Related Research Articles

Orange County is a county located in the very southeastern corner of the U.S. state of Texas, sharing a boundary with Louisiana, within the Golden Triangle of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 84,808. The county seat is the city of Orange, and it falls within the Beaumont–Port Arthur metropolitan area.

Ennis is a city in eastern Ellis County, Texas, United States. The population is 20,159 according to the 2020 census, with an estimated population of 23,686 in 2023. Ennis is home to the annual National Polka Festival.

Sabine Pass is the natural outlet of Sabine Lake into the Gulf of Mexico. It borders Jefferson County, Texas, and Cameron Parish, Louisiana.
Sabine Pass is a neighborhood in Port Arthur, Texas. It had been incorporated in 1861 before being formally annexed by Port Arthur in 1978. However, Sabine Pass retains its own distinct identity with its own school district, post office, and port authority. The Port Arthur Convention and Visitors Bureau stated that Sabine Pass is "often regarded as" being a "self-contained" community.

The Missouri Pacific Railroad, commonly abbreviated as MoPac, was one of the first railroads in the United States west of the Mississippi River. MoPac was a Class I railroad growing from dozens of predecessors and mergers. In 1967, the railroad operated 9,041 miles of road and 13,318 miles of track, not including DK&S, NO&LC, T&P, and its subsidiaries C&EI and Missouri-Illinois.

The St. Louis Southwestern Railway Company, known by its nickname of "The Cotton Belt Route" or simply "Cotton Belt", was a Class I railroad that operated between St. Louis, Missouri, and various points in the U.S. states of Arkansas, Tennessee, Louisiana, and Texas from 1891 to 1980, when the system added the Rock Island's Golden State Route and operations in Kansas, Oklahoma, and New Mexico. The Cotton Belt operated as a Southern Pacific subsidiary from 1932 until 1992, when its operation was assumed by Southern Pacific Transportation Company.
The Buffalo Bayou, Brazos, and Colorado Railway, also called the Harrisburg Road or Harrisburg Railroad, was the first operating railroad in Texas. It completed its first segment of track between Harrisburg, Texas and Stafford's Point, Texas in 1853. The company established a western terminus at Alleyton, Texas prior to the Civil War. The railroad was sold after the war and reincorporated as the Galveston, Harrisburg, & San Antonio Railroad. This right of way was acquired by the Southern Pacific Railroad and is today a property of the Union Pacific Railroad.

The Texas and New Orleans Railroad (TNO) was an American rail company in Texas and Louisiana. It operated 3,713 miles (5,975 km) of railroad in 1934; by 1961, 3,385 miles (5,448 km) remained when it merged with parent company Southern Pacific.
Sabine River and Northern Railroad operates freight service 32 miles (51 km) from Bessmay to Echo, Texas, and over an 8-mile (13 km) branch line from Buna to Evadale. SRN has connections with Union Pacific Railroad at Echo and Mauriceville, with CPKC at Lemonville, and with BNSF Railway at Bessmay and Evadale, TX. Traffic consists of pulp and paper products.

The Sam Houston Zephyr was a named passenger train operated by the Burlington-Rock Island Railroad, a subsidiary of both the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad and the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad. It was the first streamlined passenger train in Texas.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.

Yegua Creek is a river in Central Texas and is part of the Brazos River drainage basin. Yegua Creek forms in Lee County at the confluence of the Middle Yegua Creek and East Yegua Creek about three miles west of Somerville Lake. It is the primary tributary to form Somerville Lake. The Yegua flows east and becomes part of the Burleson County line for about 31 miles and then joins the Brazos River in southeastern Washington County. The Yegua below the Somerville Dam is a slow-moving, gentle river but is nevertheless used for some mild recreational canoeing and kayaking.
Valley Junction is a small unincorporated community in Robertson County, Texas, United States. It is located near what was formerly Robertson's Colony, the colony founded by Sterling C. Robertson when he moved from Nashville, Tennessee.

The Port Terminal Railroad Association is an American terminal railroad that operates 185 miles (298 km) of track at the Port of Houston in Houston, Texas. It is an independent association comprising Port of Houston Authority, the Houston Belt & Terminal Railway, Union Pacific Railroad, BNSF Railway and Kansas City Southern Railway.
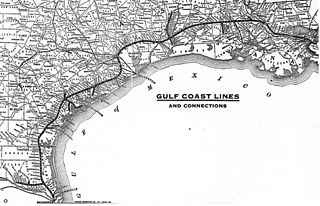
The Gulf Coast Lines was the name of a railroad system comprising three principal railroads, as well as some smaller ones, that stretched from New Orleans, Louisiana, via Baton Rouge and Houston to Brownsville, Texas. Originally chartered as subsidiaries of the Frisco Railroad, the system became independent in 1916 and was purchased by the Missouri Pacific Railroad in 1925.
The Houston and Texas Central Railway (H&TC) was an 872-mile (1403-km) railway system chartered in Texas in 1848, with construction beginning in 1856. The line eventually stretched from Houston northward to Dallas and Denison, Texas, with branches to Austin and Waco.
Texas Midland Railroad (TM) was incorporated in Texas on December 1, 1892, by Hetty Green. The original standard gauge 52 mile line was built between Garrett and Midland Junction by the Houston and Texas Central Railroad in 1882. This original line was known as the Northeast Extension of the Houston and Texas Central. The line went bankrupt in 1885 and the Northeast Extension was sold at foreclosure on April 22, 1891, and became the Texas Central. This portion of the Texas Central was sold on October 27, 1892, to Hetty Green. Hetty Green sold the 52 mile railroad to the Texas Midland on January 27, 1893, and installed her son Edward Howland Robinson Green as president and General Manager. Headquarters city of the Texas Midland was Terrell, Texas. At start up the new company had five steam locomotives a 2-4-4, three 4-4-0s and a 4-6-0. Initial capitalization of the Texas Midland was $500,000. Over the next two decades Hetty Green invested some $1.8 million in the Texas Midland.
The history of the Southern Pacific ("SP") stretched from 1865 to 1998.
References
- ↑ Howard C. Williams: Texas And New Orleans Railroad from the Handbook of Texas Online. Retrieved December 24, 2008.
- ↑ "Handbook of Texas Online - ECHO, TX". Tshaonline.org. Retrieved 2013-10-11.
- ↑ "Handbook of Texas Online - SABINE RIVER AND NORTHERN RAILROAD". Tshaonline.org. Retrieved 2013-10-11.