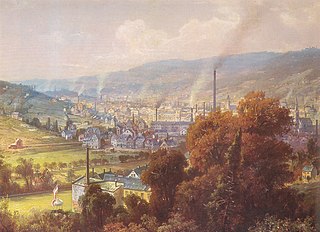The Industrial Revolution, also known as the First Industrial Revolution, was a period of global transition of the human economy towards more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes that succeeded the Agricultural Revolution, starting from Great Britain and spreading to continental Europe and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines; new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes; the increasing use of water power and steam power; the development of machine tools; and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and the result was an unprecedented rise in population and the rate of population growth. The textile industry was the first to use modern production methods, and textiles became the dominant industry in terms of employment, value of output, and capital invested.

In numismatics, the term milled coinage is used to describe coins which are produced by some form of machine, rather than by manually hammering coin blanks between two dies or casting coins from dies.

Matthew Boulton was an English businessman, inventor, mechanical engineer, and silversmith. He was a business partner of the Scottish engineer James Watt. In the final quarter of the 18th century, the partnership installed hundreds of Boulton & Watt steam engines, which were a great advance on the state of the art, making possible the mechanisation of factories and mills. Boulton applied modern techniques to the minting of coins, striking millions of pieces for Britain and other countries, and supplying the Royal Mint with up-to-date equipment.

A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins that can be used as currency.

John "Iron-Mad" Wilkinson was an English industrialist who pioneered the manufacture of cast iron and the use of cast-iron goods during the Industrial Revolution. He was the inventor of a precision boring machine that could bore cast iron cylinders, such as cannon barrels and piston cylinders used in the steam engines of James Watt. His boring machine has been called the first machine tool. He also developed a blowing device for blast furnaces that allowed higher temperatures, increasing their efficiency, and helped sponsor the first iron bridge in Coalbrookdale. He is notable for his method of cannon boring, his techniques at casting iron and his work with the government of France to establish a cannon foundry.

Birmingham has seen 1400 years of growth, during which time it has evolved from a small 7th century Anglo Saxon hamlet on the edge of the Forest of Arden at the fringe of has early Mercia into a major city. A combination of immigration, innovation and civic pride helped to bring about major social and economic reforms and create the Industrial Revolution, inspiring the growth of similar cities across the world.

Handsworth is an inner-city area of Birmingham in the West Midlands, England. Historically in Staffordshire, Handsworth lies just outside Birmingham City Centre and near the town of Smethwick.

Boulton & Watt was an early British engineering and manufacturing firm in the business of designing and making marine and stationary steam engines. Founded in the English West Midlands around Birmingham in 1775 as a partnership between the English manufacturer Matthew Boulton and the Scottish engineer James Watt, the firm had a major role in the Industrial Revolution and grew to be a major producer of steam engines in the 19th century.

The Soho Manufactory was an early factory which pioneered mass production on the assembly line principle, in Soho, Birmingham, England, at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. It operated from 1766–1848 and was demolished in 1853.
The toy industry in Birmingham was an economic sector that produced small goods in any material. Edmund Burke described Birmingham in Parliament in 1777 as "the great Toy Shop of Europe".
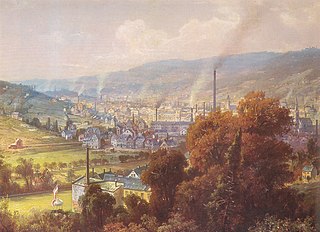
Textile manufacture during the British Industrial Revolution was centred in south Lancashire and the towns on both sides of the Pennines in the United Kingdom. The main drivers of the Industrial Revolution were textile manufacturing, iron founding, steam power, oil drilling, the discovery of electricity and its many industrial applications, the telegraph and many others. Railroads, steamboats, the telegraph and other innovations massively increased worker productivity and raised standards of living by greatly reducing time spent during travel, transportation and communications.
Improvements to the steam engine were some of the most important technologies of the Industrial Revolution, although steam did not replace water power in importance in Britain until after the Industrial Revolution. From Englishman Thomas Newcomen's atmospheric engine, of 1712, through major developments by Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer James Watt, the steam engine began to be used in many industrial settings, not just in mining, where the first engines had been used to pump water from deep workings. Early mills had run successfully with water power, but by using a steam engine a factory could be located anywhere, not just close to a water source. Water power varied with the seasons and was not always available.
Birmingham is one of England's principal industrial centres and has a history of industrial and scientific innovation. It was once known as 'city of a thousand trades' and in 1791, Arthur Young described Birmingham as "the first manufacturing town in the world". Right up until the mid-19th century Birmingham was regarded as the prime industrial urban town in Britain and perhaps the world, the town's rivals were more specific in their trade bases. Mills and foundries across the world were helped along by the advances in steam power and engineering that were taking place in the city. The town offered a vast array of industries and was the world's leading manufacturer of metal ware, although this was by no means the only trade flourishing in the town.

The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of textiles: yarn, cloth and clothing. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry.

The Jewellery Quarter is an area of central Birmingham, England, in the north-western area of Birmingham City Centre, with a population of 19,000 in a 1.07-square-kilometre (264-acre) area.

Matthew Murray was an English steam engine and machine tool manufacturer, who designed and built the first commercially viable steam locomotive, the twin-cylinder Salamanca in 1812. He was an innovative designer in many fields, including steam engines, machine tools and machinery for the textile industry.

Soho Mint was created by Matthew Boulton in 1788 in his Soho Manufactory in Handsworth, West Midlands, England. A mint was erected at the manufactory containing eight machines, to his own patent design, driven by steam engine, each capable of striking 70 to 85 coins per minute.
The United Kingdom, where the Industrial Revolution began in the late 18th century, has a long history of manufacturing, which contributed to Britain's early economic growth. During the second half of the 20th century, there was a steady decline in the importance of manufacturing and the economy of the United Kingdom shifted toward services. Manufacturing, however, remains important for overseas trade and accounted for 44% of goods exports in 2014. In June 2010, manufacturing in the United Kingdom accounted for 8.2% of the workforce and 12% of the country's national output. The East Midlands and West Midlands were the regions with the highest proportion of employees in manufacturing. London had the lowest at 2.8%.
Samuel Garbett was a prominent citizen of Birmingham England, during the industrial revolution, and a friend of Matthew Boulton. Historian Carl Chinn argues that he:
stood alongside Boulton as one of the key figures responsible for Birmingham's rapid expansion into one of the world's leading industrial towns.

The machine industry or machinery industry is a subsector of the industry, that produces and maintains machines for consumers, the industry, and most other companies in the economy.