
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels. The term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture. A colloid has a dispersed phase and a continuous phase. The dispersed phase particles have a diameter of approximately 1 nanometre to 1 micrometre.

Electrophoresis, from Ancient Greek ἤλεκτρον and φόρησις, is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. Electrophoresis of positively charged particles (cations) is sometimes called cataphoresis, while electrophoresis of negatively charged particles (anions) is sometimes called anaphoresis.
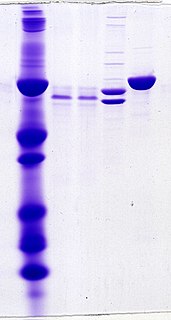
Protein electrophoresis is a method for analysing the proteins in a fluid or an extract. The electrophoresis may be performed with a small volume of sample in a number of alternative ways with or without a supporting medium: SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, free-flow electrophoresis, electrofocusing, isotachophoresis, affinity electrophoresis, immunoelectrophoresis, counterelectrophoresis, and capillary electrophoresis. Each method has many variations with individual advantages and limitations. Gel electrophoresis is often performed in combination with electroblotting immunoblotting to give additional information about a specific protein. Because of practical limitations, protein electrophoresis is generally not suited as a preparative method.
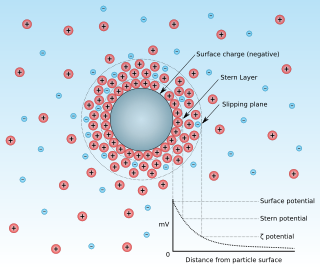
Zeta potential is the electrical potential at the slipping plane. This plane is the interface which separates mobile fluid from fluid that remains attached to the surface.
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a family of electrokinetic separation methods performed in submillimeter diameter capillaries and in micro- and nanofluidic channels. Very often, CE refers to capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE), but other electrophoretic techniques including capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE), capillary isoelectric focusing (CIEF), capillary isotachophoresis and micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC) belong also to this class of methods. In CE methods, analytes migrate through electrolyte solutions under the influence of an electric field. Analytes can be separated according to ionic mobility and/or partitioning into an alternate phase via non-covalent interactions. Additionally, analytes may be concentrated or "focused" by means of gradients in conductivity and pH.
Electrophoresis is the motion of dispersed particles relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field.
Dr George B. Johnson is a science educator who for many years has written a weekly column "On Science" in the St. Louis Post-Dispatch. For over 30 years he was a biology professor at Washington University and a genetics professor at their school of medicine. He has authored 44 scientific papers and ten high school and college widely used biology texts. Over 3 million students have learned biology from these texts.
High-Mobility Group or HMG is a group of chromosomal proteins that are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair.
Radio resource management (RRM) is the system level management of co-channel interference, radio resources, and other radio transmission characteristics in wireless communication systems, for example cellular networks, wireless local area networks, wireless sensor systems, and radio broadcasting networks. RRM involves strategies and algorithms for controlling parameters such as transmit power, user allocation, beamforming, data rates, handover criteria, modulation scheme, error coding scheme, etc. The objective is to utilize the limited radio-frequency spectrum resources and radio network infrastructure as efficiently as possible.
Electroacoustic phenomena arise when ultrasound propagates through a fluid containing ions. The associated particle motion generates electric signals because ions have electric charge. This coupling between ultrasound and electric field is called electroacoustic phenomena. The fluid might be a simple Newtonian liquid, or complex heterogeneous dispersion, emulsion or even a porous body. There are several different electroacoustic effects depending on the nature of the fluid.
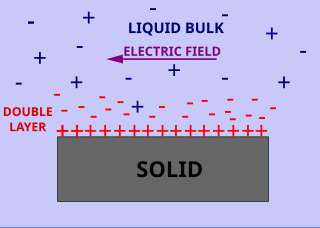
Surface conductivity is an additional conductivity of an electrolyte in the vicinity of the charged interfaces. Surface and volume conductivity of liquids correspond to the electrically driven motion of ions in an electric field. A layer of counter ions of the opposite polarity to the surface charge exists close to the interface. It is formed due to attraction of counter-ions by the surface charges. This layer of higher ionic concentration is a part of the interfacial double layer. The concentration of the ions in this layer is higher as compared to the ionic strength of the liquid bulk. This leads to the higher electric conductivity of this layer.
Electrophoretic light scattering is based on dynamic light scattering. The frequency shift or phase shift of an incident laser beam depends on the dispersed particles mobility. With dynamic light scattering, Brownian motion causes particle motion. With electrophoretic light scattering, oscillating electric field performs this function.

