
The Sudanese Armed Forces are the military forces of the Republic of the Sudan. In 2011, IISS estimated the forces' numbers at 109,300 personnel. The CIA estimates that, before the current war in Sudan broke out in 2023, the SAF may have had up to 200,000 personnel. In 2024, Al Jazeera reported that the SAF has around 300,000 personnel.

The Beja people are a Cushitic ethnic group native to the Eastern Desert, inhabiting a coastal area from southeastern Egypt through eastern Sudan and into northwestern Eritrea. They are descended from peoples who have inhabited the area since 4000 BC or earlier, although they were Arabized by Arabs who settled in the region. They are nomadic and live primarily in the Eastern Desert. The Beja number around 1,900,000 to 2,759,000.

The South African Army is the principal land warfare force of South Africa, a part of the South African National Defence Force (SANDF), along with the South African Air Force, South African Navy and South African Military Health Service. The Army is commanded by the Chief of the Army, who is subordinate to the Chief of the SANDF.
The Janjaweed are an Arab nomad militia group operating in the Sahel region that operates in Sudan, particularly in Darfur and eastern Chad. They are also active in Yemen due to participating in the Saudi Arabian–led intervention in Yemen. According to the United Nations definition, Janjaweed membership consists of Arab nomad tribes from the Sahel, the core of whom are Abbala Arabs, traditionally employed in camel herding, with significant recruitment from the Baggara.

The East African campaign was fought in East Africa during the Second World War by Allies of World War II, mainly from the British Empire, against Italy and its colony of Italian East Africa, between June 1940 and November 1941. The British Middle East Command with troops from the United Kingdom, South Africa, British India, Uganda Protectorate, Kenya, Somaliland, West Africa, Northern and Southern Rhodesia, Sudan and Nyasaland participated in the campaign. These were joined by the Allied Force Publique of Belgian Congo, Imperial Ethiopian Arbegnoch and a small unit of Free French Forces.

Jungle warfare or woodland warfare is warfare in forests, jungles, or similar environments. The term encompasses military operations affected by the terrain, climate, vegetation, and wildlife of densely-wooded areas, as well as the strategies and tactics used by military forces in these situations and environments.
El-Gadarif, also spelt Gedaref or Gedarif, is the capital of the state of Al Qadarif in Sudan. It lies on the road that connects Khartoum with Gallabat on the Ethiopian border, about 410 kilometres (250 mi) from the capital.

The Egyptian Army, officially the Egyptian Ground Forces, is the land warfare branch of the Egyptian Armed Forces. It is the largest service branch of the Egyptian Armed Forces. It was known as the Royal Egyptian Army until the declaration of the Republic and the abolishment of the monarchy on 18 June 1953.

Marines are military personnel generally trained to operate on both land and sea, with a particular focus on amphibious warfare. Historically, the main tasks undertaken by marines have included raiding ashore and the boarding of vessels during ship-to-ship combat or capture of prize ships. Marines also assisted in maintaining security, discipline, and order aboard ships. While maintaining many of their historical roles, in modern times, marines also engage in duties including rapid-response operations, humanitarian aid, disaster relief, special operations roles, and counter-terrorism operations. In most nations, marines are an integral part of that state's navy, such as the United Kingdom's Royal Marines; in some countries their marine forces can also instead be part of the land army, such as the French Troupes de Marine; or, more uncommonly, a nation’s marine forces may be an independent military branch such as the United States Marine Corps or the Ukrainian Marine Corps.

In January 1899, an Anglo-Egyptian agreement restored Egyptian rule in Sudan but as part of a condominium, or joint authority, exercised by the United Kingdom and Egypt. The agreement designated territory south of the twenty-second parallel as Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. Although it emphasized Egypt's indebtedness to Britain for its participation in the reconquest, the agreement failed to clarify the juridical relationship between the two condominium powers in Sudan or to provide a legal basis for continued British governing of the territory on behalf of the Khedive. Article II of the agreement specified that
the supreme military and civil command in Sudan shall be vested in one officer, termed the Governor-General of Sudan. He shall be appointed by Khedival Decree on the recommendation of Her Britannic Majesty's Government and shall be removed only by Khedival Decree with the consent of Her Britannic Majesty's Government.

