Sources
 Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Ekkehard". Catholic Encyclopedia . New York: Robert Appleton Company.
Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Ekkehard". Catholic Encyclopedia . New York: Robert Appleton Company.
Ekkehard V (died c. 1220), called Minimus (the Least), was a monk of the Abbey of Saint Gall. He is the last of the Saint Gall Ekkehards, and flourished towards the end of the twelfth, and the beginning of the thirteenth, century. No particulars are known concerning his life, and tradition is silent as to his origin, the year of his birth and of his death. He was dean of the abbey in the reign of Innocent III.
About 1214 he wrote a life of St. Notker Balbulus, a learned monk of St. Gall, who lived towards the end of the ninth, and the beginning of the tenth, century (Acta SS., April, I, 579), from which work we gather that its author was versed in ecclesiastical music.

The Abbey of Saint Gall is a dissolved abbey (747–1805) in a Catholic religious complex in the city of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The Carolingian-era monastery existed from 719, founded by Saint Othmar on the spot where Saint Gall had erected his hermitage. It became an independent principality between 9th and 13th centuries, and was for many centuries one of the chief Benedictine abbeys in Europe. The library of the Abbey is one of the oldest monastic libraries in the world.

Gall according to hagiographic tradition was a disciple and one of the traditional twelve companions of Columbanus on his mission from Ireland to the continent. However, he may have originally come from the border region between Lorraine and Alemannia and only met Columbanus at the monastery of Luxeuil in the Vosges. Gall is known as a representative of the Irish monastic tradition. The Abbey of Saint Gall in the city of Saint Gallen, Switzerland was built upon his original hermitage. Deicolus was the elder brother of Gall.

Einsiedeln Abbey is a Catholic monastery administered by the Benedictine Order in the village of Einsiedeln, Switzerland. The abbey is dedicated to Our Lady of the Hermits, in recognition of Meinrad of Einsiedeln, a hermit Catholic saint. The monastery is not under the jurisdiction of a diocese or a bishop because it is a territorial abbey.

Notker the Stammerer, Notker Balbulus, or simply Notker, was a Benedictine monk at the Abbey of Saint Gall active as a composer, poet and scholar. Described as "a significant figure in the Western Church", Notker made substantial contributions to both the music and literature of his time. He is usually credited with two major works of the Carolingian period: the Liber Hymnorum, which includes an important collection of early musical sequences, and an early biography of Charlemagne, the Gesta Karoli Magni. His other works include a biography of Saint Gall known as the Vita Sancti Galli and a martyrology, among others.
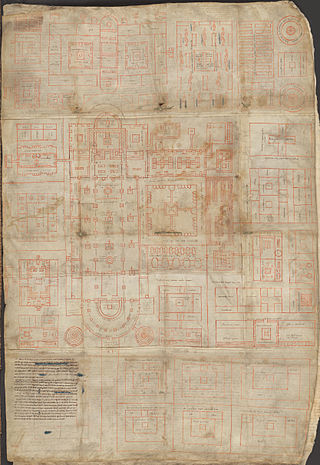
The Plan of Saint Gall is a medieval architectural drawing of a monastic compound dating from 820–830 AD. It depicts an entire Benedictine monastic compound, including churches, houses, stables, kitchens, workshops, brewery, infirmary, and a special house for bloodletting. According to calculations based on the manuscript's tituli the complex was meant to house about 110 monks, 115 lay visitors, and 150 craftmen and agricultural workers. The Plan was never actually built, and was so named because it is dedicated to Gozbert abbot of Saint Gall. The planned church was intended to keep the relics of Saint Gall. The plan was kept at the famous medieval monastery library of the Abbey of St. Gall, the Stiftsbibliothek Sankt Gallen where it remains to this day.

The Folchart Psalter, or Folchard Psalter, is a Carolingian illuminated manuscript. It was produced about 872–883 in the scriptorium of the Abbey of St. Gall, Switzerland, under the direction of the scribe Folchardus, usually modernized as Folchard or Folchart.

The Hiberno-Scottish mission was a series of expeditions in the 6th and 7th centuries by Gaelic missionaries originating from Ireland that spread Celtic Christianity in Scotland, Wales, England and Merovingian France. Celtic Christianity spread first within the Kingdom of Dál Riata, within Ireland and the western coast of Scotland. Since the 8th and 9th centuries, these early missions were called 'Celtic Christianity'.

Notker Labeo, also known as Notker the German or Notker III, was a Benedictine monk active as a scholar and teacher. He was the first commentator on Aristotle active in the Middle Ages and translated the works of earlier Latin writers such as Boethius and Martianus Capella. Notker is also attributed the authorship of five short essays on music.
Ekkehard IV was a monk of the Abbey of Saint Gall and the author of the Casus sancti Galli and Liber Benedictionum.
Ekkehard is a German given name. It is composed of the elements ekke "edge, blade; sword" and hart "brave; hardy". Variant forms include Eckard, Eckhard, Eckhart, Eckart. The Anglo-Saxon form of the name was Ecgheard, possibly attested in the toponym Eggerton.
Notker Physicus, sometimes called Notker II, was a monk at the Abbey of Saint Gall, active as a physician, painter, and composer. Besides physicus, he was also nicknamed piperis granum on account of his strict discipline.

Tuotilo was a Frankish monk at the Abbey of Saint Gall. He was a composer, and according to Ekkehard IV a century later, also a poet, musician, painter and sculptor. Various trope melodies can be assigned to Tuotilo, but works of other mediums are attributed with less certainty. He was a student of Iso of St. Gallen and friends with the fellow monk Notker the Stammerer.

Deicolus is venerated as a saint in both the Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches. He was an elder brother of Saint Gall.

Ekkehard I, called Major or Senex, was a monk of the Abbey of Saint Gall. He was of noble birth, of the Jonschwyl family in Toggenburg, and was educated in the monastery of St. Gall; after joining the Benedictine Order, he was appointed director of the inner school there. Later, under Abbot Kralo, who trusted him implicitly, he was elected dean of the monastery, and for a while directed all the affairs of the abbey.
Ekkehard II, called Palatinus, was a monk of the Abbey of Saint Gall who became known for his sequence poetry.
Ekkehard III was a monk of the Abbey of Saint Gall and a nephew of Ekkehard I and a cousin of Ekkehard II. He shared the educational advantages of his cousin and, at his invitation, accompanied him to Hohentwiel to superintend and direct the studies of the local clergy. On his return to St. Gall he was made dean of the abbey, and is reported to have filled this office for thirty years. He died early in the eleventh century.
Craloh was abbot of the Benedictine Abbey of Saint Gall from 942 to 958. During his time in office, the first anti-abbot was elected.
Purchart was abbot of the Abbey of Saint Gall from 1001 to 1022.
Eglolf Blarer was abbot of the Abbey of Saint Gall from 1426 to 1442.
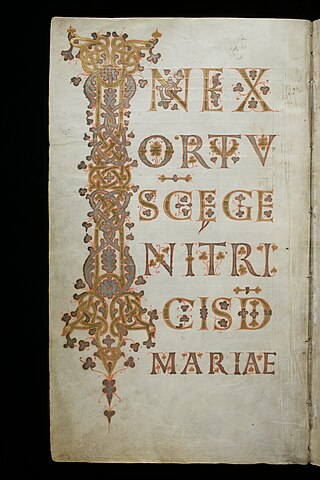
The Evangelium longum is an illuminated manuscript Latin evangeliary that was made around 894 at the Abbey of Saint Gall in Switzerland. It consists of texts drawn from the Gospels for the use of the preacher during Mass.