This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

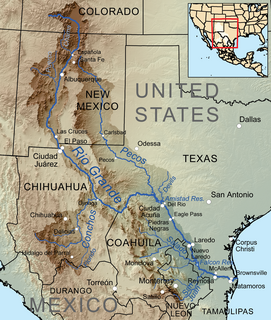
The Rio Grande is one of the principal rivers in the southwest United States and northern Mexico. The Rio Grande begins in south-central Colorado in the United States and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. Along the way, it forms part of the Mexico–United States border. According to the International Boundary and Water Commission, its total length was 1,896 miles (3,051 km) in the late 1980s, though course shifts occasionally result in length changes. Depending on how it is measured, the Rio Grande is either the fourth- or fifth-longest river system in North America.

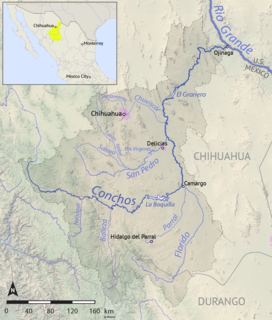
Delicias is a city in the Mexican state of Chihuahua and serves as the seat of the municipality of the same name. It is located southeast of the state capital, Chihuahua. Delicias was declared an official municipality of the state of Chihuahua on January 7, 1935. Delicias is a small industrial city and a major agricultural center located in the Conchos River Valley. As of 2015, the city of Delicias had a population of 148,045 inhabitants, while the metropolitan area had a population of 223,993 inhabitants. It was founded on 30 April 1933, making it one of Mexico's youngest cities. The municipality of Delicias is one of the smallest in the state in terms of size area.

Amistad Reservoir is a reservoir on the Rio Grande at its confluence with the Devils River 12 miles (19 km) northwest of Del Rio, Texas. The lake is bounded by Val Verde County on the United States side of the international border and by the state of Coahuila on the Mexican side of the border; the American shoreline forms the Amistad National Recreation Area. The reservoir was formed in 1969 by the construction of Amistad Dam. The dam and lake are managed jointly by the governments of the United States and Mexico through the International Boundary and Water Commission. The name of the dam and lake is the Spanish word for "friendship". The reservoir is also known as Lake Amistad.
Concha and Concho means "shell" in the Spanish and Portuguese languages. The word can also refer to:
Antonio de Espejo was a Spanish explorer who led an expedition into New Mexico and Arizona in 1582–83. The expedition created interest in establishing a Spanish colony among the Pueblo Indians of the Rio Grande valley.

Rio Conchos is a 1964 Cinemascope Western starring Richard Boone, Stuart Whitman, Anthony Franciosa, Edmond O'Brien, and in his motion picture debut, Jim Brown, based on Clair Huffaker's novel "Guns of Rio Conchos" published in 1958.

San Francisco de Conchos is one of the 67 municipalities of Chihuahua, in northern Mexico. The municipal seat lies at San Francisco de Conchos. The municipality covers an area of
1,169.1 km².
The Balleza River, or Río Balleza, is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
The Chuviscar River, is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
The San Pedro River (Chihuahua) is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
The Parral River, is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Florido, which flows into the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
Florido River is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.

The American Diversion Dam is a diversion dam on the Rio Grande in El Paso, Texas. It is about 140 feet (43 m) north of the point where the west bank of the river enters Mexico, 3.5 miles (5.6 km) from the business center. The dam is operated by the International Boundary and Water Commission.
It started operation in 1938.

The International Diversion Dam is a diversion dam on the Rio Grande in Ciudad Juárez. The dam is operated by the International Boundary and Water Commission, and diverts water into the Acequia Madre for use in irrigation in Mexico.
Water is diverted under the terms of the 1906 treaty on usage of Rio Grande water between the United States and Mexico.

La Boquilla Dam is a masonry arch-gravity dam on the Rio Conchos in Chihuahua, Mexico. It was built in 1910 to provide hydroelectricity, irrigation and flood control, and forms Toronto Lake with a capacity of 2.903 cubic kilometres (2,354,000 acre⋅ft). The dam and the nearby town of Boquilla de Conchos are named for the abrupt narrowing of the Conchos valley where the dam was built: boquilla means "nozzle" or "mouth".

Lago Colina Dam is a concrete and earth-embankment gravity dam on the Rio Conchos in Chihuahua, Mexico. The dam forms Lake Colina. Its primary purpose is to divert water for irrigation, and regulate the outflow of the larger La Boquilla Dam upstream.