
The Common Desktop Environment (CDE) is a desktop environment for Unix and OpenVMS, based on the Motif widget toolkit. It was part of the UNIX 98 Workstation Product Standard, and was for a long time the Unix desktop associated with commercial Unix workstations. It helped to influence early implementations of successor projects such as KDE and GNOME desktop environment, which largely replaced CDE following the turn of the century.

Cygwin is a POSIX-compatible programming and runtime environment that runs natively on Microsoft Windows. Under Cygwin, source code designed for Unix-like operating systems may be compiled with minimal modification and executed.

The X Window System is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphical shell. The desktop environment was seen mostly on personal computers until the rise of mobile computing. Desktop GUIs help the user to easily access and edit files, while they usually do not provide access to all of the features found in the underlying operating system. Instead, the traditional command-line interface (CLI) is still used when full control over the operating system is required.

An X window manager is a window manager that runs on top of the X Window System, a windowing system mainly used on Unix-like systems.

Xfce or XFCE is a free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.
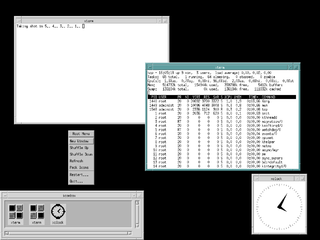
In computing, Motif refers to both a graphical user interface (GUI) specification and the widget toolkit for building applications that follow that specification under the X Window System on Unix and Unix-like operating systems. The Motif look and feel is distinguished by its use of rudimentary square and chiseled three-dimensional effects for its various user interface elements.

OPEN LOOK is a graphical user interface (GUI) specification for UNIX workstations. It was originally defined in the late 1980s by Sun Microsystems and AT&T Corporation.

Window Maker is a free and open-source window manager for the X Window System, allowing graphical applications to be run on Unix-like operating-systems. It is designed to emulate NeXTSTEP's GUI as an OpenStep-compatible environment. Window Maker is part of the GNU Project.

Visual User Environment is a discontinued desktop environment developed by Hewlett-Packard, intended for use on Unix workstations. VUE is based on the Motif widget toolkit and targets the X Window System.
In computing, the X Window System is a network-transparent windowing system for bitmap displays. This article details the protocols and technical structure of X11.

In the X Window System, an X display manager is a graphical login manager which starts a login session on an X server from the same or another computer.
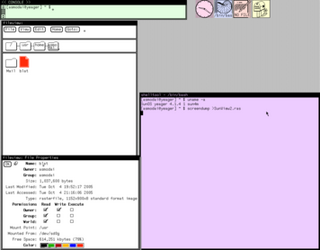
SunView is a discontinued windowing system from Sun Microsystems developed in the early 1980s. It was included as part of SunOS, Sun's UNIX implementation; unlike later UNIX windowing systems, much of it was implemented in the system kernel. SunView ran on Sun's desktop and deskside workstations, providing an interactive graphical environment for technical computing, document publishing, medical, and other applications of the 1980s, on high resolution monochrome, greyscale and color displays.

OpenWindows is a discontinued desktop environment for Sun Microsystems workstations which combined SunView, NeWS, and X Window System protocols. OpenWindows was included in later releases of the SunOS 4 and Solaris operating systems, until its removal in Solaris 9 in favor of Common Desktop Environment (CDE) and GNOME 2.0.

In computing, a virtual desktop is a term used with respect to user interfaces, usually within the WIMP paradigm, to describe ways in which the virtual space of a computer's desktop environment is expanded beyond the physical limits of the screen's display area through the use of software. This compensates limits of the desktop area and is helpful in reducing clutter of running graphical applications.

IRIX Interactive Desktop is a desktop environment normally used as the default desktop on Silicon Graphics workstations running IRIX. The IRIX Interactive Desktop uses the Motif widget toolkit on top of the X Window System found on most Unix systems. The default window manager on the IRIX Interactive Desktop is 4Dwm.

In computing, a tiling window manager is a window manager with an organization of the screen into mutually non-overlapping frames, as opposed to the more common approach of coordinate-based stacking of overlapping objects (windows) that tries to fully emulate the desktop metaphor.
A desktop environment is a collection of software designed to give functionality and a certain look and feel to an operating system.

i3 is a tiling window manager designed for X11, inspired by wmii and written in C. It supports tiling, stacking, and tabbing layouts, which it handles dynamically. Its configuration is achieved via a plain text file and extending i3 is possible using its Unix domain socket and JSON based IPC interface from many programming languages.
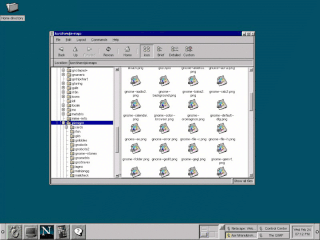
GNOME 1 is the first major release of the GNOME desktop environment. Its primary goal was to provide a consistent user-friendly environment in conjunction with the X Window System. It was also a modern and free and open source software alternative to older desktop environments such as the Common Desktop Environment (CDE), but also to the K Desktop Environment (KDE). Each desktop environment was built-upon then proprietary-licensed widget toolkits, whereas GNOME's goal from the onset, was to be freely-licensed, and utilize the GTK toolkit instead.

















