
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics, is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders.
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten or lengthen it or to change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum. The operation is done under a general anaesthetic.

Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant, that is, a hip prosthesis. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total replacement or a hemi (half) replacement. Such joint replacement orthopaedic surgery is generally conducted to relieve arthritis pain or in some hip fractures. A total hip replacement consists of replacing both the acetabulum and the femoral head while hemiarthroplasty generally only replaces the femoral head. Hip replacement is one of the most common orthopaedic operations, though patient satisfaction varies widely. Approximately 58% of total hip replacements are estimated to last 25 years. The average cost of a total hip replacement in 2012 was $40,364 in the United States, and about $7,700 to $12,000 in most European countries.
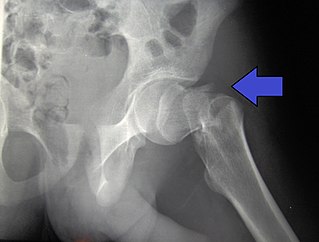
A hip fracture is a break that occurs in the upper part of the femur. Symptoms may include pain around the hip, particularly with movement, and shortening of the leg. Usually the person cannot walk.

In vertebrate anatomy, hip refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.

Slipped capital femoral epiphysis is a medical term referring to a fracture through the growth plate (physis), which results in slippage of the overlying end of the femur (metaphysis).

A dynamic compression plate (DCP) is a metallic plate used in orthopedics for internal fixation of bone, typically after fractures. As the name implies, it is designed to exert dynamic pressure between the bone fragments to be transfixed. Dynamic compression is achieved either by attaching a tension device to a plate or by using a special dynamic compression plate. However, compression plating requires a longer surgical incision to allow insertion of the tension device and the possibility of refracture after the plate is removed. A neutralization plate is used to bridge a comminuted fracture; it also transmits bending or torsional forces from the proximal to the distal fragment. Plates used for buttressing prevent collapse by supporting an area of thin cortex or cancellous bone graft.

Replacement arthroplasty, or joint replacement surgery, is a procedure of orthopedic surgery in which an arthritic or dysfunctional joint surface is replaced with an orthopedic prosthesis. Joint replacement is considered as a treatment when severe joint pain or dysfunction is not alleviated by less-invasive therapies. It is a form of arthroplasty, and is often indicated from various joint diseases, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.

A hip dislocation is when the thighbone (femur) separates from the hip bone (pelvis). Specifically it is when the ball–shaped head of the femur separates from its cup–shaped socket in the hip bone, known as the acetabulum. The joint of the femur and pelvis is very stable, secured by both bony and soft-tissue constraints. With that, dislocation would require significant force which typically results from significant trauma such as from a motor vehicle collision or from a fall from elevation. Hip dislocations can also occur following a hip replacement or from a developmental abnormality known as hip dysplasia.
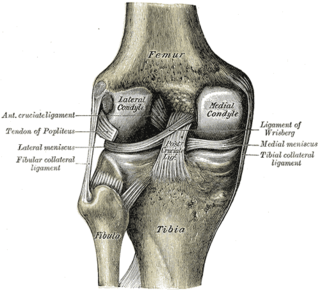
The lateral condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of the femur. The other one is the medial condyle. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is broader both in its front-to-back and transverse diameters.

The intertrochanteric line is a line located on the anterior side of the proximal end of the femur.
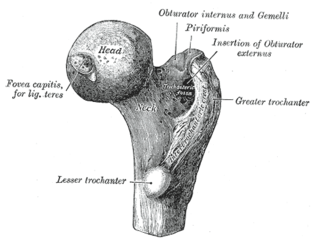
The femoral neck is a flattened pyramidal process of bone, connecting the femoral head with the femoral shaft, and forming with the latter a wide angle opening medialward.

Hip resurfacing has been developed as a surgical alternative to total hip replacement (THR). The procedure consists of placing a cap, which is hollow and shaped like a mushroom, over the head of the femur while a matching metal cup is placed in the acetabulum, replacing the articulating surfaces of the person's hip joint and removing very little bone compared to a THR. When the person moves the hip, the movement of the joint induces synovial fluid to flow between the hard metal bearing surfaces lubricating them when the components are placed in the correct position. The surgeon's level of experience with hip resurfacing is most important; therefore, the selection of the right surgeon is crucial for a successful outcome. Health-related quality of life measures are markedly improved and the person's satisfaction is favorable after hip resurfacing arthroplasty.
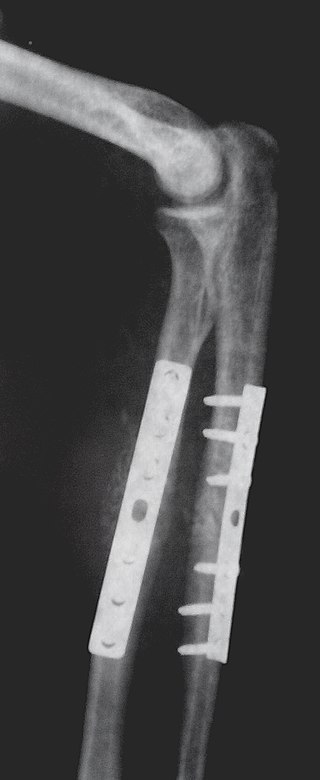
Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-nineteenth century and was made applicable for routine treatment in the mid-twentieth century. An internal fixator may be made of stainless steel, titanium alloy, or cobalt-chrome alloy. or plastics.

A femoral fracture is a bone fracture that involves the femur. They are typically sustained in high-impact trauma, such as car crashes, due to the large amount of force needed to break the bone. Fractures of the diaphysis, or middle of the femur, are managed differently from those at the head, neck, and trochanter.
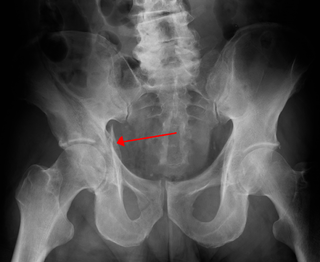
Fractures of the acetabulum occur when the head of the femur is driven into the pelvis. This injury is caused by a blow to either the side or front of the knee and often occurs as a dashboard injury accompanied by a fracture of the femur.

The Garden classification is a system of categorizing intracapsular hip fractures of the femoral neck. This fracture often disrupt the blood supply to the femoral head.
An orthopedic plate is a form of internal fixation used in orthopaedic surgery to hold fractures in place to allow bone healing. Most modern plates include bone screws to help the orthopedic plate stay in place.
Bone malrotation refers to the situation that results when a bone heals out of rotational alignment from another bone, or part of bone. It often occurs as the result of a surgical complication after a fracture where intramedullary nailing (IMN) occurs, especially in the femur and tibial bones, but can also occur genetically at birth. The severity of this complication is often neglected due to its complexity to detect and treat, yet if left untreated, bone malrotation can significantly impact regular bodily functioning, and even lead to severe arthritis. Detection throughout history has become more advanced and accurate, ranging from clinical assessment to ultrasounds to CT scans. Treatment can include an osteotomy, a major surgical procedure where bones are cut and realigned correctly, or compensatory methods, where individuals learn to externally or internally rotate their limb to compensate for the rotation. Further research is currently being examined in this area to reduce occurrences of malrotation, including detailed computer navigation to improve visual accuracy during surgery.

















