
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe. Its members have a combined area of 4,233,255.3 km2 (1,634,469.0 sq mi) and an estimated total population of about 447 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market, enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development. For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished. A monetary union was established in 1999, coming into full force in 2002, and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency.

Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, is one of the four official capitals of the European Union and the seat of the European Court of Justice, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbours, making it essentially a mixture of French and German cultures, as evident by the nation's three official languages: French, German, and the national language of Luxembourgish. The repeated invasions by Germany, especially in World War II, resulted in the country's strong will for mediation between France and Germany and, among other things, led to the foundation of the European Union.

The economy of France is highly developed and free-market-orientated. It is the world's 7th largest economy by 2019 nominal figures and the 10th largest economy by PPP figures. It is the 3rd largest economy in the European Union after Germany and United Kingdom.

Elections to the European Parliament were held between 10 and 13 June 2004 in the 25 member states of the European Union, using varying election days according to local custom. The European Parliamental parties could not be voted for, but elected national parties aggregated in European Parliamental parties after the elections.
The languages of the European Union are languages used by people within the member states of the European Union (EU).
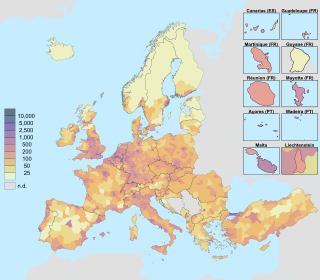
Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics or NUTS is a geocode standard for referencing the subdivisions of countries for statistical purposes. The standard, adopted in 2003, is developed and regulated by the European Union, and thus only covers the member states of the EU in detail. The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics is instrumental in the European Union's Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund delivery mechanisms and for locating the area where goods and services subject to European public procurement legislation are to be delivered.

The special territories of the European Union are 21 territories of EU member states which, for historical, geographical, or political reasons, enjoy special status within or outside the European Union. The special territories divide themselves in three categories: 9Outermost Regions (OMR) that form part of the European Union, though they benefit from derogations from some EU laws due to their geographical remoteness from mainland Europe, 13 Overseas Countries and Territories (OCT) that do not form part of the European Union, though they cooperate with the EU via the Overseas Countries and Territories Association, and 10special cases where EU law make ad hoc provisions.
The economy of Europe comprises more than 744 million people in 50 different countries. Formation of the European Union (EU) and in 1999, the introduction of a unified currency – the euro brings participating European countries closer through the convenience of a shared currency and has led to a stronger European cash flow. The difference in wealth across Europe can be seen roughly in former Cold War divide, with some countries breaching the divide. Whilst most European states have a GDP per capita higher than the world's average and are very highly developed, some European economies, despite their position over the world's average in the Human Development Index, are poorer.

Turkey is negotiating its accession to the European Union (EU) as a member state, following its application accede to the European Economic Community, the predecessor of the EU, on 14 April 1987. After the ten founding members, Turkey was one of the first countries to become a member of the Council of Europe in 1949. The country was also an associate member of the Western European Union from 1992 to its end in 2011. Turkey signed a Customs Union agreement with the EU in 1995 and was officially recognised as a candidate for full membership on 12 December 1999, at the Helsinki summit of the European Council.
Figures for the population of Europe vary according to how one defines the boundaries of Europe. According to the United Nations, the population within the standard physical geographical boundaries comprised 737 million in 2010. In 2010 the population was 711 million, defining Europe's boundaries as the continental divides of the Caucasus and Ural mountains and the Bosporous, and including the European parts of the countries of Russia and of Turkey.

The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member countries of the European Union (EU). It is the second largest economy in the world both in nominal terms and according to purchasing power parity or PPP. The European Union's GDP was estimated to be $18.8 trillion (nominal) in 2018, representing ~22% of global economy.
Statistics in the European Union are collected by Eurostat.

Relations between the European Union (EU) and China - which is either the People's Republic of China (PRC) or the Republic of China (ROC) - or Sino–European relations are biliteral relations that were established in 1975 between the PRC and the European Community. According to the European External Action Service, the EU and China relations aim for cooperation in the areas of "peace, prosperity, sustainable development and people-to-people exchanges." The EU is the PRC's largest trading partner, and the PRC and the ROC are the EU's second and fifteenth largest trade partners after the United States, while the EU has put an arms embargo and numerous anti-dumping measures against the PRC in place.

Switzerland is not a member state of the European Union (EU). It is associated with the Union through a series of bilateral treaties in which Switzerland has adopted various provisions of European Union law in order to participate in the Union's single market, without joining as a member state. All but one of Switzerland's neighbouring countries are EU member states.

Religion in the European Union is diverse. The largest religion in the EU is Christianity, which accounts for 72.8% of EU population. Smaller groups include those of Islam, Buddhism, Judaism, Hinduism, and some East Asian religions, most concentrated in Germany, Britain and France. Also present are revival movements of pre-Christianity European folk religions including Heathenism, Rodnovery, Romuva, and Druidry.
Immigration to Europe has a long history, but increased substantially in the later 20th century. Western European countries, especially, saw a high growth in immigration after World War II and many European nations today have sizeable immigrant populations, both of European and non-European origin. In contemporary globalization, migrations to Europe have accelerated in speed and scale. Over the last decades, there has been an increase in negative attitudes towards immigration, and many studies have emphasized marked differences in the strength of anti-immigrant attitudes among European countries.

The demographics of the European Union show a highly populated, culturally diverse union of 27 member states. As of 1 February 2020, the population of the EU is about 445 million people.

The Russian Federation supplies a significant volume of fossil fuels and is the largest exporter of oil, natural gas and hard coal to the European Union. In 2017, energy products accounted around 60% of the EU's total imports from Russia. According to Eurostat, 30% of the EU's petroleum oil imports and 39% of total gas imports came from Russia in 2017. For Estonia, Poland, Slovakia and Finland, more than 75 % of their imports of petroleum oils originated in Russia.

The European Union and Yemen enjoy longstanding relations, which date back to 1997 when the first official cooperation agreement was signed. This relationship has kept growing ever since. In December 2009, the EU established a full diplomatic representation to the Republic of Yemen. Many EU Member States enjoy strong and historical relations with Yemen that date back to the 1930s. The United Kingdom, France, Germany and the Netherlands are among Yemen's main donors; France has far ranging economic relations while Italy was the first state to open diplomatic relations with Yemen. Seven Member States are represented in Sana’a: Bulgaria, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain and the United Kingdom.
The EU three, also known as EU big three, EU triumvirate or EU trio, refers to France, Germany and Italy, a group that consists of the three large founding members of the European Union.












