
Massage is the rubbing or kneading of the body's soft tissues. Massage techniques are commonly applied with hands, fingers, elbows, knees, forearms, feet or a device. The purpose of massage is generally for the treatment of body stress or pain. In European countries, a person professionally trained to give massages is traditionally known as a masseur (male) or masseuse (female). In the United States, these individuals are often referred to as "massage therapists". In some provinces of Canada, they are called "registered massage therapists."

Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve compression syndrome associated with the collected signs and symptoms of compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome is an idiopathic syndrome but there are environmental, and medical risk factors associated with the condition. CTS can affect both wrists.

The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.

Compartment syndrome is a condition in which increased pressure within one of the body's anatomical compartments results in insufficient blood supply to tissue within that space. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Compartments of the leg or arm are most commonly involved.

De Quervain syndrome occurs when two tendons that control movement of the thumb become constricted by their tendon sheath in the wrist. This results in pain and tenderness on the thumb side of the wrist. Radial abduction of the thumb is painful. On some occasions, there is uneven movement or triggering of the thumb with radial abduction. Symptoms can come on gradually or be noted suddenly.
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have many possible underlying causes. Paresthesias are usually painless and can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly occur in the arms and legs.
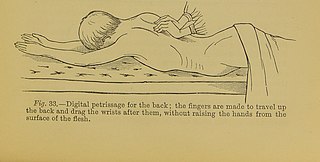
Petrissage is a massage technique that applies deep pressure to the underlying muscles. Kneading, wringing, skin rolling, and pick-up-and-squeeze are the petrissage movements. They are all performed with the padded palmar surface of the hand, the surface of the finger and also the thumbs.
The primary goals of stroke management are to reduce brain injury and promote maximum patient recovery. Rapid detection and appropriate emergency medical care are essential for optimizing health outcomes. When available, patients are admitted to an acute stroke unit for treatment. These units specialize in providing medical and surgical care aimed at stabilizing the patient's medical status. Standardized assessments are also performed to aid in the development of an appropriate care plan. Current research suggests that stroke units may be effective in reducing in-hospital fatality rates and the length of hospital stays.

A shin splint, also known as medial tibial stress syndrome, is pain along the inside edge of the shinbone (tibia) due to inflammation of tissue in the area. Generally this is between the middle of the lower leg and the ankle. The pain may be dull or sharp, and is generally brought on by high-impact exercise that overloads the tibia. It generally resolves during periods of rest. Complications may include stress fractures.

Myofascial trigger points (MTrPs), also known as trigger points, are described as hyperirritable spots in the skeletal muscle. They are associated with palpable nodules in taut bands of muscle fibers. They are a topic of ongoing controversy, as there is limited data to inform a scientific understanding of the phenomenon. Accordingly, a formal acceptance of myofascial "knots" as an identifiable source of pain is more common among bodyworkers, physical therapists, chiropractors, and osteopathic practitioners. Nonetheless, the concept of trigger points provides a framework which may be used to help address certain musculoskeletal pain.
Myofascial release is an alternative medicine therapy claimed to be useful for treating skeletal muscle immobility and pain by relaxing contracted muscles, improving blood and lymphatic circulation and stimulating the stretch reflex in muscles.
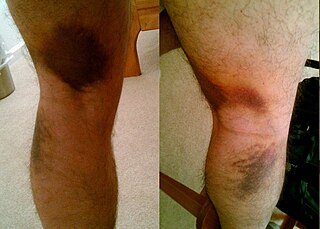
A strain is an acute or chronic soft tissue injury that occurs to a muscle, tendon, or both. The equivalent injury to a ligament is a sprain. Generally, the muscle or tendon overstretches and partially tears, under more physical stress than it can withstand, often from a sudden increase in duration, intensity, or frequency of an activity. Strains most commonly occur in the foot, leg, or back. Immediate treatment typically includes four steps abbreviated as R.I.C.E.: rest, ice, compression, elevation.
Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS), also known as chronic myofascial pain (CMP), is a syndrome characterized by chronic pain in multiple myofascial trigger points ("knots") and fascial constrictions. It can appear in any body part. Symptoms of a myofascial trigger point include: focal point tenderness, reproduction of pain upon trigger point palpation, hardening of the muscle upon trigger point palpation, pseudo-weakness of the involved muscle, referred pain, and limited range of motion following approximately 5 seconds of sustained trigger point pressure.
Counterstrain is a technique used in osteopathic medicine, osteopathy, physical therapy, massage therapy, and chiropractic to treat somatic dysfunction. It is a system of diagnosis and treatment that uses tender points, which are produced by trauma, inflammation, postural strain, or disease, to identify structures to manipulate. The manipulation uses light pressure to decompress the local nociceptors and mechanoreceptors responsible for the sensation of pain, returning central sensitization to its normal state. This technique extends Strain-counterstrain, a technique inhibits the reflexes by putting the tissues in a position of ease directly opposite to that of the reflex. Strain-counterstrain is also known as the Jones technique,, and spontaneous release by position. Counterstrain was developed by Lawrence Jones in 1955 and was originally called “Spontaneous Release by Positioning,” before being termed “strain-counterstrain.”
Anterior interosseous syndrome is a medical condition in which damage to the anterior interosseous nerve (AIN), a distal motor and sensory branch of the median nerve, classically with severe weakness of the pincer movement of the thumb and index finger, and can cause transient pain in the wrist.

Pronator teres syndrome is a compression neuropathy of the median nerve at the elbow. It is rare compared to compression at the wrist or isolated injury of the anterior interosseous branch of the median nerve.
Cat massage is a practice used by veterinarians and at home by pet owners to apply massage therapy techniques to domestic cats, primarily for relieving pain and discomfort, as well as a means of strengthening the cat–human bond through intimate interaction.

Injuries to the arm, forearm or wrist area can lead to various nerve disorders. One such disorder is median nerve palsy. The median nerve controls the majority of the muscles in the forearm. It controls abduction of the thumb, flexion of hand at wrist, flexion of digital phalanx of the fingers, is the sensory nerve for the first three fingers, etc. Because of this major role of the median nerve, it is also called the eye of the hand. If the median nerve is damaged, the ability to abduct and oppose the thumb may be lost due to paralysis of the thenar muscles. Various other symptoms can occur which may be repaired through surgery and tendon transfers. Tendon transfers have been very successful in restoring motor function and improving functional outcomes in patients with median nerve palsy.
This article is about physical therapy in carpal tunnel syndrome.
Fascial Manipulation is a manual therapy technique developed by Italian physiotherapist Luigi Stecco in the 1980s, aimed at evaluating and treating global fascial dysfunction by restoring normal motion/gliding to the system.









