
Alajuela is a province of Costa Rica. It is located in the north-central part of the country, bordering Nicaragua to the north. It also borders the provinces of Heredia to the east, San José to the south, Puntarenas to the southwest and Guanacaste to the west. As of 2011, the province had a population of 885,571. Alajuela is composed of 16 cantons, which are divided into 111 districts. It covers an area of 9,757.53 square kilometers.

Guanacaste is a province of Costa Rica located in the northwestern region of the country, along the coast of the Pacific Ocean. It is bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Alajuela Province to the east, and Puntarenas Province to the southeast. It is the most sparsely populated of all the provinces of Costa Rica. The province covers an area of 10,141 square kilometres (3,915 sq mi) and as of 2010, had a population of 354,154, with annual revenue of $2 billion.
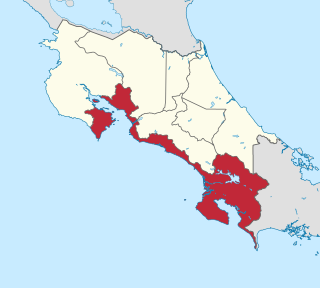
Puntarenas is a province of Costa Rica. It is located in the western part of the country, covering most of Costa Rica's Pacific Ocean coast, and it is the largest province in Costa Rica. Clockwise from the northwest it borders on the provinces Guanacaste, Alajuela, San José and Limón, and the neighbouring country of Panama.

San José is a province of Costa Rica. It is located in the central part of the country, and borders the provinces of Alajuela, Heredia, Limón, Cartago and Puntarenas. The provincial and national capital is San José. The province covers an area of 4,965.9 km². and has a population of 1,404,242.
The 2006 UNCAF Interclub Cup was the 24th edition of the international club football competition held in the UNCAF region representing the seven nations of Central America. This was the eighth year of the current format using the name UNCAF Interclub Cup. The tournament was also a qualifying event for the 2007 CONCACAF Champions' Cup. Sixteen teams representing seven football associations took part, beginning with the first qualifying games on August 22, 2006. The tournament concluded with a two-legged final that was won by Puntarenas of Costa Rica making them the Central American club football champions. The top three finishers in the tournament qualify for the 2007 CONCACAF Champions' Cup.

Rail transport in Costa Rica is primarily under the stewardship of Incofer, an autonomous institution of the state. Incofer owns the national railway infrastructure and operates virtually all freight and passenger services, which consist primarily of commuter trains through the highly populated Central Valley. The whole Incofer network is 1,067 mm narrow gauge, although there are several small tourist railways of other gauges.

The Archdiocese of San José de Costa Rica is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Costa Rica. A metropolitan see, there are seven suffragan dioceses in its ecclesiastical province: the Diocese of Alajuela, Cartago, Ciudad Quesada, Limón, Puntarenas, San Isidro de El General, and Tilarán. Erected on 28 February 1850, the Diocese of San José de Costa Rica was elevated to an archdiocese on 16 February 1921. It is the sole archdiocese in Costa Rica.

A referendum on the Dominican Republic–Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) was held in Costa Rica on 7 October 2007. It was originally to be held on 23 September 2007, but it was postponed on 5 June 2007 due to a court challenge. Opinion polls from April, July and August 2007 suggested that a majority of voters were in favour, while a poll from June saw a majority against. It was ultimately approved by 51.56% of voters.

Tourism in Costa Rica has been one of the fastest growing economic sectors of the country and by 1995 became the largest foreign exchange earner. Since 1999, tourism has earned more foreign exchange than bananas, pineapples and coffee exports combined. The tourism boom began in 1987, with the number of visitors up from 329,000 in 1988, through 1.03 million in 1999, over 2 million in 2008, to a historical record of 2.66 million foreign visitors in 2015. In 2012, tourism contributed with 12.5% of the country's GDP and it was responsible for 11.7% of direct and indirect employment. In 2009, tourism attracted 17% of foreign direct investment inflows, and 13% in average between 2000 and 2009. In 2010, the tourism industry was responsible for 21.2% of foreign exchange generated by all exports. According to a 2007 report by ECLAC, tourism contributed to a reduction in poverty of 3% in the country.

According to the Political Constitution of Costa Rica of 1949, in article 168, the territorial division of Costa Rica is organized by law into three types of subnational entity:

José María Alfaro Zamora was the Costa Rican Head of State between the periods of 1842 and 1844 as well as 1846 and 1847 and President of Costa Rica between May 1 and May 8, 1847.
The 2012 Costa Rica earthquake occurred at 08:42 local time on September 5. The epicenter of the 7.6 Mw earthquake was in the Nicoya Peninsula, 11 kilometers east-southeast of Nicoya. A tsunami warning was issued shortly afterwards, but later cancelled. Two people are known to have died, one from a heart attack and another, a construction worker, crushed by a collapsing wall. It was the second strongest earthquake recorded in Costa Rica's history, following the 1991 Limon earthquake.

Costa Rica’s municipal system is organized under the Municipal Code, the specific law that regulates the local governments. Municipalities are the second-level administration in Costa Rica after the central government. Each one of the 82 cantons of Costa Rica has a Municipality or Municipal Government constituted by a mayor and a proportional number of members of the Municipal Council. Districts of each of the cantons also have their local authorities and representatives. Some of the services manage by local governments include; solid waste management, building and administration of local roads, parks, libraries and schools, recollection of municipal taxes and in some cases local security. Worth noticing that in Costa Rica city and municipality are not the same thing, as a canton can have several cities within its borders, generally as districts.
Head of State elections were held in Costa Rica in 1844. They were the first in which direct suffrage was used to elect the Head of State, in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution of 9 April 1844. A method that was abolished by the next election returning to indirect suffrage until 1913.
General elections were held in Costa Rica between 2 and 9 December 1849. They were the first presidential elections after the Reformed Constitution of 1848 created the title of "President". Previously the equivalent office was called "Head of State".
The League War was the second civil war of Costa Rica, as a member state of the Federal Republic of Central America. It passed between September and October 1835 in the Central Valley of Costa Rica. Its immediate trigger was the repeal of the "Ambulance Law", the law that established the rotation of the country's capital among the four constituent cities. The most important consequence was the triumph of the city of San José over the cities of Alajuela, Heredia and Cartago, which allowed its consolidation as the capital of Costa Rica.

National Primary Route 4, or Route 4, is a national primary road, which covers the northern region of the country, through the provinces of Limón, Heredia, Alajuela and Guanacaste.
National Primary Route 21, or just Route 21 is a National Road Route of Costa Rica, located in the Guanacaste, Puntarenas provinces.
National Secondary Route 170, or just Route 170 is a National Road Route of Costa Rica, located in the Alajuela, Guanacaste provinces.

The National Technical University (UTN), was founded on 4 June 2008 as the fifth public university of Costa Rica. Its purpose is to provide the means for scientific and technical education to pursue the requirements of the country.










