Related Research Articles

Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. The urinary tract or the intestines may be infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stool, or blood in the urine. Those who have been infected for a long time may experience liver damage, kidney failure, infertility, or bladder cancer. In children, it may cause poor growth and learning difficulties.

Helminthiasis, also known as worm infection, is any macroparasitic disease of humans and other animals in which a part of the body is infected with parasitic worms, known as helminths. There are numerous species of these parasites, which are broadly classified into tapeworms, flukes, and roundworms. They often live in the gastrointestinal tract of their hosts, but they may also burrow into other organs, where they induce physiological damage.

Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacterial and eukaryotic cells, as well as some sub-cellular structures, specifically their resistance to decolorization by acids during laboratory staining procedures. Once stained as part of a sample, these organisms can resist the acid and/or ethanol-based decolorization procedures common in many staining protocols, hence the name acid-fast.

Haemonchus contortus, also known as the barber's pole worm, is a very common parasite and one of the most pathogenic nematodes of ruminants. Adult worms attach to abomasal mucosa and feed on the blood. This parasite is responsible for anemia, oedema, and death of infected sheep and goats, mainly during summer in warm, humid climates.
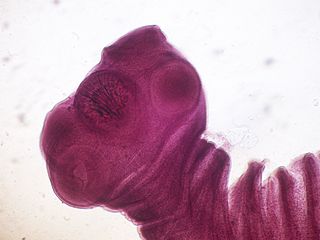
Taenia solium, the pork tapeworm, belongs to the cyclophyllid cestode family Taeniidae. It is found throughout the world and is most common in countries where pork is eaten. It is a tapeworm that uses humans as its definitive host and pigs as the intermediate or secondary hosts. It is transmitted to pigs through human feces that contain the parasite eggs and contaminate their fodder. Pigs ingest the eggs, which develop into larvae, then into oncospheres, and ultimately into infective tapeworm cysts, called cysticercus. Humans acquire the cysts through consumption of uncooked or under-cooked pork and the cysts grow into adult worms in the small intestine.
Schistosoma japonicum is an important parasite and one of the major infectious agents of schistosomiasis. This parasite has a very wide host range, infecting at least 31 species of wild mammals, including nine carnivores, 16 rodents, one primate (human), two insectivores and three artiodactyls and therefore it can be considered a true zoonosis. Travelers should be well-aware of where this parasite might be a problem and how to prevent the infection. S. japonicum occurs in the Far East, such as China, the Philippines, Indonesia and Southeast Asia.

Schistosoma mansoni is a water-borne parasite of humans, and belongs to the group of blood flukes (Schistosoma). The adult lives in the blood vessels near the human intestine. It causes intestinal schistosomiasis. Clinical symptoms are caused by the eggs. As the leading cause of schistosomiasis in the world, it is the most prevalent parasite in humans. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease. As of 2021, the World Health Organization reports that 251.4 million people have schistosomiasis and most of it is due to S. mansoni. It is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Caribbean, Brazil, Venezuela and Suriname.

Schistosoma intercalatum is a parasitic worm found in parts of western and central Africa. There are two strains: the Lower Guinea strain and the Zaire strain. S. intercalatum is one of the major agents of the rectal form of schistosomiasis, also called bilharzia. It is a trematode, and being part of the genus Schistosoma, it is commonly referred to as a blood-fluke since the adult resides in blood vessels.

Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels.
Diphyllobothriasis is the infection caused by tapeworms of the genus Diphyllobothrium.
Opisthorchiasis is a parasitic disease caused by certain species of genus Opisthorchis. Chronic infection may lead to cholangiocarcinoma, a cancer of the bile ducts.

A fecal sac is a mucous membrane, generally white or clear with a dark end, that surrounds the feces of some species of nestling birds. It allows parent birds to more easily remove fecal material from the nest. The nestling usually produces a fecal sac within seconds of being fed; if not, a waiting adult may prod around the youngster's cloaca to stimulate excretion. Young birds of some species adopt specific postures or engage in specific behaviors to signal that they are producing fecal sacs. For example, nestling curve-billed thrashers raise their posteriors in the air, while young cactus wrens shake their bodies. Other species deposit the sacs on the rim of the nest, where they are likely to be seen by parent birds.
Indicator organisms are used as a proxy to monitor conditions in a particular environment, ecosystem, area, habitat, or consumer product. Certain bacteria, fungi and helminth eggs are being used for various purposes.
The Kato technique is a laboratory method for preparing human stool samples prior to searching for parasite eggs.

Fasciolopsis is a genus of trematodes. They are also known as giant intestinal flukes.
Schistosoma mekongi is a species of trematodes, also known as flukes. It is one of the five major schistosomes that account for all human infections, the other four being S. haematobium, S. mansoni, S. japonicum, and S. intercalatum. This trematode causes schistosomiasis in humans.

Teladorsagia circumcincta is a nematode that is one of the most important parasites of sheep and goats. It was previously known as Ostertagia circumcincta and is colloquially known as the brown stomach worm. It is common in cool, temperate areas, such as south-eastern and south-western Australia and the United Kingdom. There is considerable variation among lambs and kids in susceptibility to infection. Much of the variation is genetic and influences the immune response. The parasite induces a type I hypersensitivity response which is responsible for the relative protein deficiency which is characteristic of severely infected animals. There are mechanistic mathematical models which can predict the course of infection. There are a variety of ways to control the infection and a combination of control measures is likely to provide the most effective and sustainable control.
Ostertagia ostertagi, commonly known as the medium stomach worm or brown stomach worm, is a parasitic nematode of cattle. O. ostertagi can also be found to a lesser extent in sheep, goats, wild ruminants, and horses. It causes ostertagiosis, which is potentially fatal in cattle. It is found worldwide and is economically important to cattle industries, particularly those found in temperate climates.
The fecal egg count reduction test was suggested in the World Association for the Advancement of Veterinary Parasitology guideline for estimating the reduction in fecal egg counts and its corresponding confidence interval. The results of this test can be used to determine the anthelmintic resistance status of the animals.

Trematodiasis is a group of parasitic infections due different species of flukes, the trematodes. Symptoms can range from mild to severe depending on the species, number and location of trematodes in the infected organism. Symptoms depend on type of trematode present, and include chest and abdominal pain, high temperature, digestion issues, cough and shortness of breath, diarrhoea and change in appetite.
References
- ↑ "Doing a fecal egg count - Parasite series - Horsetalk.co.nz". www.horsetalk.co.nz. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
- ↑ "Willis technique". Saunders Comprehensive Veterinary Dictionary (3rd ed.). 2007. Archived from the original on 13 October 2017 – via TheFreeDictionary by Farlex.
- ↑ "McMaster Egg Counting Technique". cal.vet.upenn.edu. Archived from the original on 15 February 2019. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
- ↑ Castelino, J. B.; Herbert, I. V. (13 October 1972). "Investigation of the accuracy of the Clayton-Lane faecal egg flotation technique for estimating the numbers of Hyostrongylus rubidus (Hassall and Stiles, 1892) eggs in pig faeces". Journal of Helminthology. 46 (4): 387–397. doi:10.1017/s0022149x00023397. PMID 4674460. S2CID 26489485.