerted a profound influence on 19th-century art, literature, and philosophy.

The Rump Parliament was the English Parliament after Colonel Thomas Pride commanded soldiers to purge the Long Parliament, on 6 December 1648, of those members hostile to the Grandees' intention to try King Charles I for high treason.

Colonel Thomas Pride was a Parliamentarian commander during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, best known as one of the regicides of Charles I and as the instigator of Pride's Purge.

Sir Oliver St John was an English judge and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1640-53. He supported the Parliamentary cause in the English Civil War.

Henry Cromwell was the fourth son of Oliver Cromwell and Elizabeth Bourchier, and an important figure in the Parliamentarian regime in Ireland.

Sir Edmund Verney was an English politician, soldier and favourite of King Charles I. At the outbreak of the English Civil War he supported the Royalist cause and was killed at the Battle of Edgehill.

The Haunted Bookshop is a 1919 novel by Christopher Morley, now in the public domain in the United States. It has remained a popular representative of the "bibliomystery," a mystery story set in the world of books.

Past and Present is a book by the Scottish essayist, historian and philosopher Thomas Carlyle. It was published in April 1843 in England and the following month in the United States. It combines medieval history with criticism of 19th-century British society. Carlyle wrote it in seven weeks as a respite from the harassing labor of writing Oliver Cromwell's Letters and Speeches. He was inspired by the recently published Chronicles of the Abbey of Saint Edmund's Bury, which had been written by Jocelin of Brakelond at the close of the 12th century. This account of a medieval monastery had taken Carlyle's fancy, and he drew upon it in order to contrast the monks' reverence for work and heroism with the sham leadership of his own day.

Cromwell, Protector of the Vaudois (1877) is a painting by Ford Madox Brown which depicts Oliver Cromwell in conversation with John Milton dictating a letter to Andrew Marvell protesting at the Piedmontese Easter massacre (1655), an attack on the Vaudois (Waldenses), a persecuted Protestant sect in Piedmont, northern Italy. It was Brown's second Cromwell painting, following Cromwell on his Farm (1875).

Cromwell on his Farm (1874) is a painting by Ford Madox Brown which depicts Oliver Cromwell observing a bonfire on his farm and thinking of a passage in the Book of Psalms: "Lord, how long wilt thou hide thyself - forever? And shall thy wrath burn like fire?". The words are inscribed on the painting's frame along with a quotation from one of Cromwell's speeches, in which he describes his life before entering into politics: "living neither in any considerable height, nor yet in obscurity, I did endeavour to discharge the duty of an honest man."

History of Friedrich II. of Prussia, Called Frederick the Great is a biography of Friedrich II of Prussia by Scottish essayist, historian and philosopher Thomas Carlyle. It was first published in six volumes from 1858 to 1865.

Lieutenant-Colonel George Joyce was an officer and Agitator in the Parliamentary New Model Army during the English Civil War.

John Claypole was an officer in the Parliamentary army in 1645 during the English Civil War. He was created Lord Claypole by Oliver Cromwell, but this title was not recognised after the Restoration of 1660.

A tenaille is an advanced defensive-work, in front of the main defences of a fortress, which takes its name from resemblance to the lip of a pair of pincers. It is "from French, literally: tongs, from Late Latin tenācula, pl of tenaculum".
Thomas Kitson Cromwell (1792–1870) was an English dissenting minister and antiquary.

Mark Noble (1754–1827) was an English clergyman, biographer and antiquary.
A statue of Oliver Cromwell stands on Market Hill in St Ives, Cambridgeshire, England. It is a sculpture of Oliver Cromwell, Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland. The statue was designed by F. W. Pomeroy and erected in 1901. The statue is one of five public statues of Cromwell in the United Kingdom and is Grade II listed for its architectural merit.
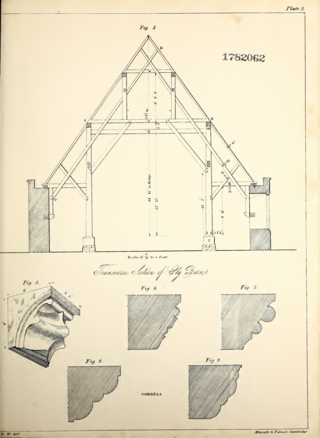
The Sextry Barn was a 13th-century tithe barn in Ely, Cambridgeshire, England. It was one of the largest medieval barns in Europe, and was demolished in 1842. It was used to store the corn tithes due to Ely Cathedral, and took its name from the sacrist of the monastery who was in charge of it.

Oliver Cromwell's Letters and Speeches: with Elucidations is a book by the Scottish essayist, historian and philosopher Thomas Carlyle. It "remains one of the most important works of British history published in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries."
















