
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. At the heart of the Indochinese Peninsula, Laos is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and southwest. Its capital and largest city is Vientiane.
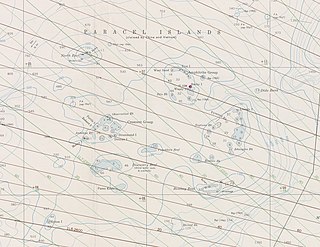
The Paracel Islands, also known as the Xisha Islands and the Hoàng Sa Archipelago, are a disputed archipelago in the South China Sea.

Southeast Asia is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and north-west of mainland Australia which is part of Oceania. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia and the Indian Ocean. Apart from the British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of 26 atolls of Maldives in South Asia, Maritime Southeast Asia is the only other subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. Mainland Southeast Asia is entirely in the Northern Hemisphere. East Timor and the southern portion of Indonesia are the parts of Southeast Asia that lie south of the Equator.

French Indochina, officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1947 as the Indochinese Federation, was a grouping of French colonial territories in Mainland Southeast Asia until its demise in 1954. It comprised Cambodia, Laos, the Chinese territory of Guangzhouwan, and the Vietnamese regions of Tonkin in the north, Annam in the centre, and Cochinchina in the south. The capital for most of its history (1902–1945) was Hanoi; Saigon was the capital from 1887 to 1902 and again from 1945 to 1954.

Ho Chi Minh City, formerly known as Saigon, is the most populous city in Vietnam, with a population of around 9.3 million in 2023. The city's geography is defined by rivers and canals, the largest of which is the eponymously-named Saigon River. As a municipality, Ho Chi Minh City consists of 16 urban districts, six rural districts, and one municipal city. As the largest financial centre in Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh City has the highest gross regional domestic product out of all Vietnam provinces and municipalities, contributing around a quarter of the country's total GDP. Ho Chi Minh City metropolitan is ASEAN 6th largest economy, also the biggest outside ASEAN country capital.

The history of Vietnam can be traced back to around 20,000 years ago. The first modern humans to arrive and settle in the area of modern-day Vietnam are known as the Hoabinhians, who can be traced as the ancestors of modern-day Negritos. Archaeological findings from 1965, which are still under research, show the remains of two hominins closely related to the Sinanthropus, dating as far back as the Middle Pleistocene era, roughly half a million years ago.

The cycle rickshaw is a small-scale local means of transport. It is a type of hatchback tricycle designed to carry passengers on a for-hire basis. It is also known by a variety of other names such as bike taxi, velotaxi, pedicab, bikecab, cyclo, beca, becak, trisikad, sikad, tricycle taxi, trishaw, or hatchback bike.

Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about 331,000 square kilometres (128,000 sq mi) and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's fifteenth-most populous country. Vietnam shares land borders with China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City.

Lonely Planet is a travel guide book publisher. Founded in Australia in 1973, the company has printed over 150 million books.

The Vietnamese people or the Kinh people, also recognized as the Viet people or the Viets, are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to modern-day Northern Vietnam and Southern China who speak Vietnamese, the most widely spoken Austroasiatic language.

This list of Buddhism by country shows the distribution of the Buddhist religion, practiced by about 535 million people as of the 2010s, representing 7% to 8% of the world's total population.

Da Lat or Dalat, is the capital of Lâm Đồng Province and the largest city of the Central Highlands region in Vietnam. The city is located 1,500 m (4,900 ft) above sea level on the Langbian Plateau. Da Lat is one of the most popular tourist destinations in Vietnam.

Cathedral of Our Lady of the Assumption, also known as Matâ'Utu Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral, and a national monument of France, located in the town of Mata Utu on Uvea, in Wallis and Futuna. It is a dominant edifice in downtown Mata-Utu town, capital of Wallis Island. It bears the royal insignia of Wallis, a Maltese cross between its towers. The cathedral is also known as the "Our Lady of Good Hope Cathedral". It is the seat of Bishop Susitino Sionepoe.
This is a timeline of Vietnamese history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Vietnam and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of Vietnam.

Le Mistral, or the Mistral, was an express train between Paris and Nice in France. Introduced in 1950, it was operated by SNCF, and was regarded as the company's flagship train.
The Laotian diaspora consists of roughly 800,000 people, both descendants of early emigrants from Laos, as well as more recent refugees who escaped the country following its communist takeover as a result of the Laotian Civil War. The overwhelming majority of overseas Laotians live in just three countries: Thailand, the United States, and France.
The United Front for the Liberation of Oppressed Races waged a nearly three decade long insurgency against the governments of North and South Vietnam, and later the unified Socialist Republic of Vietnam. The FULRO insurgents represented the interests of indigenous Muslim and Hindu Cham, Montagnards, and Buddhist Khmer Krom against the ethnic Kinh Vietnamese. They were supported and equipped by China and Cambodia according to those countries' interests in the Indochina Wars.













