
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), or the National People's Party of China, is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially based on the Chinese mainland and then in Taiwan since 1949. The KMT is a centre-right to right-wing party and the largest in the Pan-Blue Coalition, one of the two main political groups in Taiwan. Its primary rival is the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), the largest party in the Pan-Green Coalition. As of 2024, the KMT is the largest single party in the Legislative Yuan. The current chairman is Eric Chu.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, also known as Formosa, lies between the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. It has an area of 35,808 square kilometres, with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanized population is concentrated. The combined territories under ROC control consist of 168 islands in total covering 36,193 square kilometres. The largest metropolitan area is formed by Taipei, New Taipei City, and Keelung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries.

The Taiwan independence movement is a political movement which advocates the formal declaration of an independent and sovereign Taiwanese state, as opposed to Chinese unification or the status quo in Cross-Strait relations.

"Mainland China", also referred to as "the Chinese mainland", is a geopolitical term defined as the territory under direct administration of the People's Republic of China (PRC) in the aftermath of the Chinese Civil War. In addition to the geographical mainland, the geopolitical sense of the term includes islands such as Hainan, Chongming, and Zhoushan. By convention, territories outside of mainland China include:
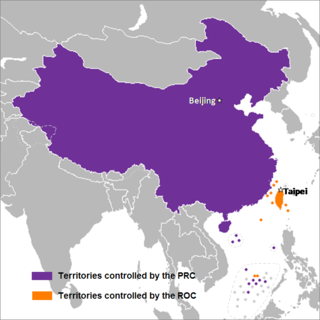
Chinese unification, also known as Cross-Strait unification or Chinese reunification, is the potential unification of territories currently controlled, or claimed, by the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China ("Taiwan") under one political entity, possibly the formation of a political union between the two republics. Together with full Taiwan independence, unification is one of the main proposals to address questions on the political status of Taiwan, which is a central focus of Cross-Strait relations.
The history of the Republic of China began in 1912 with the end of the Qing dynasty, when the Xinhai Revolution and the formation of the Republic of China put an end to 2,000 years of imperial rule. The Republic experienced many trials and tribulations after its founding which included being dominated by elements as disparate as warlord generals and foreign powers.
As a result of the surrender and occupation of Japan at the end of World War II, the islands of Taiwan and Penghu were placed under the governance of the Republic of China (ROC), ruled by the Kuomintang (KMT), on 25 October 1945. Following the February 28 massacre in 1947, martial law was declared in 1949 by the Governor of Taiwan, Chen Cheng, and the ROC Ministry of National Defense. Following the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1949, the ROC government retreated from the mainland as the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China. The KMT retreated to Taiwan and declared Taipei the temporary capital of the ROC. For many years, the ROC and PRC each continued to claim in the diplomatic arena to be the sole legitimate government of "China". In 1971, the United Nations expelled the ROC and replaced it with the PRC.

In ethnogeography, Greater China is the region sharing cultural and economic ties with the Chinese people. The notion contains a "great deal of ambiguity in its geographical coverage and politico-economic implications", because some users use it to refer to "the commercial ties among ethnic Chinese, whereas others are more interested in cultural interactions, and still others in the prospects for political reunification" but usually refers to an area encompassing the People’s Republic of China and the Republic of China, places where the majority population is culturally Chinese. Some analysts may also include places which have predominantly ethnic Chinese population such as Singapore. The term may sometimes be generalised to encompass "linkages among regional Chinese communities".

The Bank of Taiwan is a commercial bank headquartered in Taipei, Taiwan. It was established in 1897-1899 as a Japanese policy institution or "special bank", similarly as the Nippon Kangyo Bank, Hokkaido Takushoku Bank, Industrial Bank of Japan, and Bank of Chōsen. Its aim was to finance industrial demand in Japanese-ruled Taiwan and also to promote trade between South China, Southeast Asia and the Japanese possessions in the Pacific.

The Taiwan Area, fully the "Taiwan Area of the Republic of China", also the free area of the Republic of China, the "Tai-Min Area ", is a term used to refer to the territories under the effective control of the Republic of China. It has been in official use since the Additional Articles of the Constitution of the Republic of China took effect to end temporary anti-communist provisions on 1 May 1991. The term is also used in the 1992 Cross-Strait Act.

Taiwan Province refers to a notional administrative division claimed by the People's Republic of China. The PRC constitution asserts Taiwan as part of its territories, although the PRC has never controlled Taiwan since the PRC's establishment in 1949. The territory of the claimed province, including the entire island of Taiwan, is in actuality administered by the Republic of China (ROC) but is not coextensive with the smaller Taiwan Province of the ROC.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Taiwan:

The Kuomintang (KMT) is a Chinese political party that ruled mainland China from 1927 to 1949 prior to its relocation to Taiwan as a result of the Chinese Civil War. The name of the party translates directly as "National People's Party of China" or "Chinese National Party" and was historically referred to as the Chinese Nationalists. The party was initially founded on 23 August 1912, by Sun Yat-sen but dissolved in November 1913. It reformed on October 10, 1919, again led by Sun Yat-sen, and became the ruling party in China. After Sun's death, the party was dominated from 1927 to 1975 by Chiang Kai-shek. After the KMT lost the civil war with the Chinese Communist Party in 1949, the party retreated to Taiwan and remains a major political party of the Republic of China based in Taiwan.
The Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA) is a free trade agreement (FTA) between the governments of the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China, that aims to reduce tariffs and commercial barriers between the two sides, as well as improve cross-strait relations.
The economic history of China is covered in the following articles:
The economic history of the Republic of China is covered in the following articles:
The Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement Television Debate was a televised debate between the President of the Republic of China, Ma Ying-jeou, who is also chairman of the Nationalist Party (Kuomintang), and the chairperson of Democratic Progressive Party, Tsai Ing-wen, which aired on April 25, 2010.

The Republic of China (ROC) began on 1 January 1912 as a sovereign state in mainland China following the 1911 Revolution, which overthrew the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and ended China's imperial history. From 1927, the Kuomintang (KMT) reunified the country and ruled it as a one-party state with Nanjing as the national capital. In 1949, the KMT-led government was defeated in the Chinese Civil War and lost control of the mainland to the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The CCP established the People's Republic of China (PRC) while the ROC was forced to retreat to Taiwan; the ROC retains control over the Taiwan Area, and its political status remains disputed. The ROC is recorded as a founding member of both the League of Nations and the United Nations, and previously held a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council until 1971, when the PRC took China's seat in the United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2758. It was also a member of the Universal Postal Union and the International Olympic Committee. The ROC claimed 11.4 million km2 (4.4 million sq mi) of territory, and its population of 541 million in 1949 made it the most populous country in the world.
Republic of China is the official name of Taiwan, a country in East Asia.