The Beni-Amer, also known as Beni-Amir, are a population inhabiting northeast Africa. They are considered by some to comprise a subgroup of the Beja people. They live in Sudan and Eritrea. They are mostly Muslim and constitute the largest tribal confederation in Eritrea.

The Battle of Keren took place from 3 February to 27 March 1941. Keren was attacked by the British during the East African Campaign of the Second World War. A force of Italian regular and colonial troops defended the position against British troops and Free French forces. The town of Keren, in the colony of Italian East Africa, was of tactical importance to both sides. The road and railway through Keren were the main routes to the colonial capital of Italian Eritrea at Asmara and the Red Sea port of Massawa, which surrendered to the British after the battle.

The Sudan Defence Force (SDF) was a British Colonial Auxiliary Forces unit raised in the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan in 1925 to assist local police in internal security duties and maintain the condominium's territorial integrity. During World War II, it also served in East Africa as part of the East African campaign and in North Africa during the Western Desert campaign.
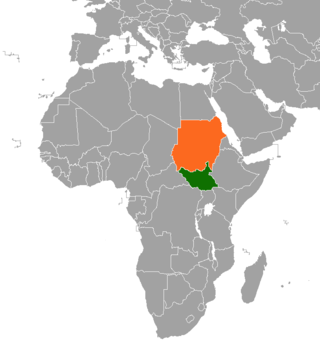
Sudanese nomadic conflicts are non-state conflicts between rival nomadic tribes taking place in the territory of Sudan and, since 2011, South Sudan. Conflict between nomadic tribes in Sudan is common, with fights breaking out over scarce resources, including grazing land, cattle and drinking water. Some of the tribes involved in these clashes have been the Messiria, Maalia, Rizeigat and Bani Hussein Arabic tribes inhabiting Darfur and West Kordofan, and the Dinka, Nuer and Murle African ethnic groups inhabiting South Sudan. Conflicts have been fueled by other major wars taking place in the same regions, in particular the Second Sudanese Civil War, the War in Darfur and the Sudanese conflict in South Kordofan and Blue Nile.

The Kenya Army is the land arm of the Kenya Defence Forces.

The invasion of Darfur was the military invasion and occupation of the Sultanate of Darfur by the British Empire and the Sultanate of Egypt from 16 March to 6 November 1916. The sultan of Darfur, Ali Dinar, had been reinstated by the British after their victory in the Mahdist War but during World War I he grew restive, refusing his customary tribute to the Sudanese government and showing partiality to the Ottoman Empire in 1915.
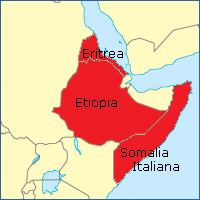
Operations on the Northern front, East Africa, 1940 in the Second World War, were conducted by the British in Sudan and the Armed Forces Command of Italian East Africa in Eritrea and Ethiopia. On 1 June 1940, Amedeo, Duke of Aosta the Viceroy and Governor-General of the Africa Orientale Italiana, commander in chief of the Armed Forces Command of the Royal Italian Army and General of the Air Force, had about 290,476 local and metropolitan troops and by 1 August, mobilisation had increased the number to 371,053 troops. General Archibald Wavell, General Officer Commanding-in-Chief (GOC-in-C) of Middle East Command, had about 86,000 troops at his disposal for Libya, Iraq, Syria, Iran and East Africa. About 36,000 troops were in Egypt and 27,500 men were training in Palestine.

The Battle of Agordat was fought near Agordat in Eritrea from 26 to 31 January 1941, by the Italian army and Royal Corps of Colonial Troops against British, Commonwealth and Indian forces, during the East African Campaign of the Second World War. The British had the advantage of breaking Italian codes and cyphers before the offensive and received copious amounts of information from Italian sources on the order of battle and plans of the Regia Aeronautica and the Italian army.
The paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) has waged a major offensive against the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) in Sennar State, resulting in widespread violence and displacement, as part of the ongoing Sudanese civil war.
















