
Central America is sometimes defined as a subregion of the Americas. This region is bordered by Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south. Central America consists of seven countries: El Salvador, Costa Rica, Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and Panama. The combined population of Central America is estimated at 44.53 million (2016).

Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a transcontinental country in Central America and South America, bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half the country's 4 million people.
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Panama, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The economy of Panama is based mainly on the services sector, which accounts for nearly 80% of its GDP and accounts for most of its foreign income. Services include the Panama Canal, banking, commerce, the Colón Free Trade Zone, insurance, container ports, and flagship registry, medical and health and tourism. The country's industry includes manufacturing of aircraft spare parts, cement, drinks, adhesives and textiles. Additionally, exports from Panama include bananas, shrimp, sugar, coffee, and clothing. Panama's economy is a fully dollarized, with the US dollar being legal tender in the country. Panama is a high-income economy with a history of low inflation.
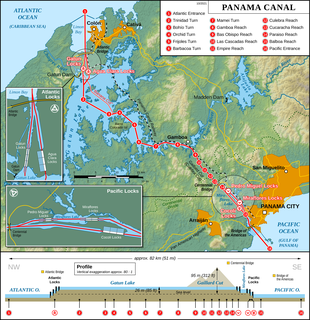
The Panama Canal is an artificial 82 km (51 mi) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. One of the largest and most difficult engineering projects ever undertaken, the Panama Canal shortcut greatly reduces the time for ships to travel between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, enabling them to avoid the lengthy, hazardous Cape Horn route around the southernmost tip of South America via the Drake Passage or Strait of Magellan and the even less popular route through the Arctic Archipelago and the Bering Strait.

Panama City, also simply known as Panama, is the capital and largest city of Panama. It has an urban population of 880,691, with over 1.5 million in its metropolitan area. The city is located at the Pacific entrance of the Panama Canal, in the province of Panama. The city is the political and administrative center of the country, as well as a hub for banking and commerce.

Tocumen International Airport is the international airport of Panama City, the capital of Panama. The airport serves as the homebase for Copa Airlines and is a regional hub to and from The Caribbean, South, North and Central America and additionally features routes to some European and Asian cities.

The United States Invasion of Panama, codenamed Operation Just Cause, lasted over a month between mid-December 1989 and late January 1990. It occurred during the administration of President George H. W. Bush and ten years after the Torrijos–Carter Treaties were ratified to transfer control of the Panama Canal from the U.S. to Panama by 1 January 2000. During the invasion, de facto Panamanian leader, general and dictator Manuel Noriega, who for a long time worked with the Central Intelligence Agency, was deposed citing racketeering and drug trafficking. Following the operation, the Panama Defense Forces were dissolved and President-elect Guillermo Endara was sworn into office.

The Panama Canal Zone was an unincorporated territory of the United States from 1903 to 1979, centered on the Panama Canal and surrounded by the Republic of Panama. The zone consisted of the canal and an area generally extending five miles (8.0 km) on each side of the centerline, excluding Panama City and Colón, which otherwise would have been partly within the limits of the Zone. Its border spanned three of Panama's provinces. When reservoirs were created to assure a steady supply of water for the locks, those lakes were included within the Zone.

Colón is a city and seaport in Panama, beside the Caribbean Sea, lying near the Atlantic entrance to the Panama Canal. It is the capital of Panama's Colón Province and has traditionally been known as Panama's second city. Originally it was located entirely on Manzanillo Island, surrounded by Limon Bay, Manzanillo Bay, and the Folks River; however, since the disestablishment of the Panama Canal Zone, the city's limits have been redefined to include Fort Gulick, a former U.S. Army base, as well the former Panama Canal Zone towns of Cristobal, Margarita, and Coco Solo.

A Panama hat, also known as an Ecuadorian hat or a toquilla straw hat, is a traditional brimmed straw hat of Ecuadorian origin. Traditionally, hats were made from the plaited leaves of the Carludovica palmata plant, known locally as the toquilla palm or jipijapa palm, although it is a palm-like plant rather than a true palm.

The Panama–Pacific International Exposition was a world's fair held in San Francisco, California, United States, from February 20 to December 4, 1915. Its stated purpose was to celebrate the completion of the Panama Canal, but it was widely seen in the city as an opportunity to showcase its recovery from the 1906 earthquake. The fair was constructed on a 636 acre(1 sq. mi., 2.6 km2) site along the northern shore, between the Presidio and Fort Mason, now known as the Marina District.
The Panama national football team represents Panama in men's international association football and it is governed by Panamanian Football Federation, The team represents all three FIFA, CONCACAF and the regional UNCAF.

The United States Air Forces Southern Command is an inactive Major Command of the United States Air Force. It was headquartered at Albrook Air Force Base, Canal Zone, being inactivated on 1 January 1976.
Señorita Panamá is a national beauty pageant in Panama. As of 2019, its winners represent Panama in Miss Universe, Miss International. The Miss Panama brand started in 1952, when the Panamanian Institute of Tourism received an invitation from Miss Universe to send a representative. In 1975, the Señorita Panamá name was used for the first time, reverting to Miss Panama in 1976. In 1982, Señorita Panamá was created by RPC Channel 4 as an alternative to send its winners to the Miss World contest in London. These pageants, along with smaller pageants such as Miss International Panamá and Miss World Panamá celebrated to select delegates for international representations.
Football in Panama is run by the Federación Panameña de Fútbol. The association administers the national football team, as well as the ANAPROF. Football is the second most popular sport in Panama, after baseball. Panama qualified for the 2018 FIFA World Cup.

Panamanians are people identified with Panama, a country in Central America, whose connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural. For most Panamanians, several or all of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their Panamanian identity. Panama is a multilingual and multicultural society, home to people of many different ethnicities and religions. Therefore, many Panamanians do not equate their nationality with ethnicity, but with citizenship and allegiance to Panama. The overwhelming majority of Panamanians are the product of varying degrees of admixture between European ethnic groups with native Amerindians who are indigenous to Panama's modern territory.

The Panama Papers are 11.5 million leaked documents that detail financial and attorney–client information for more than 214,488 offshore entities. The documents, some dating back to the 1970s, were created by, and taken from, Panamanian law firm and corporate service provider Mossack Fonseca, and were leaked in April 2016.
The Republic of Panama is one of the oldest and best-known tax havens in the Caribbean, as well as one of the most established in the region. Panama has had a reputation for tax avoidance since the early 20th century, and Panama has been cited repeatedly in recent years as a jurisdiction which does not cooperate with international tax transparency initiatives.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Panama is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have spread to Panama on 9 March 2020. One of the dead was a 64-year-old male, who also suffered from complications of diabetes and pneumonia. Of those infected, 83 were admitted to hospital. The infected individuals belong to the 29-59 age group and had each recently travelled abroad. A 13-year-old girl died of COVID-19 on 23 March.