Zeta potential titration is a titration of heterogeneous systems, for example colloids and emulsions. Solids in such systems have very high surface area. This type of titration is used to study the zeta potential of these surfaces under different conditions. Details of zeta potential definition and measuring techniques can be found in the International Standard.
John Texter is an American engineer, chemist, and educator. He is professor emeritus of polymer and coating technology at Eastern Michigan University (EMU) in Ypsilanti, Michigan, and managing consultant of Strider Research Corporation (SRC). He is best known for his work in applied dispersion technology, small particle science, and stimuli-responsive polymers based on ionic liquids, for his international conference organization activities, including Particles 2001, Particles 2002, etc., and the Gordon Research Conferences, Chemistry at Interfaces and Chemistry of Supramolecules and Assemblies, and for his editing of the Primers page for nanoparticles.org.
Colloid-facilitated transport designates a transport process by which colloidal particles serve as transport vector of diverse contaminants in the surface water and in underground water circulating in fissured rocks (limestone, sandstone, granite, ...). The transport of colloidal particles in surface soils and in the ground can also occur, depending on the soil structure, soil compaction, and the particles size, but the importance of colloidal transport was only given sufficient attention during the 1980 years. Radionuclides, heavy metals, and organic pollutants, easily sorb onto colloids suspended in water and that can easily act as contaminant carrier.

Affinity electrophoresis is a general name for many analytical methods used in biochemistry and biotechnology. Both qualitative and quantitative information may be obtained through affinity electrophoresis. The methods include the so-called electrophoretic mobility shift assay, charge shift electrophoresis and affinity capillary electrophoresis. The methods are based on changes in the electrophoretic pattern of molecules through biospecific interaction or complex formation. The interaction or binding of a molecule, charged or uncharged, will normally change the electrophoretic properties of a molecule. Membrane proteins may be identified by a shift in mobility induced by a charged detergent. Nucleic acids or nucleic acid fragments may be characterized by their affinity to other molecules. The methods have been used for estimation of binding constants, as for instance in lectin affinity electrophoresis or characterization of molecules with specific features like glycan content or ligand binding. For enzymes and other ligand-binding proteins, one-dimensional electrophoresis similar to counter electrophoresis or to "rocket immunoelectrophoresis", affinity electrophoresis may be used as an alternative quantification of the protein. Some of the methods are similar to affinity chromatography by use of immobilized ligands.
Electrofiltration is a method that combines membrane filtration and electrophoresis in a dead-end process.
Brookhaven Instruments Corporation is a Nova Instruments company established in the late 1960s. Brookhaven Instruments designed modern techniques in characterizing nanoparticles, proteins, and polymers using light scattering techniques such as dynamic, static, electrophoretic, and phase analysis for: particle size, zeta potential, molecular mass, and absolute molar mass analysis.
Dispersion Technology Inc is a scientific instrument manufacturer located in Bedford Hills, New York. It was founded in 1996 by Philip Goetz and Dr. Andrei Dukhin. The company develops and sells analytical instruments intended for characterizing concentrated dispersions and emulsions, complying with the International Standards for acoustic particle sizing ISO 20998 and Electroacoustic zeta potential measurement ISO 13099.

Synchronous coefficient of drag alteration (SCODA) is a biotechnology method for purifying, separating and/or concentrating bio-molecules. SCODA has the ability to separate molecules whose mobility can be altered in sync with a driving field. This technique has been primarily used for concentrating and purifying DNA, where DNA mobility changes with an applied electrophoretic field. Electrophoretic SCODA has also been demonstrated with RNA and proteins.







